Abstract
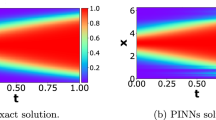
Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) are a promising application of deep neural networks for the numerical solution of nonlinear partial differential equations (PDEs). However, it has been observed that standard PINNs may not be able to accurately fit all types of PDEs, leading to poor predictions for specific regions in the domain. A common solution is to partition the domain by time and train each time interval separately. However, this approach leads to the prediction errors being accumulated over time, which is especially the case when solving “stiff” PDEs. To address these issues, we propose a new PINN training scheme, called DP-PINN (Dual-Phase PINN). DP-PINN divides the training into two phases based on a carefully chosen time point \(t_s\). The phase-1 training aims to generate the accurate solution at \(t_s\), which will serve as the additional intermediate condition for the phase-2 training. New sampling strategies are also proposed to enhance the training process. These design considerations improve the prediction accuracy significantly. We have conducted the experiments to evaluate DP-PINN with both “stiff” and non-stiff PDEs. The results show that the solutions predicted by DP-PINN exhibit significantly higher accuracy compared to those obtained by the state-of-the-art PINNs in literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, W.F.: Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations. Academic Press (2014)
Baydin, A.G., Pearlmutter, B.A., Radul, A.A., Siskind, J.M.: Automatic differentiation in machine learning: a survey. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18, 1–43 (2018)
Burden, R.L.: Numerical Analysis. Brooks/Cole Cengage Learning (2011)
Dissanayake, M., Phan-Thien, N.: Neural-network-based approximations for solving partial differential equations. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 10(3), 195–201 (1994)
Huang, S., Feng, W., Tang, C., Lv, J.: Partial differential equations meet deep neural networks: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.05567 (2022)
Lee, J.Y., Ko, S., Hong, Y.: Finite element operator network for solving parametric PDES. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.04690 (2023)
Mattey, R., Ghosh, S.: A novel sequential method to train physics informed neural networks for allen cahn and cahn hilliard equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 390, 114474 (2022)
McClenny, L., Braga-Neto, U.: Self-adaptive physics-informed neural networks using a soft attention mechanism. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.04544 (2020)
Pang, Y., Xie, J., Khan, M.H., Anwer, R.M., Khan, F.S., Shao, L.: Mask-guided attention network for occluded pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4967–4975 (2019)
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 686–707 (2019)
Rumelhart, D.E., Durbin, R., Golden, R., Chauvin, Y.: Backpropagation: the basic theory. In: Backpropagation, pp. 1–34. Psychology Press (2013)
Wang, F., et al.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3156–3164 (2017)
Wang, S., Teng, Y., Perdikaris, P.: Understanding and mitigating gradient flow pathologies in physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(5), A3055–A3081 (2021)
Wight, C.L., Zhao, J.: Solving Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations using the adaptive physics informed neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.04542 (2020)
Zawawi, M.H., et al.: A review: fundamentals of computational fluid dynamics (CFD). In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2030. AIP Publishing (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, D., He, L. (2024). DP-PINN: A Dual-Phase Training Scheme for Improving the Performance of Physics-Informed Neural Networks. In: Franco, L., de Mulatier, C., Paszynski, M., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M.A. (eds) Computational Science – ICCS 2024. ICCS 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14832. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63749-0_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63749-0_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-63748-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-63749-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)