Abstract
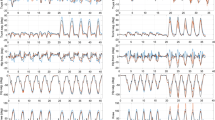
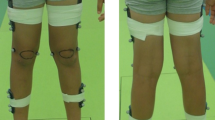
Markerless systems and inertial sensors, such as inertial measurement units, offer significant advantages over traditional marker-based methods by eliminating the need for laboratory conditions or markers placement. Virtual reality is an innovative technology used in rehabilitation, recently investigated for obtaining kinematic motion data. This research aims to validate a markerless system using a MediaPipe-based algorithm to reconstruct joint kinematics during exercises with the Nirvana virtual reality rehabilitation system. In the first phase, the markerless system was evaluated against the Xsens inertial measurement unit system, analyzing knee, hip, elbow and shoulder movements of 7 healthy participants at the Politecnico di Milano. The MediaPipe algorithm showed high performance in tracking lower limb movements but was less accurate for upper limbs, as indicated by RMSE and %RMSE values. However, it accurately replicated the time course of all angles based on ICC and Spearman’s coefficient, suggesting virtual reality’s feasibility in rehabilitation and movement analysis. In the second phase, a pilot study was carried out at the Fondazione TOG on 2 participants with left hemiparesis to assess the efficacy of the system in a pathological context. The results provide a basis for evaluating the potential clinical applicability of the system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borghese, N.A., Bianchi, L., Lacquaniti, F.: Kinematic determinants of human locomotion. J. Physiol. 494(3), 863–879 (1996)
Mündermann, L., Corazza, S., Andriacchi, T.P.: The evolution of methods for the capture of human movement leading to markerless motion capture for biomechanical applications. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 3, 1–11 (2006)
Chung, J.L., Ong, L.Y., Leow, M.C.: Comparative analysis of skeleton-based human pose estimation. Future Internet 14(12), 380 (2022)
Armstrong, K., Zhang, L., Wen, Y., Willmott, A.P., Lee, P., Ye, X.: A marker-less human motion analysis system for motion-based biomarker identification and quantification in knee disorders. Front. Digit. Health 6, 1324511 (2024)
Hii, C.S.T., et al.: Automated gait analysis based on a marker-free pose estimation model. Sensors 23(14), 6489 (2023)
Nijmeijer, E.M., Heuvelmans, P., Bolt, R., Gokeler, A., Otten, E., Benjaminse, A.: Concurrent validation of the Xsens IMU system of lower-body kinematics in jump-landing and change-of-direction tasks. J. Biomech. 154, 111637 (2023)
Rose, T., Nam, C.S., Chen, K.B.: Immersion of virtual reality for rehabilitation-review. Appl. Ergon. 69, 153–161 (2018)
Karatsidis, A., et al.: Validation of wearable visual feedback for retraining foot progression angle using inertial sensors and an augmented reality headset. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 15(1), 1–12 (2018)
Settimo, C., et al.: Virtual reality technology to enhance conventional rehabilitation program: results of a single-blind, randomized, controlled pilot study in patients with global developmental delay. J. Clin. Med. 12(15), 4962 (2023)
De Luca, R., et al.: Improvement of brain functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorder: an exploratory study on the potential use of virtual reality. J. Neural Transm. 128, 371–380 (2021)
Kim, J.W., Choi, J.Y., Ha, E.J., Choi, J.H.: Human pose estimation using MediaPipe pose and optimization method based on a humanoid model. Appl. Sci. 13(4), 2700 (2023)
Tong, K., Granat, M.H.: A practical gait analysis system using gyroscopes. Med. Eng. Phys. 21(2), 87–94 (1999)
Jarque, C.M., Bera, A.K.: A test for normality of observations and regression residuals. Int. Stat. Rev./Revue Int. Stat., 163–172 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Francia, C. et al. (2024). Validation of a MediaPipe System for Markerless Motion Analysis During Virtual Reality Rehabilitation. In: De Paolis, L.T., Arpaia, P., Sacco, M. (eds) Extended Reality. XR Salento 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15029. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-71710-9_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-71710-9_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-71709-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-71710-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)