Abstract
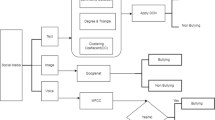
Toxicology can take many forms, ranging from overt approaches such as abusive language and bullying to more subtle means. Almost all corners of the Internet are affected by this practice, but gaming, news, blogging, and social media are particularly prevalent. Using a Convolutional Spiking Neural Network (CSNN) leveraging multi-modality, we explore a method for detecting toxicity. To enhance the capability of toxicity detection, the method utilizes both text and audio features from the DeToxy dataset. The CSNN has been composed of two modalities, one for text and one for audio, and a late fusion was applied to combine the final output. An embedding layer has been applied to textual data in the first step. Text tokens can be mapped into vector representations in order to extract features. In the audio modality, the convolution and max-pooling layers are two-dimensional; a flattening layer is applied prior to the linear layer. We fuse audio and text outputs using a fusion layer. Concatenating the spikes from the two modalities will construct the fusion layer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albawi, S., Mohammed, T.A., Al-Zawi, S.: Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In: 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2017)
Cech, M.: macech at SemEval-2021 task 5: toxic spans detection. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2021), pp. 1003–1008 (2021)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
El Sayad, I., Pannu, M., Gourde, J., Al Nakshabandi, M.: Third generation neural nets and their applications in multi-modal deep learning: a survey. In: Arai, K. (ed.) FTC 2023. LNNS, vol. 816, pp. 31–45. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47448-4_3
Ghosh, S., Lepcha, S., Sakshi, S., Shah, R.R., Umesh, S.: DeToxy: a large-scale multimodal dataset for toxicity classification in spoken utterances. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.07592 (2021)
Hunsberger, E., Eliasmith, C.: Training spiking deep networks for neuromorphic hardware. CoRR, abs/1611.05141 (2016)
Kasabov, N.K.: NeuCube: a spiking neural network architecture for mapping, learning and understanding of spatio-temporal brain data. Neural Netw. 52, 62–76 (2014)
Lee, C., Panda, P., Srinivasan, G., Roy, K.: Training deep spiking convolutional neural networks with STDP-based unsupervised pre-training followed by supervised fine-tuning. Front. Neurosci. 12, 435 (2018)
Li, Z., Liu, F., Yang, W., Peng, S., Zhou, J.: A survey of convolutional neural networks: analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33, 1–21 (2021)
Matsugu, M., Mori, K., Ishii, M., Mitarai, Y.: Convolutional spiking neural network model for robust face detection. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, 2002. ICONIP 2002, vol. 2, pp. 660–664. IEEE (2002)
Newmarch, J., Newmarch, J.: FFmpeg/Libav. Linux sound programming, pp. 227–234 (2017)
Pfeiffer, M., Pfeil, T.: Deep learning with spiking neurons: Opportunities and challenges. Front. Neurosci. 12 (2018)
Rueckauer, B., Lungu, I.-A., Yuhuang, H., Pfeiffer, M., Liu, S.-C.: Conversion of continuous-valued deep networks to efficient event-driven networks for image classification. Front. Neurosci. 11, 12 (2017)
Tavanaei, A., Ghodrati, M., Kheradpisheh, S.R., Masquelier, T., Maida, A.: Deep learning in spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 111, 47–63 (2019)
Turkson, R.E., Qu, H., Wang, Y., Eghan, M.J.: Unsupervised multi-layer spiking convolutional neural network using layer-wise sparse coding. In: Yang, H., Pasupa, K., Leung, A.C.-S., Kwok, J.T., Chan, J.H., King, I. (eds.) ICONIP 2020. LNCS, vol. 12534, pp. 353–365. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63836-8_30
Yousefi, M., Emmanouilidou, D.: Audio-based toxic language classification using self-attentive convolutional neural network. In: 2021 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 11–15. IEEE (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
El Sayad, I., Gourde, J., Pott, J., Muthayan, S., Singh, S. (2024). Multi-modal Deep Learning for Detecting Toxicity in Transcribed-Audio Conversations. In: Arai, K. (eds) Intelligent Computing. SAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 1018. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62269-4_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62269-4_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-62268-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-62269-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)