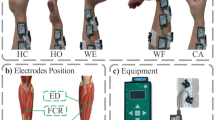
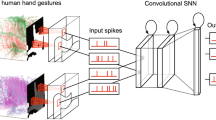
Abstract
Classification of surface electromyographic (sEMG) signals for the precise identification of hand gestures is a crucial area in the advancement of complex prosthetic devices and human-machine interfaces. This study presents a real-time sEMG classification system, exploiting a Spiking Neural Network (SNN) to distinguish among twelve distinct hand gestures. The system is implemented on a Lattice iCE40-UltraPlus FPGA, explicitly designed for low-power applications. Evaluation on the NinaPro DB5 dataset confirms an accuracy of 85.6%, demonstrating the model’s effectiveness. The power consumption for this architecture is approximately 1.7 mW, leveraging the inherent energy efficiency of SNNs for low-power classification.
This work was supported by Key Digital Technologies Joint Undertaking (KDT JU) in “EdgeAI Edge AI Technologies for Optimised Performance Embedded Processing” project, grant agreement No 101097300.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lava-DL SLAYER (2023). https://lava-nc.org/lava-lib-di/slayer/slayer.html. Accessed 8 Jan 2023
LAVA-NC (2023). https://lava-nc.org/index.html. Accessed Jan 8 2023
Behrenbeck, J., et al.: Classification and regression of spatio-temporal signals using NeuCube and its realization on spinnaker neuromorphic hardware. J. Neural Eng. 16(2), 026014 (2019)
Cheng, L., Liu, Y., Hou, Z.G., Tan, M., Du, D., Fei, M.: A rapid spiking neural network approach with an application on hand gesture recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 13(1), 151–161 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCDS.2019.2918228
Davies, M., et al.: Advancing neuromorphic computing with Loihi: a survey of results and outlook. Proc. IEEE 109(5), 911–934 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2021.3067593
Furber, S.B., et al.: Overview of the spinnaker system architecture. IEEE Trans. Comput. 62(12), 2454–2467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TC.2012.142
Leone, G., Raffo, L., Meloni, P.: On-FPGA spiking neural networks for end-to-end neural decoding. IEEE Access 11, 41387–41399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3269598
Pizzolato, S., Tagliapietra, L., Cognolato, M., Reggiani, M., Müller, H., Atzori, M.: Comparison of six electromyography acquisition setups on hand movement classification tasks. PLoS One 12(10), e0186132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186132
Shrestha, S.B., Orchard, G.: Slayer: spike layer error reassignment in time. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1419–1428. NIPS’18, Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA (2018)
Tanzarella, S., Iacono, M., Donati, E., Farina, D., Bartolozzi, C.: Neuromorphic decoding of spinal motor neuron behaviour during natural hand movements for a new generation of wearable neural interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabili. Eng. 31, 3035–3046 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3295658
Vitale, A., Donati, E., Germann, R., Magno, M.: Neuromorphic edge computing for biomedical applications: gesture classification using EMG signals. IEEE Sens. J. 22(20), 19490–19499 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3194678
Xu, M., Chen, X., Sun, A., Zhang, X., Chen, X.: A novel event-driven spiking convolutional neural network for electromyography pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 70(9), 2604–2615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2023.3258606
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Scrugli, M.A., Leone, G., Busia, P., Meloni, P. (2024). sEMG-Based Gesture Recognition with Spiking Neural Networks on Low-Power FPGA. In: Dias, T., Busia, P. (eds) Design and Architectures for Signal and Image Processing. DASIP 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14622. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62874-0_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62874-0_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-62873-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-62874-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)