Abstract
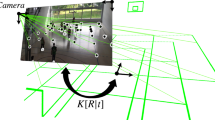
In this paper, we present a new framework that combines deep semantic segmentation with homography estimation to address challenges in racket sports court registration from broadcast videos. In particular, we deal with courts presenting the following problems: (a) brushed and occluded lines, (b) illumination variations, and (c) unknown camera parameters. Given an input frame from a broadcast video, our approach employs an encoder-decoder deep neural network to predict a precise pixel-level segmentation mask, which is then used to estimate the homography matrix between the input frame and its reference court model. For a comprehensive evaluation, we have developed two datasets for badminton and tennis that meet our specific needs. Since datasets and state-of-the-art methods with code are not publicly available, we compared our framework with a commonly handcrafted approach largely used as a baseline method in racket sports analysis. We show that our method outperforms the baseline in terms of registration accuracy and inference latency per frame.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, C.D., Smith, A.B., Roberts, E.F.: Article title. In: Proceedings Title, vol. II, pp. 803–806. IEEE (2003)
Farin, D., Krabbe, S., de With, Peter H.N., Effelsberg, W.: Robust camera calibration for sport videos using court models. In: Storage and Retrieval Methods and Applications for Multimedia 2004. LNCS, vol. 5307, pp. 80–91. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2003)
Han, J., Farin, D., de With, P.H.N.: Generic 3-D modeling for content analysis of court-net sports sequences. In: Cham, T.-J., Cai, J., Dorai, C., Rajan, D., Chua, T.-S., Chia, L.-T. (eds.) MMM 2007. LNCS, vol. 4352, pp. 279–288. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69429-8_28
Dang, B., Tran, A., Dinh, T., Dinh, T.: A real time player tracking system for broadcast tennis video. In: Nguyen, N.T., Le, M.T., Świątek, J. (eds.) ACIIDS 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5991, pp. 105–113. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12101-2_12
Mihai, P., Andreea-Oana, P., Hassan, B.L., Bruno, F., Cédric, B.: Real time tennis match tracking with low cost equipment. In: The Florida AI Research Society (2018). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:44157580
Silvia, V.M.: Computer vision and machine learning for in-play tennis analysis: framework, algorithms and implementation (2018). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:198358283
Jorge, J. M.: Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm: implementation and theory (1977). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:203694768
Jiang, W., Gamboa Higuera, J.C., Angles, B., Sun, W., Javan, M., Yi, K.M.: Optimizing through learned errors for accurate sports field registration. In: 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 201–210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093581
Nie, X., Chen, S., Hamid, R.: A robust and efficient framework for sports-field registration. In: 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1935–1943 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00198
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Harltey, A., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edn (2006). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:8641226
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Sudre, C.H., Li, W., Vercauteren, T., Ourselin, S., Jorge Cardoso, M.: Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. In: Cardoso, M.J., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2017. LNCS, vol. 10553, pp. 240–248. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67558-9_28
Huang, M.: Theory and implementation of linear regression. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), pp. 210–217 (2020).https://doi.org/10.1109/CVIDL51233.2020.00-99
Chu, Y.-J., et al.: Sports field registration via keypoints-aware label condition. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 3522–3529 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00396
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Shi, F., Marchwica, P., Gamboa Higuera, J.C., Jamieson, M., Javan, M., Siva, P.: Self-supervised shape alignment for sports field registration. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 3768–3777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV51458.2022.00382
Keerthana, R., Muhammad, A.A., Nur, A.R., Nurul, F.G., Saharudin, I.: Deep learning in sport video analysis: a review. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control 18, 1926–1933 (2020). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:216200176
Maglo, A., Orcesi, A., Pham, Q.-C.: KaliCalib: a framework for basketball court registration. In: Proceedings of the 5th International ACM Workshop on Multimedia Content Analysis in Sports, pp. 111–116. Association for Computing Machinery (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3552437.3555701
Fischler, M.A., Bolles, R.C.: Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 24(6), 381–395 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1145/358669.358692
Allam, S.H., Sherien, M., Mohamed, S., Mohammad, E.R.: A survey on hough transform, theory, techniques and applications. arXiv, abs/1502.02160 (2015). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:11028590
Citraro, L., et al.: Real-time camera pose estimation for sports fields. Mach. Vision Appl. 31 (2020). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:214632673
Tarashima, S.: Sports field recognition using deep multi-task learning. J. Inf. Process. 29, 328–335 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2197/ipsjjip.29.328
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., et al.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115, 211–252 (2014). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:2930547
Shih, H.-C.: A survey of content-aware video analysis for sports. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(5), 1212–1231 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2655624
Tan, M., Le, Q.V.: EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. arXiv, abs/1905.11946 (2019). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:167217261
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv, abs/1706.05587 (2017). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:22655199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jouini, A., Elloumi, M., Chaieb, F. (2024). A Deep Learning-Based Framework for Racket Sports Court Registration. In: Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Macintyre, J., Avlonitis, M., Papaleonidas, A. (eds) Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. AIAI 2024. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 713. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63219-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63219-8_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-63218-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-63219-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)