Abstract
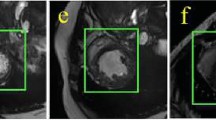
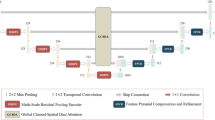
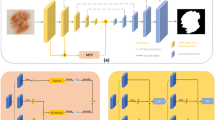
Encoder-decoder architectures are widely adopted for medical image segmentation tasks. These models utilize lateral skip connections to capture and fuse both semantic and resolution information in deep layers, enhancing segmentation accuracy. However, in many applications, such as images with blurry boundaries, these models often struggle to precisely locate complex boundaries and segment tiny isolated parts due to the fuzzy information passed through the skip connections from the encoder layers. To solve this challenging problem, we first analyze why simple skip connections are insufficient for accurately locating indistinct boundaries. Based on this analysis, we propose a semantic-guided encoder feature learning strategy. This strategy aims to learn high-resolution semantic encoder features, enabling more accurate localization of blurry boundaries and enhancing the network’s ability to selectively learn discriminative features. Additionally, we further propose a soft contour constraint mechanism to model the blurry boundary detection. Experimental results on real clinical datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy, particularly in regions with blurry boundaries. Further analysis confirms that our proposed network components significantly contribute to performance improvements. Experiments on additional datasets validate the generalization ability of our proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo, Y., et al.: Deformable MR prostate segmentation via deep feature learning and sparse patch matching. IEEE TMI 35, 1077–1089 (2016)
Heller, N., Dean, J., Papanikolopoulos, N.: Imperfect segmentation labels: how much do they matter? In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) LABELS/CVII/STENT -2018. LNCS, vol. 11043, pp. 112–120. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01364-6_13
Lamme, V., et al.: Separate processing dynamics for texture elements in primary visual cortex of the macaque monkey. Cerebral Cortex 9(4), 406–413 (1999)
Lee, H.J., Kim, J.U., Lee, S., Kim, H.G., Ro, Y.M.: Structure boundary preserving segmentation for medical image with ambiguous boundary. In: CVPR, pp. 4817–4826 (2020)
Litjens, G., et al.: Evaluation of prostate segmentation algorithms for MRI: the PROMISE12 challenge. Media 18(2), 359–373 (2014)
Long, J., et al.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Ravishankar, H., et al.: Joint deep learning of foreground and shape for robust contextual segmentation. In: IPMI (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Roy, A.G., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Concurrent spatial and channel ‘Squeeze & Excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11070, pp. 421–429. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00928-1_48
Wang, J., Wei, L., Wang, L., Zhou, Q., Zhu, L., Qin, J.: Boundary-aware transformers for skin lesion segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 206–216. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_20
Wu, Z., et al.: W-Net: a boundary-enhanced segmentation network for stroke lesions. Expert Syst. Appl. 230, 120637 (2023)
Xu, J., Li, M., Zhu, Z.: Automatic data augmentation for 3D medical image segmentation. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12261, pp. 378–387. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_37
Yu, L., et al.: Volumetric ConvNets with mixed residual connections for automated prostate segmentation from 3D MR images. In: AAAI (2017)
Zhou, S., et al.: High-resolution encoder-decoder networks for low-contrast medical image segmentation. TIP 29, 461–475 (2019)
Zhu, Q., et al.: Boundary-weighted domain adaptive neural network for prostate MR image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.08128 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiao, Q., Nie, D. (2024). Blurry Boundary Segmentation with Semantic-Aware Feature Learning. In: Yap, M.H., Kendrick, C., Behera, A., Cootes, T., Zwiggelaar, R. (eds) Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. MIUA 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14860. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66958-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-66958-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-66957-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-66958-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)