Abstract
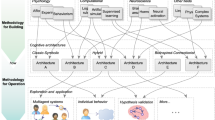
The Artificial Intelligence field is flooded with optimisation methods. In this paper, we change the focus to developing modelling methods with the aim of getting us closer to Artificial General Intelligence. To do so, we propose a novel way to interpret reality as an information source, that is later translated into a computational framework able to capture and represent such information. This framework is able to build elements of classical cognitive architectures, like Long Term Memory and Working Memory, starting from a simple primitive that only processes Spatial Distributed Representations. Moreover, it achieves such level of verticality in a seamless scalable hierarchical way.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, S., Hawkins, J.: How do neurons operate on sparse distributed representations? A mathematical theory of sparsity, neurons and active dendrites. CoRR abs/1601.00720 (2016)
Cui, Y., Ahmad, S., Hawkins, J.: The HTM spatial pooler - a neocortical algorithm for online sparse distributed coding. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 111 (2017)
van Duijn, M., Keijzer, F., Franken, D.: Principles of minimal cognition: casting cognition as sensorimotor coordination. Adapt. Behav. 14(2), 157–170 (2006)
Fodor, J.A., Pylyshyn, Z.W.: Connectionism and cognitive architecture: a critical analysis. Cognition 28(1–2), 3–71 (1988)
Foldiak, P.: Sparse coding in the primate cortex. In: The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks (2003)
Ha, D., Schmidhuber, J.: Recurrent world models facilitate policy evolution. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2018, NeurIPS 2018, 3–8 December 2018, Montréal, Canada, pp. 2455–2467 (2018)
Hawkins, J., Blakeslee, S.: On Intelligence. Times Books, USA (2004)
Laird, J.E., Lebiere, C., Rosenbloom, P.S.: A standard model of the mind: toward a common computational framework across artificial intelligence, cognitive science, neuroscience, and robotics. AI Mag. 38(4), 13–26 (2017)
Rogers, T.T., McClelland, J.L.: Parallel distributed processing at 25: further explorations in the microstructure of cognition. Cogn. Sci. 38(6), 1024–1077 (2014)
Yon, D., Heyes, C., Press, C.: Beliefs and desires in the predictive brain. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 4404 (2020)
Zhang, L., Xiong, Y., Yang, Z., Casas, S., Hu, R., Urtasun, R.: Learning unsupervised world models for autonomous driving via discrete diffusion. CoRR abs/2311.01017 (2023)
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Daniel Pinyol, Hector Antona and Pere Mayol for our insightful discussions about the topic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ibias, A., Ramirez-Miranda, G., Guinovart, E., Alarcon, E. (2024). From Manifestations to Cognitive Architectures: A Scalable Framework. In: Thórisson, K.R., Isaev, P., Sheikhlar, A. (eds) Artificial General Intelligence. AGI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14951. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-65572-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-65572-2_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-65571-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-65572-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)