Abstract
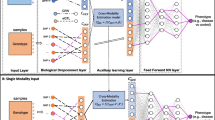
Using brain imaging data to predict the non-neuroimaging phenotypes at the individual level is a fundamental goal of system neuroscience. Despite its significance, the high acquisition cost of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) hampers its clinical translation in phenotype prediction, while the analysis based solely on cost-efficient T1-weighted (T1w) MRI yields inferior performance than fMRI. The reasons lie in that existing works ignore two significant challenges. 1) they neglect the knowledge transfer from fMRI to T1w MRI, failing to achieve effective prediction using cost-efficient T1w MRI. 2) They are limited to predicting a single phenotype and cannot capture the intrinsic dependence among various phenotypes, such as strength and endurance, preventing comprehensive and accurate clinical analysis. To tackle these issues, we propose an FMRI to T1w MRI knowledge transfer Network (F2TNet) to achieve cost-efficient and effective analysis on brain multi-phenotype, representing the first attempt in this field, which consists of a Phenotypes-guided Knowledge Transfer (PgKT) module and a modality-aware Multi-phenotype Prediction (MpP) module. Specifically, PgKT aligns brain nodes across modalities by solving a bipartite graph-matching problem, thereby achieving adaptive knowledge transfer from fMRI to T1w MRI through the guidance of multi-phenotype. Then, MpP enriches the phenotype codes with cross-modal complementary information and decomposes these codes to enable accurate multi-phenotype prediction. Experimental results demonstrate that the F2TNet significantly improves the prediction of brain multi-phenotype and outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/CUHK-AIM-Group/F2TNet.
Z. He—This work was done when Zhibin He was a visiting student at the Department of Electronic Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswal, B., Zerrin Yetkin, F., Haughton, V.M., Hyde, J.S.: Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar mri. Magnetic resonance in medicine 34(4), 537–541 (1995)
Buckner, R.L., Krienen, F.M., Yeo, B.T.: Opportunities and limitations of intrinsic functional connectivity mri. Nature neuroscience 16(7), 832–837 (2013)
Chen, J., Tam, A., Kebets, V., Orban, C., Ooi, L.Q.R., Asplund, C.L., Marek, S., Dosenbach, N.U., Eickhoff, S.B., Bzdok, D., et al.: Shared and unique brain network features predict cognitive, personality, and mental health scores in the abcd study. Nature communications 13(1), 1–17 (2022)
Chen, W., Liu, Y., Hu, J., Yuan, Y.: Dynamic depth-aware network for endoscopy super-resolution. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 26(10), 5189–5200 (2022)
Chen, Z., Li, W., Xing, X., Yuan, Y.: Medical federated learning with joint graph purification for noisy label learning. Medical Image Analysis 90, 102976 (2023)
Cheng, J., Zhang, X., Zhao, F., Wu, Z., Yuan, X., Wang, L., Lin, W., Li, G.: Prediction of infant cognitive development with cortical surface-based multimodal learning. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. pp. 618–627. Springer (2023)
Gao, J., Zhao, L., Zhong, T., Li, C., He, Z., Wei, Y., Zhang, S., Guo, L., Liu, T., Han, J., et al.: Prediction of cognitive scores by joint use of movie-watching fmri connectivity and eye tracking via attention-censnet. Psychoradiology 3 (2023)
Glasser, M.F., Sotiropoulos, S.N., Wilson, J.A., Coalson, T.S., Fischl, B., Andersson, J.L., Xu, J., Jbabdi, S., Webster, M., Polimeni, J.R., et al.: The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the human connectome project. Neuroimage 80, 105–124 (2013)
Gordon, E.M., Laumann, T.O., Adeyemo, B., Huckins, J.F., Kelley, W.M., Petersen, S.E.: Generation and evaluation of a cortical area parcellation from resting-state correlations. Cerebral cortex 26(1), 288–303 (2016)
He, Z., Du, L., Huang, Y., Jiang, X., Lv, J., Guo, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, T.: Gyral hinges account for the highest cost and the highest communication capacity in a corticocortical network. Cerebral Cortex 32(16), 3359–3376 (2022)
He, Z., Li, W., Zhang, T., Yuan, Y.: H 2 gm: A hierarchical hypergraph matching framework for brain landmark alignment. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. pp. 548–558. Springer (2023)
Jiang, X., Zhang, T., Zhang, S., Kendrick, K.M., Liu, T.: Fundamental functional differences between gyri and sulci: implications for brain function, cognition, and behavior. Psychoradiology 1(1), 23–41 (2021)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Li, C., Lin, M., Ding, Z., Lin, N., Zhuang, Y., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Cao, L.: Knowledge condensation distillation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 19–35. Springer Nature Switzerland Cham (2022)
Li, J., Kong, R., Liégeois, R., Orban, C., Tan, Y., Sun, N., Holmes, A.J., Sabuncu, M.R., Ge, T., Yeo, B.T.: Global signal regression strengthens association between resting-state functional connectivity and behavior. NeuroImage 196, 126–141 (2019)
Li, W., Liu, X., Yuan, Y.: Sigma: Semantic-complete graph matching for domain adaptive object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 5291–5300 (2022)
Li, W., Liu, X., Yuan, Y.: Sigma++: Improved semantic-complete graph matching for domain adaptive object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2023)
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Dvornek, N., Zhang, M., Gao, S., Zhuang, J., Scheinost, D., Staib, L.H., Ventola, P., Duncan, J.S.: Braingnn: Interpretable brain graph neural network for fmri analysis. Medical Image Analysis 74, 102233 (2021)
Liu, X., Peng, H., Zheng, N., Yang, Y., Hu, H., Yuan, Y.: Efficientvit: Memory efficient vision transformer with cascaded group attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 14420–14430 (2023)
Liu, Y., Li, W., Liu, J., Chen, H., Yuan, Y.: Grab-net: Graph-based boundary-aware network for medical point cloud segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (2023)
Liu, Y., Liu, J., Yuan, Y.: Edge-oriented point-cloud transformer for 3d intracranial aneurysm segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. pp. 97–106. Springer (2022)
Nickerson, L.D.: Replication of resting state-task network correspondence and novel findings on brain network activation during task fmri in the human connectome project study. Scientific reports 8(1), 17543 (2018)
Ooi, L.Q.R., Chen, J., Zhang, S., Kong, R., Tam, A., Li, J., Dhamala, E., Zhou, J.H., Holmes, A.J., Yeo, B.T.: Comparison of individualized behavioral predictions across anatomical, diffusion and functional connectivity mri. NeuroImage 263, 119636 (2022)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., et al.: Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019)
Sebenius, I., Campbell, A., Morgan, S.E., Bullmore, E.T., Liò, P.: Multimodal graph coarsening for interpretable, mri-based brain graph neural network. In: 2021 IEEE 31st International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP). pp. 1–6. IEEE (2021)
Van Essen, D.C., Smith, S.M., Barch, D.M., Behrens, T.E., Yacoub, E., Ugurbil, K., Consortium, W.M.H., et al.: The wu-minn human connectome project: an overview. Neuroimage 80, 62–79 (2013)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017)
Wang, Q., Zhao, S., He, Z., Zhang, S., Jiang, X., Zhang, T., Liu, T., Liu, C., Han, J.: Modeling functional difference between gyri and sulci within intrinsic connectivity networks. Cerebral Cortex 33(4), 933–947 (2023)
Wang, Q., Zhao, S., Liu, T., Han, J., Liu, C.: Temporal fingerprints of cortical gyrification in marmosets and humans. Cerebral Cortex 33(17), 9802–9814 (2023)
Yang, Q., Guo, X., Chen, Z., Woo, P.Y., Yuan, Y.: D 2-net: Dual disentanglement network for brain tumor segmentation with missing modalities. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 41(10), 2953–2964 (2022)
Zhang, S., Zhang, T., Cao, G., Zhou, J., He, Z., Li, X., Ren, Y., Liu, T., Jiang, X., Guo, L., et al.: Species-shared and-unique gyral peaks on human and macaque brains. Elife 12, RP90182 (2024)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) General Research Fund 14204321, and in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 62131009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Z. et al. (2024). F2TNet: FMRI to T1w MRI Knowledge Transfer Network for Brain Multi-phenotype Prediction. In: Linguraru, M.G., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2024. MICCAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15011. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72120-5_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72120-5_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72119-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72120-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)