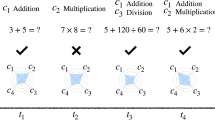
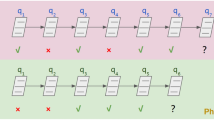
Abstract
Online education systems have gained increasing popularity due to their capability to fully preserve users’ learning data. This advantage enables researchers to assess learners’ mastery through their learning trajectories, thereby facilitating personalized education and support. Knowledge tracing, an effective educational aid, simulates students’ implicit knowledge states and predicts their mastery over knowledge based on their historical answer records. However, for newly developed online learning platforms, the lack of sufficient historical answer data may impede accurate prediction of students’ knowledge states, rendering existing knowledge tracing models less effective. This paper introduces the first pre-trained knowledge tracing model that leverages a substantial amount of existing data for pre-training and a smaller dataset for fine-tuning. Validated across several publicly available knowledge tracing datasets, our method demonstrates significant improvement in tracing performance on small datasets, with a maximum AUC increase of 5.07%. Beyond incorporating small datasets, our approach of pre-training the entire dataset has shown an enhanced AUC compared to the baseline, marking a novel direction in knowledge tracing research. Furthermore, the paper analyzed the outcomes of pre-training experiments with varying numbers of interactions as fine-tuning datasets, providing valuable insights for Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman, G., Wang, Q.: Learning data teaching strategies via knowledge tracing. Knowl.-Based Syst. 269, 110511 (2023)
Anderson, J.R., Boyle, C.F., Reiser, B.J.: Intelligent tutoring systems. Science 228(4698), 456–462 (1985)
Baker, R.S.J., Corbett, A.T., Aleven, V.: More accurate student modeling through contextual estimation of slip and guess probabilities in Bayesian knowledge tracing. In: Woolf, B.P., Aïmeur, E., Nkambou, R., Lajoie, S. (eds.) ITS 2008. LNCS, vol. 5091, pp. 406–415. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69132-7_44
Choi, Y., et al.: Towards an appropriate query, key, and value computation for knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the Seventh ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale, pp. 341–344 (2020)
Corbett, A.T., Anderson, J.R.: Knowledge tracing: modeling the acquisition of procedural knowledge. User Model. User-Adap. Inter. 4, 253–278 (1994)
Ghosh, A., Heffernan, N., Lan, A.S.: Context-aware attentive knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2330–2339 (2020)
Liu, Z., Chen, J., Luo, W.: Recent advances on deep learning based knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 1295–1296 (2023)
Nakagawa, H., Iwasawa, Y., Matsuo, Y.: Graph-based knowledge tracing: modeling student proficiency using graph neural network. In: IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence, pp. 156–163 (2019)
Pandey, S., Karypis, G.: A self-attentive model for knowledge tracing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.06837 (2019)
Pandey, S., Srivastava, J.: RKT: relation-aware self-attention for knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 1205–1214 (2020)
Piech, C., et al.: Deep knowledge tracing. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28 (2015)
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
Sha, L., Hong, P.: Neural knowledge tracing. In: Frasson, C., Kostopoulos, G. (eds.) BFAL 2017. LNCS, vol. 10512, pp. 108–117. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67615-9_10
Shin, D., Shim, Y., Yu, H., Lee, S., Kim, B., Choi, Y.: SAINT+: integrating temporal features for EdNet correctness prediction. In: LAK21: 11th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference, pp. 490–496 (2021)
Song, K., Tan, X., Qin, T., Lu, J., Liu, T.Y.: MASS: masked sequence to sequence pre-training for language generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.02450 (2019)
Song, X., Li, J., Lei, Q., Zhao, W., Chen, Y., Mian, A.: Bi-CLKT: Bi-graph contrastive learning based knowledge tracing. Knowl.-Based Syst. 241, 108274 (2022)
Sonkar, S., Waters, A.E., Lan, A.S., Grimaldi, P.J., Baraniuk, R.G.: qDKT: question-centric deep knowledge tracing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.12442 (2020)
Tato, A., Nkambou, R.: Deep knowledge tracing on skills with small datasets. In: Crossley, S., Popescu, E. (eds.) ITS 2022. LNCS, vol. 13284, pp. 123–135. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09680-8_12
Tong, S., et al.: Structure-based knowledge tracing: an influence propagation view. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 541–550. IEEE (2020)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Villano, M.: Probabilistic student models: Bayesian belief networks and knowledge space theory. In: Frasson, C., Gauthier, G., McCalla, G.I. (eds.) ITS 1992. LNCS, vol. 608, pp. 491–498. Springer, Heidelberg (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-55606-0_58
Weston, J., Chopra, S., Bordes, A.: Memory networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.3916 (2014)
Wulf, J., Blohm, I., Leimeister, J.M., Brenner, W.: Massive open online courses. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 6, 111–114 (2014)
Yang, H., Cheung, L.P.: Implicit heterogeneous features embedding in deep knowledge tracing. Cogn. Comput. 10, 3–14 (2018)
Yang, Y., et al.: GIKT: a graph-based interaction model for knowledge tracing. In: Hutter, F., Kersting, K., Lijffijt, J., Valera, I. (eds.) ECML PKDD 2020. LNCS, vol. 12457, pp. 299–315. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67658-2_18
Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R.R., Le, Q.V.: XLNet: generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Ye, Y., Shan, Z.: HGKT: hypergraph-based knowledge tracing for learner performance prediction. In: 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–9. IEEE (2023)
Zhang, J., Shi, X., King, I., Yeung, D.Y.: Dynamic key-value memory networks for knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 765–774 (2017)
Zhang, L., Xiong, X., Zhao, S., Botelho, A., Heffernan, N.T.: Incorporating rich features into deep knowledge tracing. In: Proceedings of the Fourth ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale, pp. 169–172 (2017)
Zhao, J., Bhatt, S., Thille, C., Gattani, N., Zimmaro, D.: Cold start knowledge tracing with attentive neural turing machine. In: Proceedings of the Seventh ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale, pp. 333–336 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Gansu (21YF5GA102, 21YF5GA006, 21ZD8RA008, 22ZD6GA029, 22YF7GA003), Gansu Key Talent Project (11256471037), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2022-ct06), Supercomputing Center of Lanzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yue, W. et al. (2024). A Pre-trained Knowledge Tracing Model with Limited Data. In: Strauss, C., Amagasa, T., Manco, G., Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I. (eds) Database and Expert Systems Applications. DEXA 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14910. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68309-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68309-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-68308-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-68309-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)