Abstract
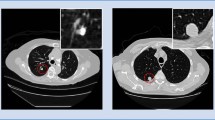
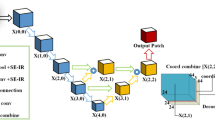
Automatic detection of lung nodules has been a key element in modern medical research in the past decade. By utilizing accurate nodule detection approaches, lung cancer can be treated in its early stages, reducing its mortality rate. Manual detection of nodules is hindered by structures contained in the computed tomography scan images such as veins, bronchioles and lymphatics. Furthermore, nodules are tiny and sometimes have haphazard boundaries making them easy to miss. In this work, we propose a two-step lung nodule detection method that uses a novel hierarchical superpixel merging (HSPM) module to reduce the number of proposed regions of interest and couples it with a new graph neural network namely, the regional downsampled residual superpixel aggregation network (dRes-SPAN) to accurately detect nodules in the lung parenchyma. Experiments on the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC-IDRI) dataset show a high improvement in performance in terms of nodule classification and detection while achieving an overall low false positive rate. A significant reduction in training time and trainable parameters has also been observed along with the relaxation in the requirement for heavy annotation compared to the state-of-the-art object detection architectures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armato, S.G., III., et al.: The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 38(2), 915–931 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3528204
Aydoghmishi, F.M., Modak, S., Abdel-Raheem, E., Rueda, L.: Examining the performance of melanoma classification using superpixel segmentation: a comparative analysis. In: 2023 International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), pp. 113–118. IEEE (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICM60448.2023.10378939
Bae, J.H., et al.: Superpixel image classification with graph convolutional neural networks based on learnable positional embedding. Appl. Sci. 12(18), 9176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189176
Van den Bergh, M., Boix, X., Roig, G., Van Gool, L.: SEEDS: superpixels extracted via energy-driven sampling. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 111, 298–314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-014-0744-2
Bu, Z., et al.: Lung nodule detection based on YOLOv3 deep learning with limited datasets. Mol. Cell. Biomech. 19(1), 17–28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.32604/mcb.2022.018318
Cheng, B., Wei, Y., Shi, H., Feris, R., Xiong, J., Huang, T.: Revisiting RCNN: on awakening the classification power of faster RCNN. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11219, pp. 473–490. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_28
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1440–1448 (2015)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 580–587 (2014)
Han, K., Wang, Y., Guo, J., Tang, Y., Wu, E.: Vision GNN: An image is worth graph of nodes. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 35, pp. 8291–8303 (2022)
Han, Y., Wang, P., Kundu, S., Ding, Y., Wang, Z.: Vision HGNN: an image is more than a graph of nodes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 19878–19888 (2023)
Hovinga, M., Sprengers, R., Kauczor, H.-U., Schaefer-Prokop, C.: CT imaging of interstitial lung diseases. In: Schoepf, U.J.J., Meinel, F.G.G. (eds.) Multidetector-Row CT of the Thorax. MR, pp. 105–130. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-30355-0_7
Ji, Z., et al.: Lung nodule detection in medical images based on improved YOLOv5s. IEEE Access (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3296530
Kim, M., et al.: Deep learning in medical imaging. Neurospine 16(4), 657 (2019). https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1938396.198
Li, R., Xiao, C., Huang, Y., Hassan, H., Huang, B.: Deep learning applications in computed tomography images for pulmonary nodule detection and diagnosis: a review. Diagnostics 12(2), 298 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020298
Liu, K.: STBi-YOLO: a real-time object detection method for lung nodule recognition. IEEE Access 10, 75385–75394 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3192034
Ma, L., Li, G., Feng, X., Fan, Q., Liu, L.: TiCNet: transformer in convolutional neural network for pulmonary nodule detection on CT images. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 37, 196–208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-023-00904-y
Mkindu, H., Wu, L., Zhao, Y.: Lung nodule detection in chest CT images based on vision transformer network with Bayesian optimization. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 85, 104866 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104866
Modak, S., Abdel-Raheem, E., Rueda, L.: Applications of deep learning in disease diagnosis of chest radiographs: a survey on materials and methods. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 5, 100076 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bea.2023.100076
Modak, S., Abdel-Raheem, E., Rueda, L.: Lung nodule segmentation on CT scan images using Patchwise Iterative Graph Clustering. In: 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS46773.2023.10181811
Modak, S., Abdel-Raheem, E., Taha, L.Y.: A novel adaptive multilevel thresholding based algorithm for QRS detection. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2, 100016 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bea.2021.100016
Nguyen, C.C., Tran, G.S., Burie, J.C., Nghiem, T.P., et al.: Pulmonary nodule detection based on faster R-CNN with adaptive anchor box. IEEE Access 9, 154740–154751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3128942
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLOv3: an incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.02767
Usman, M., Rehman, A., Shahid, A., Latif, S., Shin, Y.G.: MEDS-Net: multi-encoder based self-distilled network with bidirectional maximum intensity projections fusion for lung nodule detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 129, 107597 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107597
Yagin, F.H., Alkhateeb, A., Colak, C., Azzeh, M., Yagin, B., Rueda, L.: A fecal-microbial-extracellular-vesicles-based metabolomics machine learning framework and biomarker discovery for predicting colorectal cancer patients. Metabolites 13(5), 589 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050589
Zhang, M., Liu, S., Zeng, B.: Hierarchical region proposal refinement network for weakly supervised object detection. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 669–673. IEEE (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP42928.2021.9506087
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery Grants (RGPIN-2018-05523) and (RGPIN-2019-04696), and the University of Windsor, Office of Research Services and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Modak, S., Trivedi, Y., Abdel-Raheem, E., Rueda, L. (2024). Harnessing the Power of Graph Propagation in Lung Nodule Detection. In: Finkelstein, J., Moskovitch, R., Parimbelli, E. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14845. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66535-6_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66535-6_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-66534-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-66535-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)