Abstract
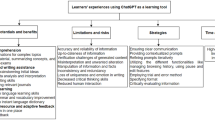
The Community of Inquiry (CoI) framework has been used for nearly two decades to provide educators with a way to design and evaluate their online courses. Integrating generative AI (GenAI) chatbots with the CoI framework will address the current lack of clear guidelines for incorporating GenAI technology in online education. This gap is significant as GenAI in education is rapidly growing, with students showing favorable attitudes towards GenAI integration. To explore this, a systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted, analyzing recent studies on the use of GenAI chatbots as intelligent tutoring systems within the CoI framework. The findings revealed that GenAI chatbots enhance cognitive presence through personalized learning paths and real-time feedback, improve social presence by fostering community and continuous support, and strengthen teaching presence by automating administrative tasks and dynamic instructional strategies. These enhancements suggest that integrating GenAI chatbots can significantly enrich online learning environments, making education more dynamic, personalized, and effective. The study concludes that a seamless integration of GenAI technologies within the CoI framework can optimize digital learning ecosystems, and future research should focus on long-term impacts and ethical guidelines to ensure responsible GenAI use in education.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M.A., Suman, R.: Understanding the role of digital technologies in education: A review. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 3, 275–285 (2022)
Garrison, D.R., Anderson, T., Archer, W.: Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: Computer conferencing in higher education. The internet and higher education 2, 87–105 (1999)
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V.I., Bond, M., Gouverneur, F.: Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators?. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 16, (2019)
Bisdas, S., et al.: Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: A Multinational Multi-Center Survey on the Medical and Dental Students' Perception. Frontiers in Public Health 9, (2021)
Garrison, D.R., Arbaugh, J.B.: Researching the community of inquiry framework: Review, issues, and future directions. The Internet and High. Educ. 10, 157–172 (2007)
Bektashi, L.: Community of inquiry framework in online learning: Use of technology. Technology and the curriculum: Summer 2018 (2018)
Fiock, H.: Designing a community of inquiry in online courses. Int. Rev. Res. Open and Distrib. Learn. 21, 135–153 (2020)
Yandra, F.P., Alsolami, B., Sopacua, I.O., Prajogo, W.: The role of community of inquiry and self-efficacy on accounting students’ satisfaction in online learning environment. Jurnal Siasat Bisnis 1-16 (2021).
Boston, W., Díaz, S.R., Gibson, A.M., Ice, P., Richardson, J., Swan, K.: An exploration of the relationship between indicators of the community of inquiry framework and retention in online programs. J. Asynchronous Learn. Netw. 13, 67–83 (2009)
Kirkpatrick, J., et al.: Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 114, 3521–3526 (2017)
Harry, A.: Role of AI in Education. Interdiciplinary J. Hummanit. (INJURITY) 2, 260–268 (2023)
Kim, W.-H., Kim, J.-H.: Individualized AI tutor based on developmental learning networks. IEEE Access 8, 27927–27937 (2020)
Conijn, R., Kahr, P., Snijders, C.: The Effects of Explanations in Automated Essay Scoring Systems on Student Trust and Motivation (accepted for publication). (2023)
Tubino, L., Adachi, C.: Developing feedback literacy capabilities through an AI automated feedback tool. ASCILITE Publications e22039-e22039 (2022)
Bozkurt, A., Sharma, R.C.: Are we facing an algorithmic renaissance or apocalypse? Generative AI, ChatBots, and emerging human-machine interaction in the educational landscape. Asian J. Distance Educ. 19, (2024)
Ding, L., Li, T., Jiang, S., Gapud, A.: Students’ perceptions of using ChatGPT in a physics class as a virtual tutor. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 20, 63 (2023)
Chan, C.K.Y., Hu, W.: Students’ voices on generative AI: perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 20, (2023)
Singh, S., Beniwal, H.: A survey on near-human conversational agents. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 34, 8852–8866 (2022)
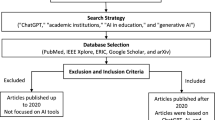
Petticrew, M., Roberts, H.: Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. John Wiley & Sons (2008)
Gough, D., Thomas, J., Oliver, S.: An introduction to systematic reviews. (2017)
Cherry, G., Boland, A., Dickson, R.: Doing a Systematic Review: A Student′ s Guide. (2023)
Aromataris, E., Pearson, A.: The systematic review: an overview. AJN The Am. J. Nurs. 114, 53–58 (2014)
Blei, D.M.: Probabilistic topic models. Commun. ACM 55, 77–84 (2012)
Nunez-Mir, G.C., Iannone, B.V., III., Pijanowski, B.C., Kong, N., Fei, S.: Automated content analysis: addressing the big literature challenge in ecology and evolution. Meth. Ecol. Evol. 7, 1262–1272 (2016)
Smith, A.E., Humphreys, M.S.: Evaluation of unsupervised semantic mapping of natural language with Leximancer concept mapping. Behav. Res. Meth. 38, 262–279 (2006)
Khan, S., Rana, S., Goel, A.: Presence of digital sources in international marketing: A review of literature using Leximancer. Int. J. Technol. Mark. 16, 246–274 (2022)
Leximancer User Guide. https://info.leximancer.com/, last accessed 1 June 2024
Shepherd, D.A., Majchrzak, A.: Machines augmenting entrepreneurs: Opportunities (and threats) at the Nexus of artificial intelligence and entrepreneurship. J. Bus. Ventur. 37, 106227 (2022)
Li, C., Xing, W., Leite, W.: Building socially responsible conversational agents using big data to support online learning: A case with Algebra Nation. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 776–803 (2022)
Gunawardena, C.N., Chen, Y., Flor, N., Sánchez, D.: Deep Learning Models for Analyzing Social Construction of Knowledge Online. Online Learn. 27, (2023)
Iftanti, E., Awalin, A.S.a., Izza, F.N.: The Use of Artificial Intelligence as the Potential Supporting Learning Tools for Doing Learning Projects. In: International Conference on Education, pp. 455-467. (2023)
Das, R.M., JV, M.: Analysing the Community of Inquiry Model in the Context of Online Learning: A Bibliometric Study. TechTrends 68, 435-447 (2024)
Hu, Y., Donald, C., Giacaman, N.: Can multi-label classifiers help identify subjectivity? A deep learning approach to classifying cognitive presence in MOOCs. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 33, 781–816 (2023)
McCotter, S.: An Interdisciplinary Scoping Review of Sustainable E-Learning within Human Resources Higher Education Provision. Sustain. 15, 15282 (2023)
Cheng, Y., Lyons, K., Chen, G., Gašević, D., Swiecki, Z.: Evidence-centered Assessment for Writing with Generative AI. In: Proceedings of the 14th Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference, pp. 178-188. (2024)
Jin, S., Zhong, Z., Li, K., Kang, C.: Investigating the effect of guided inquiry on learners with different prior knowledge in immersive virtual environments. Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Ou, A.W., Stöhr, C., Malmström, H.: Academic communication with AI-powered language tools in higher education: From a post-humanist perspective. Syst. 121, 103225 (2024)
Ali, F., Choy, D., Divaharan, S., Tay, H.Y., Chen, W.: Supporting self-directed learning and self-assessment using TeacherGAIA, a generative AI chatbot application: Learning approaches and prompt engineering. Learning: Research and Practice 9, 135-147 (2023)
Gibson, D., Kovanovic, V., Ifenthaler, D., Dexter, S., Feng, S.: Learning theories for artificial intelligence promoting learning processes. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 54, 1125–1146 (2023)
Aljuaid, H.: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Tools on Academic Writing Instruction in Higher Education: A Systematic Review. Arab World English Journal (AWEJ) Special Issue on ChatGPT (2024)
Alshahrani, A.: Revolutionizing Blended Learning: Exploring Current Trends and Future Research Directions in the Era of ChatGPT. In: 2023 7th International Conference on Business and Information Management (ICBIM), pp. 41-47. (2023)
Liu, L.: Analyzing the Text Contents Produced by ChatGPT: Prompts, Feature-Components in Responses, and a Predictive Model. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exch. 16, 49–70 (2023)
Al-Tamimi, A.-K., Moore, R., Javed, Y., Babu, S., Freeman, E.: Chatbots in Education: Addressing Student Needs and Transforming Learning in the Post-COVID-19 Era. Building Resiliency in Higher Education: Globalization, Digital Skills, and Student Wellness, pp. 99127. IGI Global (2024)
Birenbaum, M.: The Chatbots’ Challenge to Education: Disruption or Destruction? Education Sciences, vol. 13, (2023)
Maphoto, K.B.: Perceptions and innovations of academics in an open distance e-learning institution. Online J. Commun. Media Technol. 14, e202429 (2024)
Son, J.-B., Ružić, N.K., Philpott, A.: Artificial intelligence technologies and applications for language learning and teaching. J. China Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. (2023)
Ayasrah, F.T.M., Alarabi, K., Fattah, H.A.A.: A Secure Technology Environment and AI’s Effect on Science Teaching: Prospective Science Teachers. Migration Letters 20, 289–302 (2023)
Perkins, M., Roe, J., Vu, B.H., Postma, D., Hickerson, D., McGaughran, J., Khuat, H.Q.: GenAI Detection Tools, Adversarial Techniques and Implications for Inclusivity in Higher Education. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.19148 (2024)
Martinez, C., et al.: Content-Focused Formative Feedback Combining Achievement, Qualitative and Learning Analytics Data. Education Sciences 13, 1014 (2023)
Maofi, M.: Effective learning in higher education post-covid_final version. (2023)
Essel, H.B., Vlachopoulos, D., Essuman, A.B., Amankwa, J.O.: ChatGPT effects on cognitive skills of undergraduate students: Receiving instant responses from AI-based conversational large language models (LLMs). Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 6, 100198 (2024)
Engineer, R.: Exploration of Epistemic Diversity in Computer Science Education. (2023)
Chuah, K.-M., Kabilan, M.: Teachers’ views on the use of chatbots to support English language teaching in a mobile environment. Int. J. Emerging Technol. Learn. (iJET) 16, 223–237 (2021)
Balalle, H.: Exploring student engagement in technology-based education in relation to gamification, online/distance learning, and other factors: A systematic literature review. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 9, 100870 (2024)
Birenbaum, M.: The Chatbots’ Challenge to Education: Disruption or Destruction? Educ. Sci. 13, 711 (2023)
Wang, X., Pang, H., Wallace, M.P., Wang, Q., Chen, W.: Learners’ perceived AI presences in AI-supported language learning: a study of AI as a humanized agent from community of inquiry. Computer Assisted Language Learning 1-27 (2022)
Maher, D.: Blended Learning for Pre-Service Teachers. Handbook of Research on Innovative Frameworks and Inclusive Models for Online Learning, pp. 256-274. IGI Global (2023)
Pratschke, B.M.: Generativism: the new hybrid. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.12468 (2023)
Sevnarayan, K.: Exploring the dynamics of ChatGPT: Students and lecturers perspectives at an open distance e-learning university. Journal of Pedagogical Research (2024)
Taneja, K., Maiti, P., Kakar, S., Guruprasad, P., Rao, S., Goel, A.K.: Jill Watson: A Virtual Teaching Assistant powered by ChatGPT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.11070 (2024)
Indriati, L., Neo, M., Tan, H.: Improving Learning Content and Engaging Learners through the Revised Community of Inquiry (RCOI) Framework: Indonesian Design Students’ Perspectives. In: EDULEARN23 Proceedings, pp. 927-933. IATED, (2023)
Leslie, D.: Does the sun rise for ChatGPT? Scientific discovery in the age of generative AI. AI and Ethics (2023)
Lang, J.C.: Embracing Generative AI for Authentic Learning. Creative Education 15, 1–20 (2024)
AlAli, R., Wardat, Y.: Enhancing Classroom Learning: ChatGPT’s Integration and Educational Challenges. Int. J. Relig. 5, 971–985 (2024)
Gowon, O.C., Anthony, O.: Shaping the Future: Artificial Intelligence and the English Language Pedagogy. Int. J. Arts, Commun. Pedagogy 2, 1–14 (2023)
Archibald, A., et al.: A validation of AI-enabled discussion platform metrics and relationships to student efforts. TechTrends 67, 285–293 (2023)
Hew, K.F., Huang, W.: Promoting engagement in online learning beyond COVID-19: Possible strategies and directions for future research. Future in Educ. Res. 1, 2749 (2023)
Dede, C., Lidwell, W.: Developing a Next-Generation Model for Massive Digital Learning. Educ. Sci. 13, 845 (2023)
Kilinc, S.: Unknown article. Asian J. Distance Educ. 18, (2023)
Avgerinou, M.D., Karampelas, A., Stefanou, V.: Building the Plane as We Fly It: Experimenting with GenAI for Scholarly Writing. Irish J. Technol. Enhanced Learn. 7, 61–74 (2023)
Parra, J.L., Chatterjee, S.: Social Media and Artificial Intelligence: Critical Conversations and Where Do We Go from Here? Educ. Sci. 14, 68 (2024)
Han, S., Hamilton, X., Cai, Y., Shao, P., Liu, M.: Knowledge-based chatbots: a scale measuring students’ learning experiences in massive open online courses. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 71, 2431–2456 (2023)
Koh, J., Cowling, M., Jha, M., Sim, K.N.: The Human Teacher, the AI Teacher and the AIedTeacher Relationship. J. High. Educ. Theory & Pract. 23, (2023)
McCleskey, J.A., Melton, R.M.: “Better Than Human” in Partnership With AI: Enhancing Social Presence Through the Use of Technology. Humanizing Online Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, pp. 18-48. IGI Global (2024)
Nieveen, N., van der Veen, J., Ventura-Medina, E.: Pathways to innovative STEM education. (2024)
Lim, F.V., Querol-Julián, M.: Learning with technologies in the digital age: Now and the future. Designing Learning with Digital Technologies, pp. 3-19. Routledge (2024)
Egher, C.: Digital Technologies in Education. Educational Utopias: Liber Amicorum Alkeline van Lenning (2023)
Alshahrani, A.: The impact of ChatGPT on blended learning: Current trends and future research directions. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 7, 2029–2040 (2023)
Das, R.M., J.V, M.: Analysing the Community of Inquiry Model in the Context of Online Learning: A Bibliometric Study. TechTrends (2024)
Ghazali, N.E., Abdul Rahman, N.F.: Knowledge Requirement of Incorporating Artificial Intelligence in Engineering Education through TPACK. Asean J. Eng. Educ. 7, 34–40 (2023)
Qin, C., Huang, W., Hew, K.F.: Using the Community of Inquiry Framework to develop an educational chatbot: Lesson learned from a mobile instant messaging learning environment. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computers in Education, Online, pp. 23-27. (2020)
Liao, X., Zheng, Y.-H., Shi, G., Bu, H.: Automated social presence in artificial-intelligence services: Conceptualization, scale development, and validation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 203, 123377 (2024)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Olivier, C., Weilbach, L. (2024). Enhancing Online Learning Experiences: A Systematic Review on Integrating GenAI Chatbots into the Community of Inquiry Framework. In: van de Wetering, R., et al. Disruptive Innovation in a Digitally Connected Healthy World. I3E 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14907. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72234-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72234-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72233-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72234-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)