Abstract
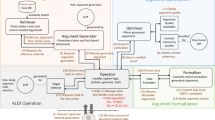
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances Large Language Model (LLM) output by providing prior knowledge as context to input. This is beneficial for knowledge-intensive and expert reliant tasks, including legal question-answering, which require evidence to validate generated text outputs. We highlight that Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) presents key opportunities to structure retrieval as part of the RAG process in an LLM. We introduce CBR-RAG, where CBR cycle’s initial retrieval stage, its indexing vocabulary, and similarity knowledge containers are used to enhance LLM queries with contextually relevant cases. This integration augments the original LLM query, providing a richer prompt. We present an evaluation of CBR-RAG, and examine different representations (i.e. general and domain-specific embeddings) and methods of comparison (i.e. inter, intra and hybrid similarity) on the task of legal question-answering. Our results indicate that the context provided by CBR’s case reuse enforces similarity between relevant components of the questions and the evidence base leading to significant improvements in the quality of generated answers.
This research is funded by SFC International Science Partnerships Fund.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Reproducible code is available: https://github.com/rgu-iit-bt/cbr-for-legal-rag.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Note: Our notation uses calligraphic font for the prompt components (\(f(\mathcal {Q}), g(\mathcal {Q}), \mathcal {C}\)) to distinguish them from those of cases. Despite the stylistic difference, both prompts and cases employ similar embedding representations.
- 5.
Test dataset available at open-australian-legal-qa-test.
References
Aleven, V., Ashley, K.D.: Teaching case-based argumentation through a model and examples: empirical evaluation of an intelligent learning environment. In: Artificial Intelligence in Education, vol. 39, pp. 87–94. Citeseer (1997)
Asai, A., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., Sil, A., Hajishirzi, H.: Self-RAG: learning to retrieve, generate, and critique through self-reflection. In: The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (2024)
Ashley, K.D.: Reasoning with cases and hypotheticals in hypo. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 34(6), 753–796 (1991)
Bromley, J., Guyon, I., LeCun, Y., Säckinger, E., Shah, R.: Signature verification using a “Siamese” time delay neural network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 6. Morgan-Kaufmann (1993)
Brüninghaus, S., Ashley, K.D.: The role of information extraction for textual CBR. In: Aha, D.W., Watson, I. (eds.) ICCBR 2001. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2080, pp. 74–89. Springer, Heidelberg (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44593-5_6
Butler, U.: Open Australian legal corpus (2024). https://huggingface.co/datasets/umarbutler/open-australian-legal-corpus
Chalkidis, I., Fergadiotis, M., Malakasiotis, P., Aletras, N., Androutsopoulos, I.: LEGAL-BERT: the muppets straight out of law school. In: Cohn, T., He, Y., Liu, Y. (eds.) Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 2898–2904. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online (2020)
Chalkidis, I., et al.: LexGLUE: a benchmark dataset for legal language understanding in English. In: Muresan, S., Nakov, P., Villavicencio, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 4310–4330 (2022)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Guha, N., et al.: LegalBench: a collaboratively built benchmark for measuring legal reasoning in large language models. Preprint arXiv:2308.11462 (2023)
Hacker, P., Engel, A., Mauer, M.: Regulating chatGPT and other large generative AI models. In: Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, pp. 1112–1123 (2023)
Jiang, A.Q., et al.: Mistral 7b. preprint arXiv:2310.06825 (2023)
Lai, J., Gan, W., Wu, J., Qi, Z., Yu, P.S.: Large language models in law: a survey. preprint arXiv:2312.03718 (2023)
Lee, J.S.: LexGPT 0.1: pre-trained GPT-J models with pile of law. preprint arXiv:2306.05431 (2023)
Lewis, P., et al.: Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 9459–9474 (2020)
Li, X., Li, J.: Angle-optimized text embeddings. Preprint arXiv:2309.12871 (2023)
Rissland, E.L., Daniels, J.J.: A hybrid CBR-IR approach to legal information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law, pp. 52–61 (1995)
Tang, C., et al.: PolicyGPT: automated analysis of privacy policies with large language models. preprint arXiv:2309.10238 (2023)
Thulke, D., Daheim, N., Dugast, C., Ney, H.: Efficient retrieval augmented generation from unstructured knowledge for task-oriented dialog. Preprint arXiv:2102.04643 (2021)
Tuggener, D., von Däniken, P., Peetz, T., Cieliebak, M.: LEDGAR: a large-scale multi-label corpus for text classification of legal provisions in contracts. In: Calzolari, N., et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, pp. 1235–1241. European Language Resources Association (2020)
Upadhyay, A., Massie, S.: A case-based approach for content planning in data-to-text generation. In: Keane, M.T., Wiratunga, N. (eds.) ICCBR 2022. LNCS, vol. 13405, pp. 380–394. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14923-8_25
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Wiratunga, N., Koychev, I., Massie, S.: Feature selection and generalisation for retrieval of textual cases. In: Funk, P., González Calero, P.A. (eds.) ECCBR 2004. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3155, pp. 806–820. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28631-8_58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wiratunga, N. et al. (2024). CBR-RAG: Case-Based Reasoning for Retrieval Augmented Generation in LLMs for Legal Question Answering. In: Recio-Garcia, J.A., Orozco-del-Castillo, M.G., Bridge, D. (eds) Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development. ICCBR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14775. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63646-2_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63646-2_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-63645-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-63646-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)