Abstract
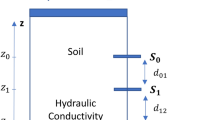
Water movement in soil is essential for weather monitoring, prediction of natural disasters, and agricultural water management. Richardson-Richards’ equation (RRE) is the characteristic partial differential equation for studying soil water movement. RRE is a non-linear PDE involving water potential, hydraulic conductivity, and volumetric water content. This equation has underlying non-linear parametric relationships called water retention curves (WRCs) and hydraulic conductivity functions (HCFs). This two-level non-linearity makes the problem of unsaturated water flow of soils challenging to solve. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) offer a powerful paradigm to combine physics in data-driven techniques. From noisy or sparse observations of one variable (water potential), we use PINNs to learn the complete system, estimate the parameters of the underlying model, and further facilitate the prediction of infiltration and discharge. We employ training on RRE, WRC, HCF, and measured values to resolve two-level non-linearity directly instead of explicitly deriving water potential or volumetric water content-based formulations. The parameters to be estimated are made trainable with initialized values. We take water potential data from simulations and use this data to solve the inverse problem with PINN and compare estimated parameters, volumetric water content, and hydraulic conductivity with actual values. We chose different types of parametric relationships and wetting conditions to show the approach’s effectiveness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The code is available at https://github.com/cvjena/InverseRRE.
References
Ahmad, W., Shadaydeh, M., Denzler, J.: Deep learning-based group causal inference in multivariate time-series. In: AAAI Workshop on AI for Time-series (2024). https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.08386, (accepted)
Al Safwan, A., Song, C., Waheed, U.: Is it time to swish? Comparing activation functions in solving the helmholtz equation using PINNs 2021(1), 1–5 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.202113254, https://www.earthdoc.org/content/papers/10.3997/2214-4609.202113254
Bandai, T., Ghezzehei, T.A.: Forward and inverse modeling of water flow in unsaturated soils with discontinuous hydraulic conductivities using physics-informed neural networks with domain decomposition. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 26(16), 4469–4495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-26-4469-2022, https://hess.copernicus.org/articles/26/4469/2022/
Büchner, T., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: Improved obstructed facial feature reconstruction for emotion recognition with minimal change CycleGANs. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Delmas, P., Philips, W., Scheunders, P. (eds.) Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. ACIVS 2023. LNCS, vol. 14124. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45382-3_22
Chen, Y., Xu, Y., Wang, L., Li, T.: Modeling water flow in unsaturated soils through physics-informed neural network with principled loss function. Comput. Geotech. 161, 105546 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105546, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0266352X23003038
Eivazi, H., Tahani, M., Schlatter, P., Vinuesa, R.: Physics-informed neural networks for solving reynolds-averaged navier-stokes equations. Phys. Fluids 34, 075117 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0095270
Farthing, M.W., Ogden, F.L.: Numerical solution of Richards’ equation: a review of advances and challenges. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 81(6), 1257–1269 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2017.02.0058, https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2136/sssaj2017.02.0058
Gao, Z., Yan, L., Zhou, T.: Failure-informed adaptive sampling for PINNs. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 45(4), A1971–A1994 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1137/22M1527763
Gardner, G.H.F.: Formation velocity and DENSITY—the diagnostic basics for stratigraphic traps. Geophysics 39(6), 770 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1440465
van Genuchten, M.T.: A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44(5), 892–898 (1980). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x, https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Huang, Y., et al.: Enhanced stability of grassland soil temperature by plant diversity. Nat. Geosci. 17, 44–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-023-01338-5
Ireson, A.M., Spiteri, R.J., Clark, M.P., Mathias, S.A.: A simple, efficient, mass-conservative approach to solving Richards’ equation (openre, v1. 0). Geosci. Model Dev. 16(2), 659–677 (2023)
Depina, I., Saket Jain, S.M.V., Gotovac, H.: Application of physics-informed neural networks to inverse problems in unsaturated groundwater flow. Georisk: Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 16(1), 21–36 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2021.1971251
Jonard, F., Weihermüller, L., Schwank, M., Jadoon, K.Z., Vereecken, H., Lambot, S.: Estimation of hydraulic properties of a sandy soil using ground-based active and passive microwave remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 53(6), 3095–3109 (2015)
Karniadakis, G.E., Kevrekidis, I.G., Lu, L., Perdikaris, P., Wang, S., Yang, L.: Physics-informed machine learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3(6), 422–440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-021-00314-5
Kingma, D., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Diega, CA, USA (2015)
Lu, L., Jin, P., Pang, G., Zhang, Z., Karniadakis, G.E.: Learning nonlinear operators via DeepONet based on the universal approximation theorem of operators. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3(3), 218–229 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-021-00302-5
Lu, L., Meng, X., Mao, Z., Karniadakis, G.E.: DeepXDE: a deep learning library for solving differential equations. SIAM Rev. 63(1), 208–228 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1137/19M1274067
Lu, L., Pestourie, R., Yao, W., Wang, Z., Verdugo, F., Johnson, S.G.: Physics-informed neural networks with hard constraints for inverse design. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(6), B1105–B1132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1137/21M1397908
Maddu, S., Sturm, D., Müller, C.L., Sbalzarini, I.F.: Inverse Dirichlet weighting enables reliable training of physics informed neural networks. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 3(1), 015026 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-2153/ac3712
Mohanty, B.P.: Soil hydraulic property estimation using remote sensing: a review. Vadose Zone J. 12(4), 1–9 (2013)
Pandey, S., Schumacher, J., Sreenivasan, K.R.: A perspective on machine learning in turbulent flows. J. Turbul. 21, 567–584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/14685248.2020.1757685
Pauwels, V.R., Balenzano, A., Satalino, G., Skriver, H., Verhoest, N.E., Mattia, F.: Optimization of soil hydraulic model parameters using synthetic aperture radar data: an integrated multidisciplinary approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 47(2), 455–467 (2009)
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 686–707 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics informed deep learning (part II): Data-driven discovery of nonlinear partial differential equations (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10566
Rasht-Behesht, M., Huber, C., Shukla, K., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for wave propagation and full waveform inversions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 127(5), e2021JB023120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JB023120, https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2021JB023120
Rezaei, M., et al.: Incorporating machine learning models and remote sensing to assess the spatial distribution of saturated hydraulic conductivity in a light-textured soil. Comput. Electron. Agric. 209, 107821 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.107821, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168169923002090
Richards, L.A.: Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1(5), 318–333 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1745010
Santanello, J.A., Jr., et al.: Using remotely-sensed estimates of soil moisture to infer soil texture and hydraulic properties across a semi-arid watershed. Remote Sens. Environ. 110(1), 79–97 (2007)
Song, C., Alkhalifah, T., Waheed, U.: Solving the frequency-domain acoustic VTI wave equation using physics-informed neural networks. Geophys. J. Int. 225(2), 846–859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab010, publisher Copyright: 2021 The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Royal Astronomical Society
Srivastava, R., Yeh, T.C.J.: Analytical solutions for one-dimensional, transient infiltration toward the water table in homogeneous and layered soils. Water Resour. Res. 27(5), 753–762 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1029/90WR02772, https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/90WR02772
Tartakovsky, A.M., Marrero, C.O., Perdikaris, P., Tartakovsky, G.D., Barajas-Solano, D.: Physics-informed deep neural networks for learning parameters and constitutive relationships in subsurface flow problems. Water Resour. Res. 56(5), e2019WR026731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR026731, https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2019WR026731, e2019WR026731 10.1029/2019WR026731
Vemuri, S.K., Denzler, J.: Gradient statistics-based multi-objective optimization in physics-informed neural networks. Sensors 23(21), 8665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218665, https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/23/21/8665
Wu, C., Zhu, M., Tan, Q., Kartha, Y., Lu, L.: A comprehensive study of non-adaptive and residual-based adaptive sampling for physics-informed neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 403, 115671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2022.115671, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045782522006260
Wu, W., Daneker, M., Jolley, M., Turner, K., Lu, L.: Effective data sampling strategies and boundary condition constraints of physics-informed neural networks for identifying material properties in solid mechanics. Appl. Math. Mech. 44, 1039–1068 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-023-2995-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vemuri, S.K., Büchner, T., Denzler, J. (2024). Estimating Soil Hydraulic Parameters for Unsaturated Flow Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks. In: Franco, L., de Mulatier, C., Paszynski, M., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M.A. (eds) Computational Science – ICCS 2024. ICCS 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14834. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63759-9_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-63759-9_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-63758-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-63759-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)