Abstract
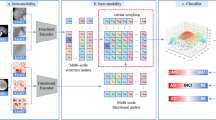
Accurately discriminating progressive stages of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is crucial for early diagnosis and prevention. It often involves multiple imaging modalities to understand the complex pathology of AD, however, acquiring a complete set of images is challenging due to high cost and burden for subjects. In the end, missing data become inevitable which lead to limited sample-size and decrease in precision in downstream analyses. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a holistic imaging feature imputation method that enables to leverage diverse imaging features while retaining all subjects. The proposed method comprises two networks: 1) An encoder to extract modality-independent embeddings and 2) A decoder to reconstruct the original measures conditioned on their imaging modalities. The encoder includes a novel ordinal contrastive loss, which aligns samples in the embedding space according to the progression of AD. We also maximize modality-wise coherence of embeddings within each subject, in conjunction with domain adversarial training algorithms, to further enhance alignment between different imaging modalities. The proposed method promotes our holistic imaging feature imputation across various modalities in the shared embedding space. In the experiments, we show that our networks deliver favorable results for statistical analysis and classification against imputation baselines with Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) study.
S. Baek and J. Sim—contributed equally to this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek, S., Choi, I., et al.: Learning covariance-based multi-scale representation of neuroimaging measures for Alzheimer classification. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. pp. 1–5. IEEE (2023)
Cui, W., Yan, et al.: Bmnet: A new region-based metric learning method for early Alzheimer’s disease identification with FDG-PET images. Frontiers in Neuroscience 16, 831533 (2022)
Destrieux, C., et al.: Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 53(1), 1–15 (2010)
Donders, A.R.T., Heijden, V.D., et al.: A gentle introduction to imputation of missing values. Journal of clinical epidemiology 59(10), 1087–1091 (2006)
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, et al.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research 17(59), 1–35 (2016)
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (2014)
Harrison, T.M., Du, et al.: Distinct effects of beta-amyloid and tau on cortical thickness in cognitively healthy older adults. Alzheimer’s & dementia 17(7), 1085–1096 (2021)
Jack Jr, C.R., Bernstein, et al.: The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (adni): MRI methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 27(4), 685–691 (2008)
Khosla, P., Teterwak, et al.: Supervised contrastive learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33, 18661–18673 (2020)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. International Conference on Learning Representations (2017)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research 9(11) (2008)
Marinescu, R.V., et al.: BrainPainter: A software for the visualisation of brain structures, biomarkers and associated pathological processes. In: Multimodal Brain Image Analysis and Mathematical Foundations of Computational Anatomy: 4th International Workshop. pp. 112–120. Springer (2019)
McNaughton, J., Fernandez, J., Holdsworth, S., otheres: Machine learning for medical image translation: A systematic review. Bioengineering 10(9), 1078 (2023)
Mirza, M., Osindero, S.: Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784 (2014)
Muzellec, B., Josse, J., Boyer, C., Cuturi, M.: Missing data imputation using optimal transport. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 7130–7140. PMLR (2020)
Napierala, M.A.: What is the bonferroni correction? Aaos Now pp. 40–41 (2012)
Ossenkoppele, R., Smith, et al.: Associations between tau, A\(\beta \), and cortical thickness with cognition in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 92(6), e601–e612 (2019)
Rubinski, A., Franzmeier, et al.: FDG-PET hypermetabolism is associated with higher tau-PET in mild cognitive impairment at low amyloid-PET levels. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 12, 1–12 (2020)
Sim, J., Jeon, S., Choi, I., Wu, G., Kim, W.H.: Learning to approximate adaptive kernel convolution on graphs. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 38, pp. 4882–4890 (2024)
Sintini, I., Graff-Radford, J., Senjem, et al.: Longitudinal neuroimaging biomarkers differ across Alzheimer’s disease phenotypes. Brain 143(7), 2281–2294 (2020)
Sohn, K., Lee, H., Yan, X.: Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (2015)
Stekhoven, D.J., Bühlmann, P.: Missforest-non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 28(1), 112–118 (2012)
Teipel, S.J., Born, C., et al.: Multivariate deformation-based analysis of brain atrophy to predict Alzheimer’s disease in mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 38(1), 13–24 (2007)
Thie, J.A.: Understanding the standardized uptake value, its methods, and implications for usage. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 45(9), 1431–1434 (2004)
Valdés Hernández, M.d.C., et al.: Do 2-year changes in superior frontal gyrus and global brain atrophy affect cognition? Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring 10(1), 706–716 (2018)
Van Buuren, S., Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K.: mice: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in r. Journal of Statistical Software 45, 1–67 (2011)
Wang, F., Liu, H.: Understanding the behaviour of contrastive loss. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 2495–2504 (2021)
Yang, H., Xu, H., Li, et al.: Study of brain morphology change in Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment compared with normal controls. gen psychiatr. 32 (2): e100005 (2019)
Yoon, J., Jordon, J., Schaar, M.: Gain: Missing data imputation using generative adversarial nets. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 5689–5698. PMLR (2018)
Yuan, Q., Liang, et al.: Altered anterior cingulate cortex subregional connectivity associated with cognitions for distinguishing the spectrum of pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 14, 1035746 (2022)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NRF-2022R1A2C2092336 (50%), RS-2022-II2202290 (20%), RS-2019-II191906 (AI Graduate Program at POSTECH, 10%) funded by MSIT, RS-2022-KH127855 (10%), RS-2022-KH128705 (10%) funded by MOHW from South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baek, S., Sim, J., Wu, G., Kim, W.H. (2024). OCL: Ordinal Contrastive Learning for Imputating Features with Progressive Labels. In: Linguraru, M.G., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2024. MICCAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15002. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72069-7_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72069-7_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72068-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72069-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)