Abstract
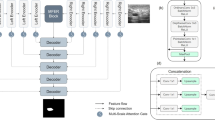
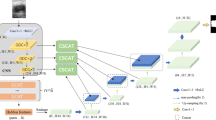
Breast cancer is a major global health concern. Pathologists face challenges in analyzing complex features from pathological images, which is a time-consuming and labor-intensive task. Therefore, efficient computer-based diagnostic tools are needed for early detection and treatment planning. This paper presents a modified version of MultiResU-Net for histopathology image segmentation, which is selected as the backbone for its ability to analyze and segment complex features at multiple scales and ensure effective feature flow via skip connections. The modified version also utilizes the Gaussian distribution-based Attention Module (GdAM) to incorporate histopathology-relevant text information in a Gaussian distribution. The sampled features from the Gaussian text feature-guided distribution highlight specific spatial regions based on prior knowledge. Finally, using the Controlled Dense Residual Block (CDRB) on skip connections of MultiResU-Net, the information is transferred from the encoder layers to the decoder layers in a controlled manner using a scaling parameter derived from the extracted spatial features. We validate our approach on two diverse breast cancer histopathology image datasets: TNBC and MonuSeg, demonstrating superior segmentation performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 July 2024
A correction has been published.
References
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.7062 (2014)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587 (2017)
Chen, L.C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 801–818 (2018)
Das, N., Saha, S., Nasipuri, M., Basu, S., Chakraborti, T.: Deep-fuzz: a synergistic integration of deep learning and fuzzy water flows for fine-grained nuclei segmentation in digital pathology. PLoS ONE 18(6), e0286862 (2023)
Diakogiannis, F.I., Waldner, F., Caccetta, P., Wu, C.: Resunet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 162, 94–114 (2020)
Feng, Z., et al.: Mutual-complementing framework for nuclei detection and segmentation in pathology image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4036–4045 (2021)
Fu, Y., Liu, J., Shi, J.: Tsca-net: transformer based spatial-channel attention segmentation network for medical images. Comput. Biol. Med. 170, 107938 (2024)
Husham, A., Hazim Alkawaz, M., Saba, T., Rehman, A., Saleh Alghamdi, J.: Automated nuclei segmentation of malignant using level sets. Microsc. Res. Tech. 79(10), 993–997 (2016)
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: Multiresunet: rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 121, 74–87 (2020)
Islam Sumon, R., et al.: Densely convolutional spatial attention network for nuclei segmentation of histological images for computational pathology. Front. Oncol. 13, 1009681 (2023)
Jadon, S.: A survey of loss functions for semantic segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2020)
Kanadath, A., Angel Arul Jothi, J., Urolagin, S.: Multilevel multiobjective particle swarm optimization guided superpixel algorithm for histopathology image detection and segmentation. J. Imaging 9(4), 78 (2023)
Keaton, M.R., Zaveri, R.J., Doretto, G.: Celltranspose: few-shot domain adaptation for cellular instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 455–466 (2023)
Kumar, N., et al.: A multi-organ nucleus segmentation challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(5), 1380–1391 (2019)
Kuo, T.C., Cheng, T.W., Lin, C.K., Chang, M.C., Cheng, K.Y., Cheng, Y.C.: Using deeplab v3+-based semantic segmentation to evaluate platelet activation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 60(6), 1775–1785 (2022)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Metter, D.M., Colgan, T.J., Leung, S.T., Timmons, C.F., Park, J.Y.: Trends in the us and canadian pathologist workforces from 2007 to 2017. JAMA Netw. Open 2(5), e194337–e194337 (2019)
Naylor, P., Laé, M., Reyal, F., Walter, T.: Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images by deep regression of the distance map. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(2), 448–459 (2018)
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Qi, J.: Dense nuclei segmentation based on graph cut and convexity-concavity analysis. J. Microsc. 253(1), 42–53 (2014)
Ranefall, P., Egevad, L., Nordin, B., Bengtsson, E.: A new method for segmentation of colour images applied to immunohistochemically stained cell nuclei. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 15(3), 145–156 (1997)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III, vol. 18, pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., Wolf, T.: Distilbert, a distilled version of bert: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01108 (2019)
Singha, A., Bhowmik, M.K.: Alexsegnet: an accurate nuclei segmentation deep learning model in microscopic images for diagnosis of cancer. Multim. Tools Appl. 82(13), 20431–20452 (2023)
Soomro, T.A., Afifi, A.J., Gao, J., Hellwich, O., Paul, M., Zheng, L.: Strided u-net model: Retinal vessels segmentation using dice loss. In: 2018 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2018)
Sornapudi, S., et al.: Deep learning nuclei detection in digitized histology images by superpixels. J. Pathol. Inform. 9(1), 5 (2018)
Su, Z., Li, W., Ma, Z., Gao, R.: An improved u-net method for the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Appl. Intell. 52(3), 3276–3288 (2022)
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Oza, P., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: Medical transformer: gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., Cattin, P.C., Cotin, S., Padoy, N., Speidel, S., Zheng, Y., Essert, C. (eds.) MICCAI 2021, pp. 36–46. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_4
Wazir, S., Fraz, M.M.: Histoseg: Quick attention with multi-loss function for multi-structure segmentation in digital histology images. In: 2022 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Systems (ICPRS, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2022)
Xia, L., Qu, Z., An, J., Gao, Z.: A weakly supervised method with colorization for nuclei segmentation using point annotations. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Measur. 72, 1–11 (2023)
Xu, H., Lu, C., Mandal, M.: An efficient technique for nuclei segmentation based on ellipse descriptor analysis and improved seed detection algorithm. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 18(5), 1729–1741 (2014)
Xu, Q., Kuang, W., Zhang, Z., Bao, X., Chen, H., Duan, W.: Sppnet: a single-point prompt network for nuclei image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12231 (2023)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Roy, A., Pramanik, P., Ghosal, S., Valenkova, D., Kaplun, D., Sarkar, R. (2024). GRU-Net: Gaussian Attention Aided Dense Skip Connection Based MultiResUNet for Breast Histopathology Image Segmentation. In: Yap, M.H., Kendrick, C., Behera, A., Cootes, T., Zwiggelaar, R. (eds) Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. MIUA 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14859. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66955-2_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66955-2_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-66954-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-66955-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)