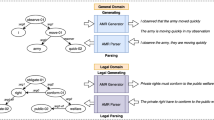
Abstract
The definition is an integral component of the legislation. It is essential to the adequacy and legitimacy of legislation. In legislation, legal definitions are used for clarity, consistency, and legitimate certainty, but also for creating new legal concepts (e.g., personal data) or crimes (e.g. stalking, mobbing). With the advancement in society with technological innovation, the significance of accurate and precise definitions in legislation is indeed more articulated. In order to avoid ambiguity and to ensure, as far as possible, a strict interpretation of Law, Legal Texts (LT) usually define the specific lexical terms used within their discourse by means of normative rules. Due to the continuous increase of LT and a large number of domain-specific rules, extracting these definitions from the LT would be costly and time-consuming if it’s done humanely. Definition extraction is widely used in Legal domains to perform legal and compliance analysis. In this paper, we detect and annotate the legal definitions using Symbolic Artificial Intelligence (AI) based on Natural Language Processing (NLP) and fostering LegalXML annotation. The goal is to qualify a very valuable part of legislation for supporting further AI applications also in the judiciary domain. The detection and annotation of definitions are performed on the delimiting type of definitions. The dataset consists of EU Legislation in the span of time from 2010 to 2021 in Akoma Ntoso (AKN) file format. The resultant 15082 AKN files are annotated. (Akoma Ntoso OASIS LegalDocML XML Standard. http://docs.oasis-open.org/legaldocml/akn-core/v1.0/akn-core-v1.0-part1-vocabulary.html)
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qureshi, M.A., et al.: A novel auto-annotation technique for aspect level sentiment analysis. CMC-Comput. Mater. Continua 70(3), 4987–5004 (2022)
Oral, B., Eryiğit, G.: Fusion of visual representations for multimodal information extraction from unstructured transactional documents. Int. J. Document Analy. Recogn. (IJDAR), 1–19 (2022)
Senave, E., Jans, M.J., Srivastava, R.P.: The application of text mining in accounting. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 50, 100624 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accinf.2023.100624
Mohammed, N.F.P., Shaikh, F.R., Talawar Priya, K.K., Jamadar, S.: Obtaining and Analyzing Data from Texts, vol. 12, p. 2023
Gupta, T., Zaki, M., Krishnan, N.A., Mausam.: MatSciBERT: A materials domain language model for text mining and information extraction. NPJ Comput. Mater. 8(1) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-022-00784-w
Kumar, A., Dabas, V., Hooda, P.: Text classification algorithms for mining unstructured data: a SWOT analysis. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 12(4), 1159–1169 (2020)
Singh, S.: Natural language processing for information extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.02383 (2018)
Toluhi, D., Schmidt, R., Parsia, B.: Concept description and definition extraction for the ANEMONE system. In: Engineering Multi-Agent Systems: 9th International Workshop, EMAS 2021, Virtual Event, May 3--4, 2021, Revised Selected Papers, pp. 352–372 (2022)
Gardner, N., Khan, H., Hung, C.-C.: Definition modeling: literature review and dataset analysis. Appl. Comput. Intell. 2(1), 83–98 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3934/aci.2022005
Zaki-Ismail, A., Osama, M., Abdelrazek, M., Grundy, J., Ibrahim, A.: RCM-extractor: an automated NLP-based approach for extracting a semi formal representation model from natural language requirements. Autom. Softw. Eng. 29(1), 1–33 (2022)
Veyseh, A., Dernoncourt, F., Dou, D., Nguyen, T.: A joint model for definition extraction with syntactic connection and semantic consistency. In: AAAI 2020 - 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 9098–9105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i05.6444
Claassen, L., et al.: Cold brew coffee—Pilot studies on definition, extraction, consumer preference, chemical characterization and microbiological hazards. Foods 10(4), 865 (2021)
Kumar, P., Singh, A., Kumar, P., Kumar, C.: An explainable machine learning approach for definition extraction. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, Image Processing, Network Security and Data Sciences, pp. 145–155 (2020)
Kanapala, A., Pal, S., Pamula, R.: Text summarization from legal documents: a survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 51(3), 371–402 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9566-2
Niculiţă, C., Dumitriu, L. The relational parts of speech in text analysis for definition detection, for romanian language. In: 2019 18th RoEduNet Conference: Networking in Education and Research (RoEduNet), pp. 1–6 (2019)
Ferneda, E., do Prado, H.A., Batista, A.H., Pinheiro, M.S.: Extracting definitions from brazilian legal texts, In: International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications, pp. 631–646 (2012)
Höfler, S., Bünzli, A., Sugisaki, K.: Detecting legal definitions for automated style checking in draft laws. Technical Reports in Computational Linguistics, no. CL-2011.01 (2011)
Padayachy, T., Scholtz, B., Wesson, J.: An information extraction model using a graph database to recommend the most applied case. In: 2018 International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (iCCECE), pp. 89–94 (2018)
Weissweiler, L., Hofmann, V., Sabet, M.J., Schütze, H.: CaMEL: Case Marker Extraction without Labels (2022). http://arxiv.org/abs/2203.10010
Dai, F., Leach, M., Macrae, A.M., Minero, M., Costa, E.D.: Does thirty-minute standardised training improve the inter-observer reliability of the horse grimace scale (HGS)? A case study. Animals 10(5) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050781
Acknowledgments
This study is funded by PON grants of the Italian Government and also the ERC HyperModeLex.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Asif, M., Palmirani, M. (2024). Legal Definition Annotation in EU Legislation Using Symbolic AI. In: Kö, A., Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I. (eds) Electronic Government and the Information Systems Perspective. EGOVIS 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14913. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68211-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68211-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-68210-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-68211-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)