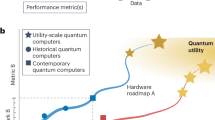
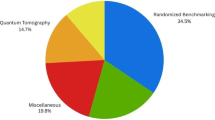
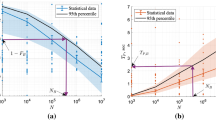
Abstract
Quantum Computing (QC) is undergoing a high rate of development, investment and research devoted to its improvement. However, there is little consensus in the industry and wider literature as to what improvement might consist of beyond ambiguous statements of “more qubits” and “fewer errors”. Before one can decide how to improve something, it is first necessary to define the criteria for success: what are the metrics or statistics that are relevant to the problem? The lack of clarity surrounding this question has led to a rapidly developing capability with little consistency or standards present across the board. This paper lays out a framework by which any user, developer or researcher can define, articulate and justify the success criteria and associated benchmarks that have been used to solve their problem or make their claim.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonov, D., Ben-Or, M.: Fault-tolerant quantum computation with constant error rate. SIAM J. Comput. 38(4), 1207–1282 (2008)
Ahn, C., Doherty, A.C., Landahl, A.J.: Continuous quantum error correction via quantum feedback control. Phys. Rev. A 65(4), 042301 (2002)
Albash, T., Martin-Mayor, V., Hen, I.: Analog errors in Ising machines. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4(2), 02LT03 (2019)
Allwright, S.: What is a good F1 score and how do I interpret it? (2022). https://stephenallwright.com/good-f1-score/. Accessed 5 Feb 2024
Ayanzadeh, R., Das, P., Tannu, S.S., Qureshi, M.: EQUAL: improving the fidelity of quantum annealers by injecting controlled perturbations. arXiv: 2108.10964 [quant-ph] (2021)
Ayanzadeh, R., Dorband, J., Halem, M., Finin, T.: Multi-qubit correction for quantum annealers. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 16119 (2021)
Barbosa, A., Pelofske, E., Hahn, G., Djidjev, H.N.: Optimizing embedding-related quantum annealing parameters for reducing hardware bias. In: Ning, L., Chau, V., Lau, F. (eds.) PAAP 2020. CCIS, vol. 1362, pp. 162–173. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0010-4_15
Boixo, S., et al.: Characterizing quantum supremacy in near-term devices. Nat. Phys. 14(6), 595–600 (2018)
Borah, S., Sarma, B., Kewming, M., Quijandria, F., Milburn, G.J., Twamley, J.: Measurement-based estimator scheme for continuous quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. Res. 4(3), 033207 (2022)
Chancellor, N., et al.: Error measurements for a quantum annealer using the one-dimensional Ising model with twisted boundaries. NPJ Quantum Inf. 8(1), 1–8 (2022)
Cross, A.W., Bishop, L.S., Sheldon, S., Nation, P.D., Gambetta, J.M.: Validating quantum computers using randomized model circuits. Phys. Rev. A 100(3), 032328 (2019)
D-Wave Systems: D-Wave system documentation. https://docs.dwavesys.com/docs/latest. Accessed 16 May 2022
Hargreaves, T.: Is it time to ditch the MNIST dataset? (2020). https://www.ttested.com/ditch-mnist/. Accessed 28 Apr 2023
Hennrich, M., et al.: Experimental repetitive quantum error correction with trapped ions. In: CLEO: 2011 - Laser Science to Photonic Applications (2011)
Kelly, J., et al.: State preservation by repetitive error detection in a superconducting quantum circuit. Nature 519(7541), 66–69 (2015)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R.: Theory of quantum error-correcting codes. Phys. Rev. A 55(2), 900–911 (1997)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Zurek, W.H.: Resilient quantum computation. Science 279(5349), 342–345 (1998)
Langione, M., Bobier, J.F., Krayer, L., Park, H., Kumar, A.: The race to quantum advantage depends on benchmarking (2022). https://www.bcg.com/publications/2022/value-of-quantum-computing-benchmarks. Accessed 26 Oct 2022
Li, W., Lu, Z.D., Deng, D.L.: Quantum neural network classifiers: a tutorial. SciPost Phys. Lect. Notes 61 (2022)
Linke, N.M., et al.: Experimental comparison of two quantum computing architectures. PNAS 114(13), 3305–3310 (2017)
Lubinski, T., et al.: Application-oriented performance benchmarks for quantum computing. arXiv: 2110.03137 [quant-ph] (2021)
Martiel, S., Ayral, T., Allouche, C.: Benchmarking quantum coprocessors in an Application-Centric, Hardware-Agnostic, and scalable way. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 2, 1–11 (2021)
Moll, N., et al.: Quantum optimization using variational algorithms on near-term quantum devices. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3(3), 030503 (2018)
Nelson, J., Vuffray, M., Lokhov, A.Y., Albash, T., Coffrin, C.: High-quality thermal Gibbs sampling with quantum annealing hardware. Phys. Rev. Applied 17(4), 044046 (2022)
Nelson, J., Vuffray, M., Lokhov, A.Y., Coffrin, C.: Single-qubit fidelity assessment of quantum annealing hardware. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 2, 1–10 (2021)
Paltenghi, M.: Cross-platform testing of quantum computing platforms. In: 2022 IEEE/ACM 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings (ICSE-Companion), pp. 269–271 (2022)
Papers with Code: Image classification on MNIST. https://paperswithcode.com/sota/image-classification-on-mnist. Accessed 28 Apr 2023
Pare, S., Bhandari, A.K., Kumar, A., Singh, G.K., Khare, S.: Satellite image segmentation based on different objective functions using genetic algorithm: a comparative study. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), pp. 730–734 (2015)
Pearson, A., Mishra, A., Hen, I., Lidar, D.A.: Analog errors in quantum annealing: doom and hope. NPJ Quantum Inf. 5(1), 1–9 (2019)
Pelofske, E., Bärtschi, A., Eidenbenz, S.: Quantum volume in practice: what users can expect from NISQ devices. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 3, 1–19 (2022)
Pelofske, E., Hahn, G., Djidjev, H.N.: Noise dynamics of quantum annealers: estimating the effective noise using idle qubits. Quantum Sci. Technol. 8(3), 035005 (2023)
Pochart, T., Jacquot, P., Mikael, J.: On the challenges of using D-Wave computers to sample Boltzmann random variables. In: 2022 IEEE 19th International Conference on Software Architecture Companion (ICSA-C), pp. 137–140 (2022)
Proctor, T., Seritan, S., Rudinger, K., Nielsen, E., Blume-Kohout, R., Young, K.: Scalable randomized benchmarking of quantum computers using mirror circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129(15), 150502 (2022)
Pudenz, K.L., Albash, T., Lidar, D.A.: Error-corrected quantum annealing with hundreds of qubits. Nat. Commun. 5, 3243 (2014)
Ronke, R., Spiller, T.P., D’Amico, I.: Effect of perturbations on information transfer in spin chains. Phys. Rev. A 83(1), 012325 (2011)
Suau, A., Nelson, J., Vuffray, M., Lokhov, A.Y., Cincio, L., Coffrin, C.: Single-qubit cross platform comparison of quantum computing hardware. arXiv: 2108.11334 [quant-ph] (2021)
Tiziano, M.: Estimating quantum volume for advantage (2020). https://support.dwavesys.com/hc/en-us/community/posts/360051945133-Estimating-Quantum-Volume-for-Advantage. Accessed 10 June 2022
Unmoved: 30k cats and dogs 150 \(\times \) 150 greyscale (2023). https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/unmoved/30k-cats-and-dogs-150x150-greyscale
Zaborniak, T., de Sousa, R.: Benchmarking Hamiltonian noise in the D-Wave quantum annealer. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 2, 1–6 (2021)
Zolotarev, Y.F., Luchnikov, I.A., López-Saldivar, J.A., Fedorov, A.K., Kiktenko, E.O.: Continuous monitoring for noisy intermediate-scale quantum processors. arXiv: 2205.06191 [quant-ph] (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Defence Science Technical Laboratory (Dstl) who are funding this research. Content includes material subject to ©Crown copyright (2024), Dstl. This material is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3, or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: psi@nationalarchives.gov.uk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, J., Stepney, S., D’Amico, I. (2024). A Methodology for Comparing and Benchmarking Quantum Devices. In: Cho, DJ., Kim, J. (eds) Unconventional Computation and Natural Computation. UCNC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14776. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63742-1_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63742-1_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-63741-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-63742-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)