Abstract
Cognitive architectures have been used to understand learning new tasks, forgetting, error making or navigation and mental map development. The insight cognitive architectures provide can be utilized to understand human behavior at a cognitive level. In this paper, we report on the recent developments of our toolbox VRAT which will provide a framework for designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and then developing cognitive models that can see and interact with the environment similar to users. The differentiating factor of our toolbox from previously developed tools is that its abilities are extended to Virtual Reality (VR). The ability to create three-dimensional visual scenes and to measure responses (i.e., gaze data, head and hand movements data) to the visual stimuli enables behavioral researchers to test hypotheses in a way and scale that were previously unfeasible. The difficulty facing the researcher is that sophisticated 3D graphics engines (e.g., Unity) have been created for game designers rather than behavioral scientists. To overcome this barrier VRAT provides a plug-and-go design to help researchers to convert their 2D experiments into VR. It also enables eye tracking and eye tracking visualization in all VR experiments. Enabling researchers to collect and analyze data more efficiently. Additionally, our tool enables (a) a straight forward transition from 2D environment design to 3D, (b) an efficient way to use data collection and visualization framework and (c) an interaction method for cognitive models to extend their capabilities and see and interact with VR environments similar to users.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
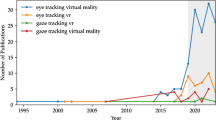
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
A demo of the PyIBL model is available at the GitHub page of VRAT (https://github.com/HCAI-Lab/Virtual-Reality-Analysis-Tool-VRAT--).
References
Anderson, J.R.: How Can the Human Mind Occur in the Physical Universe? Oxford University Press, Oxford (2007)
Arrabales, R., Ledezma, A., Sanchis, A.: Towards conscious-like behavior in computer game characters. In: 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games (2009)
Bagherzadeh, A., Tehranchi, F.: Comparing cognitive, cognitive instance-based, and reinforcement learning models in an interactive task. In: Proceedings of ICCM-2022–20th International Conference on Cognitive Modeling (2022)
Bagherzadeh, A., Tehranchi, F.: Computer-Based Experiments in VR: A Virtual Reality Environment to Conduct Experiments, Collect Participants’ Data and Cognitive Modeling in VR Proceedings of ICCM-2024–22nd International Conference on Cognitive Modeling (2024)
Experiments, Collect Participants’ Data and Cognitive Modeling in VR Proceedings of the 22th International Conference on Cognitive Modelling (Accepted), Tilburg, Netherlands
Bagherzadehkhorasani, A., Tehranchi, F.: Automatic error model (AEM) for user interface design: a new approach to include errors and error corrections in a cognitive user model. In: Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting (2023a)
Bagherzadehkhorasani, A., Tehranchi, F.: A pipeline for analyzing decision-making processes in a binary choice task. In: Proceedings of the 21th International Conference on Cognitive Modelling, Amsterdam, Netherland (2023b)
Best, B.J., Lebiere, C.: Cognitive agents interacting in real and virtual worlds. Cognition and multi-agent interaction: from cognitive modeling to social simulation, pp. 186–218 (2006)
Bringsjord, S., Khemlani, S., Arkoudas, K., McEvoy, C., Destefano, M., Daigle, M.: Advanced synthetic characters, evil, and E. Game-On (2005)
Byrne, M.D.: ACT-R/PM and menu selection: applying a cognitive architecture to HCI. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 55(1), 41–84 (2001)
David, E., Gutiérrez, J., Võ, M.L.-H., Coutrot, A., Da Silva, M.P., Le Callet, P.: The Salient360! toolbox: handling gaze data in 3D made easy. Comput. Graph. 103890 (2024)
Felnhofer, A., et al.: Is virtual reality emotionally arousing? Investigating five emotion inducing virtual park scenarios. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 82, 48–56 (2015)
Fleetwood, M.D., Byrne, M.D.: Modeling icon search in ACT-R/PM. Cogn. Syst. Res. 3(1), 25–33 (2002)
Gonzalez, C., Lerch, J.F., Lebiere, C.: Instance-based learning in dynamic decision making. Cogn. Sci. 27(4), 591–635 (2003)
Halbrügge, M.: ACT-CV: bridging the gap between cognitive models and the outer world. Grundlagen und anwendungen der mensch-maschine-interaktion 10, 205–210 (2013)
Hope, R.M., Schoelles, M.J., Gray, W.D.: Simplifying the interaction between cognitive models and task environments with the JSON network interface. Behav. Res. Methods 46, 1007–1012 (2014)
Katona, J.: A review of human–computer interaction and virtual reality research fields in cognitive InfoCommunications. Appl. Sci. 11(6), 2646 (2021)
Kieras, D.: Model-based evaluation. In: Human-Computer Interaction, pp. 309–326. CRC Press (2009)
Kocejko, T., Ruminski, J., Wtorek, J., Martin, B.: Eye tracking within near-to-eye display. In: 2015 8th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI) (2015)
Laird, J.E., Kinkade, K.R., Mohan, S., Xu, J.Z.: Cognitive robotics using the soar cognitive architecture. In: Workshops at the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2012)
Lawson, G., Burnett, G.: Simulation and Digital Human Modelling, pp. 201–218. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015)
Loomis, J.M., Blascovich, J.J., Beall, A.C.: Immersive virtual environment technology as a basic research tool in psychology. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 31(4), 557–564 (1999)
MacInnes, J.J., Iqbal, S., Pearson, J., Johnson, E.N.: Wearable eye-tracking for research: automated dynamic gaze mapping and accuracy/precision comparisons across devices (2018). BioRxiv, 299925
Moon, J., Anderson, J.: Modeling millisecond time interval estimation in space fortress game. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (2012)
Newell, A.: Unified Theories of Cognition. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (1994)
Oker, A., Pecune, F., Vallverdu, J.: Virtual reality for neuropsychology and affective cognitive sciences: theoretical and methodological avenues for studying human cognition. Front. Virtual Real. 3, 1100387 (2022)
Ong, R., Ritter, F.: Mechanisms for routinely tying cognitive models to interactive simulations. In: HCI International’95: Poster Sessions Abridged Proceedings (1994)
Ritter, F.E., Kukreja, U., Amant, R.S.: Including a model of visual processing with a cognitive architecture to model a simple teleoperation task. J. Cogn. Eng. Decis. Mak. 1(2), 121–147 (2007)
Ritter, F.E., Van Rooy, D., St. Amant, R.: A user modeling design tool based on a cognitive architecture for comparing interfaces. In: Kolski, C., Vanderdonckt, J. (eds.) Computer-Aided Design of User Interfaces III, pp. 111–118. Springer, Dordrecht (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0421-3_10
Salvucci, D.D.: Integration and reuse in cognitive skill acquisition. Cogn. Sci. 37(5), 829–860 (2013)
Smart, P.R., Sycara, K.: Using a cognitive architecture to control the behaviour of virtual robots (2015)
Sun, R.: Cognition and Multi-agent Interaction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Tehranchi, F.: An eyes and hands model: Extending visual and motor modules for cognitive architectures The Pennsylvania State University] (2020)
Tehranchi, F., Ritter, F.E.: An eyes and hands model for cognitive architectures to interact with user interfaces. In: MAICS (2017)
Tehranchi, F., Ritter, F.E.: Modeling visual search in interactive graphic interfaces: adding visual pattern matching algorithms to ACT-R. In: Proceedings of ICCM-2018-16th International Conference on Cognitive Modeling (2018)
Wann, J., Mon-Williams, M.: What does virtual reality NEED?: human factors issues in the design of three-dimensional computer environments. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 44(6), 829–847 (1996)
Wu, S., Bagherzadeh, A., Ritter, F., Tehranchi, F.: Long road ahead: lessons learned from the (soon to be) longest running cognitive model. In: 21st International Conference on Cognitive Modeling (ICCM) at the University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bagherzadeh, A., Tehranchi, F. (2024). Extending VRAT: From 3D Eye Tracking Visualization to Enabling ACT-R to Interact with Virtual Reality Environments. In: Thomson, R., et al. Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling. SBP-BRiMS 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14972. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72241-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72241-7_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72240-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72241-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)