Abstract
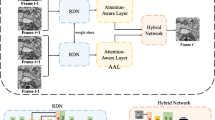
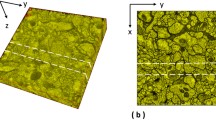
The serial section electron microscopy reconstruction method is commonly used in large volume reconstruction of biological tissue, but the inevitable section damage brings challenges to volume reconstruction. The section damage may result in imperfect section alignment and affect the subsequent neuron segmentation and data analysis. This paper proposes an aligning and restoring method for imperfect sections, which contributes to promoting the continuity reconstruction of biological tissues. To align imperfect sections, we improve the optical flow network to address the difficulties faced by traditional optical flow networks in handling issues related to discontinuous deformations and large displacements in the alignment of imperfect sections. Based on the deformations in different regions, the Guided Position of each coordinate point on the section is estimated to generate the Guided Field of the imperfect section. This Guided field aids the optical flow network in better handling the complex deformation and large displacement associated with the damaged area during alignment. Subsequently, the damaged region is predicted and seamlessly integrated into the aligned imperfect section images, ultimately obtaining aligned damage-free section images. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively resolves the alignment and restoration issues of imperfect sections, achieving better alignment accuracy than existing methods and significantly improving neuron segmentation accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/lvyanan525/Aligning-and-Restoring-Imperfect-ssEM-images.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hildebrand, D.G.C., Cicconet, M., Torres, R.M., Choi, W., Quan, T.M., Moon, J., Wetzel, A.W., Scott Champion, A., Graham, B.J., Randlett, O.: Whole-brain serial-section electron microscopy in larval zebrafish. Nature 545(7654), 345–349 (2017)
Huang, W., Chen, C., Xiong, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, D., Wu, F.: Learning to restore sstem images from deformation and corruption. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2020 Workshops: Glasgow, UK, August 23-28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16. pp. 394–410. Springer (2020)
Liu, C., Yuen, J., Torralba, A.: Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 33(5), 978–994 (2010)
Liu, L., Zhang, J., He, R., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Tai, Y., Luo, D., Wang, C., Li, J., Huang, F.: Learning by analogy: Reliable supervision from transformations for unsupervised optical flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 6489–6498 (2020)
Mahalingam, G., Torres, R., Kapner, D., Trautman, E.T., Fliss, T., Seshamani, S., Perlman, E., Young, R., Kinn, S., Buchanan, J.: A scalable and modular automated pipeline for stitching of large electron microscopy datasets. Elife 11, e76534 (2022)
Mitchell, E., Keselj, S., Popovych, S., Buniatyan, D., Seung, H.S.: Siamese encoding and alignment by multiscale learning with self-supervision. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02643 (2019)
Popovych, S., Bae, J.A., Seung, H.S.: Caesar: segment-wise alignment method for solving discontinuous deformations. In: 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). pp. 1214–1218. IEEE (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, proceedings, part III 18. pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
Saalfeld, S., Fetter, R., Cardona, A., Tomancak, P.: Elastic volume reconstruction from series of ultra-thin microscopy sections. Nature Methods 9(7), 717–U280 (2012)
Scheffer, L.K., Karsh, B., Vitaladevun, S.: Automated alignment of imperfect em images for neural reconstruction. Quantitative Biology pp. abs/1304.6034, s2013 (2013)
Wang, Z., Liu, J., Chen, X., Li, G., Han, H.: Sparse self-attention aggregation networks for neural sequence slice interpolation. BioData Mining 14, 1–19 (2021)
Wang, Z., Sun, G., Li, G., Shen, L., Zhang, L., Han, H.: Stdin: Spatio-temporal distilled interpolation for electron microscope images. Neurocomputing 505, 188–202 (2022)
Winding, M., Pedigo, B.D., Barnes, C.L., Patsolic, H.G., Park, Y., Kazimiers, T., Fushiki, A., Andrade, I.V., Khandelwal, A., Valdes-Aleman, J.: The connectome of an insect brain. Science 379(6636), eadd9330 (2023)
Witvliet, D., Mulcahy, B., Mitchell, J.K., Meirovitch, Y., Berger, D.R., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Koh, W.X., Parvathala, R., Holmyard, D.: Connectomes across development reveal principles of brain maturation. Nature 596(7871), 257–261 (2021)
Wu, Z., Wei, J., Yuan, W., Wang, J., Tasdizen, T.: Inter-slice image augmentation based on frame interpolation for boosting medical image segmentation accuracy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.11698 (2020)
Xin, T., Shen, L., Li, L., Chen, X., Han, H.: Expected affine: A registration method for damaged section in serial sections electron microscopy. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 16, 944050 (2022)
Yin, X.l., Liang, D.x., Wang, L., Qiu, J., Yang, Z.y., Dong, J.z., Ma, Z.y.: Analysis of coronary angiography video interpolation methods to reduce x-ray exposure frequency based on deep learning. Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications 6(1), 17–24 (2021)
Yoo, I., Hildebrand, D.G., Tobin, W.F., Lee, W.C.A., Jeong, W.K.: ssemnet: Serial-section electron microscopy image registration using a spatial transformer network with learned features. In: Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Third International Workshop, DLMIA 2017, and 7th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, September 14, Proceedings 3. pp. 249–257. Springer (2017)
Zheng, Z., Lauritzen, J.S., Perlman, E., Robinson, C.G., Nichols, M., Milkie, D., Torrens, O., Price, J., Fisher, C.B., Sharifi, N., et al.: A complete electron microscopy volume of the brain of adult drosophila melanogaster. Cell 174(3), 730–743 (2018)
Acknowledgments
This study were funded by STI 2030-Major Projects (2021ZD0204500, 2021ZD0204503 to L.L.), Instrument Function Development Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (E4J92301 to Y.L.) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32171461 to H.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lv, Y., Jia, H., Chen, X., Yan, H., Han, H. (2024). Aligning and Restoring Imperfect ssEM Images for Continuity Reconstruction. In: Linguraru, M.G., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2024. MICCAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15002. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72069-7_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72069-7_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72068-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72069-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)