Abstract
Phishing is the act of attackers sending malicious emails to receivers in an effort to trick them into falling for a con. Normally, the intention is to persuade users to provide private information, such as system logins or financial data. Our project investigates such email phishing attacks using AI and ML to get a reasonable conclusion about which algorithm can spot these attacks the most successfully.
In terms of cybersecurity, a phishing attack is a cybercrime that aims to obtain a user’s personal information in order to carry out some destructive actions. This attack’s effects could lead to account takeover, privilege escalation, and other issues. And in order to lessen it, this study provides information on how to spot phishing emails so that businesses can correctly deal with them.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) [26], logistic regression, and fundamental AI ideas like CNN [27] are used, along with machine learning algorithms like KNN, Naive Bayers, and these. This study aims to identify the optimal machine learning algorithm that would provide the highest level of accuracy when it comes to phishing email detection.
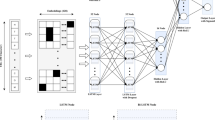
“To improve the accuracy of detecting phishing emails we have implemented CNN which is an effective approach to fulfill the target. CNN [27] can learn to recognize tiny patterns and traits that may be challenging for humans to notice, they can be a great tool for detecting phishing emails. Handling this technique is very important, hence LSTM is introduced”. The CNN model’s LSTM [27] can be thought of as its brain. LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) [27] is a form of recurrent neural network (RNN) that is frequently employed in tasks involving sequence prediction and natural language processing (NLP) [26]. It is intended to solve the vanishing gradients issue, which can arise in conventional RNNs when the gradients are extremely small and make the network struggle to learn long-term dependencies.
By understanding and executing everything we have observed that Logistic Regression is giving us the highest of 97.49% accuracy followed by KNN at 94%. This proves that how effective the model is been while handling the data and also detecting phishing emails.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shabnam Sharma, study on phishing attack
Sharma, P., Dash, B., Ansari, M.: Anti phishing techniques. IJ ARCCCE (2022)
Ansari, M.F., Sharma, P.K., Dash, B.: Prevention of phishing attacks using AI-based cybersecurity awareness training. Int. J. Smart Sensor Adhoc Netw. 3, 61–72 (2022)
Adil, M., Khan, R., Nawaz Ul Ghani, M.A.: Preventive techniques of phishing attacks in networks
Vitthal limbore, N., Todkar, R.S, Zargad, B.B,: a study of preventive measure of phishing attacks with reference to email websites (2014)
Basit, A., Zafar, M., Liu, X., Javed, A.R.: A comprehensive survey of AI-enabled phishing attacks detection techniques (2021)
Basit, A., Zafar, M., Jalil, Z.: A Review of Website Phishing Attack Detection Methods (2020)
Sahingoz, O.K., Buber, E., Diri, B.: Machine learning based phishing detection from URLs (2019)
Zhang, Z., Yeun, C.Y., Damiani, E.: Explainable Artificial Intelligence Applications in Cyber Security: State-of-the-Art in Research (2022)
Basit, A., Zafar, M., Rehman Javed, A., Jalil, Z.: A Novel Ensemble MachineLearning Method to Detect Phishing Attack
Verizon, Data Breach Report (2016)
Andronicus, A., Akinyelu, Adewumi, A.O.: Classification of Phishing
Email using Random forest Machine Learning Technique (2014)
Jameel, N.G.M., George, L.E.: Detection of phishing emails using feed forward neural network. Int. J. Compu. Appl. 77(7), 10–15 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5120/13405-1057
Fette, I., Sadeh, N., Tomasi, A.: Learning to detect phishing emails. In: Proceedings of the )International World Wide Web Conference (WWW) (2006)
Park, G., Taylor, J.M.: Using Syntactic Features for Phishing Detection (2015). https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.00037#:~:text=This%20experiment%20aimed%20to%20investigate,phishing%20emails%20and%20legitimate%20emails
Gori Mohamed, J., Mohammed Mohideen, M., Banu, S.: Email Phishing – An open threat to everyone. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 4, 1–4 (2014)
Emilin Shyni, C., Sarju, S., Swamynathan, S.: A multi-classifier based prediction model for phishing emails detection using topic modelling, named entity recognition and image processing. Circuits Syst. 07(09), 2507–2520 (2016)
Jameel, N.G.M., George, L.E.: Detection phishing emails using features decisive values. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 3, 257–259 (2014)
Verma, R., Rai, N.: Phish-IDetector: Message-ID based automatic phishing detection. In: 2015 12th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE), pp. 427–434. Colmar, France (2015)
Basnet. R., Mukkamala, S., Sung, A.H.: Detection of phishing attacks: a machine learning approach. In: Prasad, B. (eds.), Soft Computing Applications in Industry. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol. 226. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77465-5_19
Karthikeyan, H., Usha, G.: An efficient hybrid message authentication scheme in vehicular ad hoc networks. Int. J. of Recent Technol. Eng. 8(2 Special Issue 4), 258–262 (2019). https://doi.org/10.35940/ijrte.B1048.0782S419
Yasin, A., Abuhasan, A.: An intelligent classification model for phishing email detection. Int. J. Netw. Secur. Appl. 8(4), 55–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5121/ijnsa.2016.8405
NIST Information Technology Laboratory Resource Center lossary. Nortan USA Types of phishing attacks and example
Karthikeyan, H., Usha, G.: Real-time DDoS flooding attack detection in intelligent transportation systems. Comput, Electr. Eng. 101, 107995 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107995. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045790622002634)
Wang, Z.Q., Zhang. D.K.: HIDS and NIDS Hybrid Intrusion Detection System Model Design.
Usha, G., Kannimuthu, S., Vinoth, N.A.S., Karthikeyan, H.: Augmentation and orchestration of security techniques in fog computing. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 8(2 Special Issue 4), 143–148(2019). https://doi.org/10.35940/ijrte.B1025.0782S419 https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85073360770&doi=10.35940%2fijrte.B1025.0782S419&partnerID=40&md5=0490c58080aac3ef5152e1f7f2c14480
Singh, S., Khatter, K.: Natural language processing: state of the art. current trends and challenges
Deep Sentiment Representation Based on CNN and LSTM
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sarkar, S., Yadav, A., Balachander, T. (2024). Email Phishing Detection Using AI and ML. In: R., A.U., et al. Deep Sciences for Computing and Communications. IconDeepCom 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2176. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68905-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68905-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-68904-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-68905-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)