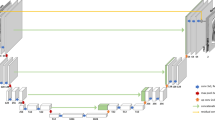
Abstract
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a widely used diagnostic tool in medicine. The long acquisition time of MRI remains to be a practical concern, leading to suboptimal patient experiences. Existing deep learning models for fast MRI acquisition struggle to handle the problem of data heterogeneity due to scanners from different vendors. This study explores the transfer learning capabilities of variational deep learning architectures to address this problem. Using standard ACR protocols, we acquired 135 ACR phantom samples from GE and Siemens 3.0T MR scanners and conducted comprehensive experiments to compare the reconstruction quality of the images produced by different models. Our experiments identified vendor differences as a major challenge in the generalization of accelerated MRI. We propose a feature refinement-based transfer learning method that outperforms the baseline networks by \(\sim \)2.0 dB (PSNR), 1.8% (SSIM) for GE, and \(\sim \)3.0 dB (PSNR), 0.8% (SSIM) for SIEMENS. Furthermore, we used experience replay to address the problem of catastrophic forgetting. We established it as a robust baseline through experiments with strong results (PSNR and SSIM performance drop reduced by 25.55% and 9.5%, respectively).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlBadawy, E.A., Saha, A., Mazurowski, M.A.: Deep learning for segmentation of brain tumors: impact of cross-institutional training and testing. Med. Phys. 45(3), 1150–1158 (2018)
Chen, E.Z., Chen, T., Sun, S.: MRI image reconstruction via learning optimization using neural odes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.13825 (2020)
Ding, P.L.K., Li, B., Chang, K.: Convex dictionary learning for single image super-resolution. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4058–4062 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2017.8297045
Ding, P.L.K., Paul, R., Patel, A., Zhou, Y., Li, B.: Variational feedback network for accelerated MRI reconstruction. ISMRM & SMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition (2021). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26769.10087
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Ellis, R.: Leveraging Large Scale Data Sets: a Transfer Learning Approach for 7T Super Resolution. University of California, San Francisco (2021)
Finn, C., Abbeel, P., Levine, S.: Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1126–1135. PMLR (2017)
Geirhos, R., Rubisch, P., Michaelis, C., Bethge, M., Wichmann, F.A., Brendel, W.: Imagenet-trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.12231 (2018)
Griswold, M.A., et al.: Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (grappa). Mag. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 47(6), 1202–1210 (2002)
Hammernik, K., Klatzer, T., Kobler, E., Recht, M.P., Sodickson, D.K., Pock, T., Knoll, F.: Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 79(6), 3055–3071 (2018)
He, K., Girshick, R., Dollár, P.: Rethinking ImageNet pre-training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4918–4927 (2019)
Huh, M., Agrawal, P., Efros, A.A.: What makes ImageNet good for transfer learning? arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.08614 (2016)
Kolesnikov, A., et al.: Large scale learning of general visual representations for transfer. 2(8) (2019). arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.11370
Kornblith, S., Shlens, J., Le, Q.V.: Do better ImageNet models transfer better? In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2661–2671 (2019)
Kwon, K., Kim, D., Park, H.: A parallel MR imaging method using multilayer perceptron. Med. Phys. 44(12), 6209–6224 (2017)
Liang, D., Cheng, J., Ke, Z., Ying, L.: Deep MRI reconstruction: unrolled optimization algorithms meet neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11711 (2019)
Lustig, M., Donoho, D.L., Santos, J.M., Pauly, J.M.: Compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25(2), 72–82 (2008)
Maas, A.L., Hannun, A.Y., Ng, A.Y.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings of ICML, vol. 30, p. 3 (2013)
Muckley, M.J., et al.: Results of the 2020 fastMRI challenge for machine learning MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(9), 2306–2317 (2021)
Ngiam, J., Peng, D., Vasudevan, V., Kornblith, S., Le, Q.V., Pang, R.: Domain adaptive transfer learning with specialist models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.07056 (2018)
Paszke, A., et al.: Automatic differentiation in PyTorch (2017)
Pooch, E.H., Ballester, P.L., Barros, R.C.: Can we trust deep learning models diagnosis? The impact of domain shift in chest radiograph classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01940 (2019)
Pruessmann, K.P., Weiger, M., Scheidegger, M.B., Boesiger, P.: Sense: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Mag. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 42(5), 952–962 (1999)
Putzky, P., et al.: i-rim applied to the fastMRI challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.08952 (2019)
Putzky, P., Welling, M.: Invert to learn to invert. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Raghu, A., Raghu, M., Bengio, S., Vinyals, O.: Rapid learning or feature reuse? Towards understanding the effectiveness of MAML. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.09157 (2019)
Raghu, M., Zhang, C., Kleinberg, J., Bengio, S.: TransFusion: understanding transfer learning for medical imaging. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Robins, A.: Catastrophic forgetting, rehearsal and pseudorehearsal. Connect. Sci. 7(2), 123–146 (1995)
Roemer, P.B., Edelstein, W.A., Hayes, C.E., Souza, S.P., Mueller, O.M.: The NMR phased array. Magn. Reson. Med. 16(2), 192–225 (1990)
Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Hajnal, J.V., Price, A., Rueckert, D.: A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for MR image reconstruction. In: Niethammer, M., et al. (eds.) IPMI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10265, pp. 647–658. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_51
Shin, P.J., et al.: Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on structured low-rank matrix completion. Magn. Reson. Med. 72(4), 959–970 (2014)
Sodickson, D.K., Manning, W.J.: Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 38(4), 591–603 (1997)
Sriram, A., et al.: End-to-end variational networks for accelerated MRI reconstruction. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12262, pp. 64–73. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59713-9_7
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., Lempitsky, V.: Instance normalization: the missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.08022 (2016)
Wang, S., et al.: Accelerating magnetic resonance imaging via deep learning. In: Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on, pp. 514–517. IEEE (2016)
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E.P., Bovik, A.C.: Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: The Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, 2003, vol. 2, pp. 1398–1402. IEEE (2003)
Yan, W., et al.: The domain shift problem of medical image segmentation and vendor-adaptation by Unet-GAN. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 623–631. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_69
Yosinski, J., Clune, J., Bengio, Y., Lipson, H.: How transferable are features in deep neural networks? In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Paul, R. et al. (2024). Transferable Variational Feedback Network for Vendor Generalization in Accelerated MRI. In: Xie, X., Styles, I., Powathil, G., Ceccarelli, M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. AIiH 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14976. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67285-9_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67285-9_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-67284-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-67285-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)