Abstract
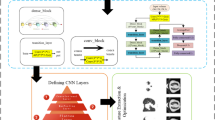
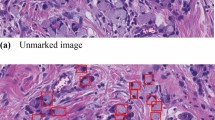
Purpose: Investigate the technical means of intelligent Gastric Cancer (GC) auxiliary diagnosis and warning, providing treatment guidance for physicians. Methods: The product is developed from a technical perspective, involving algorithm design, software development, and application design. Based on the UNet3+ digital pathology slices auxiliary diagnosis method, it enables precise segmentation of breast cancer pathology slices across the entire field of view, addressing issues such as excessive network complexity, high false positives, and inadequate capture of multi-scale information in existing algorithms. Additionally, utilizing a convolutional neural network-based cancer cell image classification algorithm enables rapid generation of predictive results for pathology slices. Key algorithms in 5G Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) for smart healthcare applications facilitate specific applications of 5G technology in integrated data exchange and device integration within medical consortia, achieving offloading of computational tasks and storage content to MEC nodes. This implementation includes patient physiological indicator warning mechanisms and device management techniques based on MEC nodes. The platform assists physicians in diagnosing more efficiently, aiding patients in earlier recovery, and providing robust support for treatment. Results: The new algorithm accurately segments and predicts entire cancer pathology slices, identifying cancerous regions. Conclusion: The “AI Pathology Anti-Cancer Guardian” intelligent GC auxiliary diagnosis and warning platform can analyze gastroscopy results more quickly and accurately, aiding physicians in diagnosis and treatment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia, J.Y., Aadam, A.A.: Advances in screening and detection of gastric cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 125(7), 1104–1109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.26844.PMID:35481909;PMCID:PMC9322671
Niu, P.H., Zhao, L.L., Wu, H.L., Zhao, D.B., Chen, Y.T.: Artificial intelligence in gastric cancer: application and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 26(36), 5408–5419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5408.PMID:33024393;PMCID:PMC7520602
Oikawa, K., Saito, A., Kiyuna, T., Graf, H.P., Cosatto, E., Kuroda, M.: Pathological diagnosis of gastric cancers with a novel computerized analysis system. J. Pathol. Inform. 28(8), 5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/2153-3539.201114.PMID:28400994;PMCID:PMC5359998
Qin, Y., Deng, Y., Jiang, H., Hu, N., Song, B.: Artificial intelligence in the imaging of gastric cancer: current applications and future direction. Front. Oncol. 21(11), 631–686 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.631686.PMID:34367946;PMCID:PMC8335156
Huang, B., et al.: Accurate diagnosis and prognosis prediction of gastric cancer using deep learning on digital pathological images: a retrospective multicentre study. EBioMedicine. 73, 103631 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103631. Epub 2021 Oct 19. PMID: 34678610; PMCID: PMC8529077
Acs, B., Rantalainen, M., Hartman, J.: Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology. J. Intern. Med. 288(1), 62–81 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13030. Epub 2020 Mar 3 PMID: 32128929
Ba, W., et al.: Assessment of deep learning assistance for the pathological diagnosis of gastric cancer. Mod Pathol. 35(9), 1262–1268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41379-022-01073-z. Epub 2022 PMID: 35396459; PMCID: PMC9424110
Noda, H., et al.: Convolutional neural network-based system for endocytoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol.Gastroenterol. 22(1), 237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-022-02312-y.PMID:35549679;PMCID:PMC9102244
Acknowledgments
The work of this paper is supported by Research on Smart Medical Demonstration Application System of Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University Based on 5G+MEC Technology (No. AD21220072), Science and Technology Base and Talent Project of Guangxi Province, and the South China University of Technology - Guilin Medical University 5G Intelligent Medical Platform and Demonstration Base Construction (No. AD21075054), Special Program of Base Construction and Outstanding Scholarship for Science and Technology Department of Guangxi Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, X., Shu, X., Hu, J., Mo, C. (2024). 5G MEC+AI Pathology “Anti-Cancer Guardian”: Design of Intelligent Gastric Cancer Auxiliary Diagnosis and Warning Platform for Smart Hospital System. In: Duffy, V.G. (eds) Digital Human Modeling and Applications in Health, Safety, Ergonomics and Risk Management. HCII 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14710. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61063-9_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61063-9_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-61062-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-61063-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)