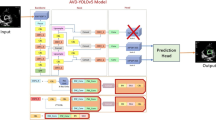
Abstract
The fundamental problem with ultrasound-guided diagnosis is that the acquired images are often 2-D cross-sections of a 3-D anatomy, potentially missing important anatomical details. This limitation leads to challenges in ultrasound echocardiography, such as poor visualization of heart valves or foreshortening of ventricles. Clinicians must interpret these images with inherent uncertainty, a nuance absent in machine learning’s one-hot labels. We propose Re-Training for Uncertainty (RT4U), a data-centric method to introduce uncertainty to weakly informative inputs in the training set. This simple approach can be incorporated to existing state-of-the-art aortic stenosis classification methods to further improve their accuracy. When combined with conformal prediction techniques, RT4U can yield adaptively sized prediction sets which are guaranteed to contain the ground truth class to a high accuracy. We validate the effectiveness of RT4U on three diverse datasets: a public (TMED-2) and a private AS dataset, along with a CIFAR-10-derived toy dataset. Results show improvement on all the datasets. Our source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/an-michaelg/RT4U.
T. Tsang and P. Abolmaesumi are joint senior authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, Y.: Screening for aortic stenosis using physical examination and echocardiography. J. Echocardiogr. 19(2), 80–85 (2021)
Ahmadi, N., Tsang, M., Gu, A., Tsang, T., Abolmaesumi, P.: Transformer-based spatio-temporal analysis for classification of aortic stenosis severity from echocardiography cine series. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 43(1), 366–376 (2024)
Algan, G., Ulusoy, I.: Image classification with deep learning in the presence of noisy labels: a survey. Knowl.-Based Syst. 215, 106771 (2021)
Ancona, R., Pinto, S.C.: Epidemiology of aortic valve stenosis (AS) and of aortic valve incompetence (AI): is the prevalence of AS/AI similar in different parts of the world. Eur. Soc. Cardiol. 18(10) (2020)
Angelopoulos, A., Bates, S., Malik, J., Jordan, M.I.: Uncertainty sets for image classifiers using conformal prediction (2022)
Angelopoulos, A.N., Bates, S.: A gentle introduction to conformal prediction and distribution-free uncertainty quantification. CoRR abs/2107.07511 (2021)
Bonow, R.O., Carabello, B.A., Chatterjee, K., et al.: ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 48(3), e1–e148 (2006)
Chamsi-Pasha, M.A., Sengupta, P.P., Zoghbi, W.A.: Handheld echocardiography: current state and future perspectives. Circulation 136(22), 2178–2188 (2017)
Chen, P., Ye, J., Chen, G., Zhao, J., Heng, P.A.: Beyond class-conditional assumption: a primary attempt to combat instance-dependent label noise. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 11442–11450 (2021)
Dai, W., Nazzari, H., Namasivayam, M., Hung, J., Stultz, C.M.: Identifying aortic stenosis with a single parasternal long-axis video using deep learning. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 36(1), 116–118 (2023)
Ginsberg, T., et al.: Deep video networks for automatic assessment of aortic stenosis in echocardiography. In: Noble, J.A., Aylward, S., Grimwood, A., Min, Z., Lee, S.-L., Hu, Y. (eds.) ASMUS 2021. LNCS, vol. 12967, pp. 202–210. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87583-1_20
Gulič, T.G., Makuc, J., Prosen, G., Dinevski, D.: Pocket-size imaging device as a screening tool for aortic stenosis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 128, 348–353 (2016)
Guo, C., Pleiss, G., Sun, Y., Weinberger, K.Q.: On calibration of modern neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1321–1330. PMLR (2017)
Guo, X.: Predicting aortic stenosis severity using deep learning. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2021)
Holste, G., Oikonomou, E.K., Mortazavi, B.J., Coppi, A., et al.: Severe aortic stenosis detection by deep learning applied to echocardiography. Eur. Heart J. 44(43), 4592–4604 (2023)
Huang, Z., Long, G., Wessler, B., Hughes, M.C.: A new semi-supervised learning benchmark for classifying view and diagnosing aortic stenosis from echocardiograms. In: Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, pp. 614–647. PMLR (2021)
Lu, C., Angelopoulos, A.N., Pomerantz, S.: Improving trustworthiness of AI disease severity rating in medical imaging with ordinal conformal prediction sets. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13438, pp. 545–554. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16452-1_52
Lu, C., Lemay, A., Chang, K., Höbel, K., Kalpathy-Cramer, J.: Fair conformal predictors for applications in medical imaging. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 12008–12016 (2022)
Nemchyna, O., Soltani, S., Solowjowa, N., Schoenrath, F., et al.: Validity of visual assessment of aortic valve morphology in patients with aortic stenosis using two-dimensional echocardiography. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 37, 813–823 (2021)
Romano, Y., Sesia, M., Candes, E.: Classification with valid and adaptive coverage. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 3581–3591. Curran Associates, Inc. (2020)
Sadinle, M., Lei, J., Wasserman, L.: Least ambiguous set-valued classifiers with bounded error levels. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 114(525), 223–234 (2019)
Satopää, V.A., Baron, J., Foster, D.P., Mellers, B.A., Tetlock, P.E., Ungar, L.H.: Combining multiple probability predictions using a simple logit model. Int. J. Forecast. 30(2), 344–356 (2014)
Strange, G., et al.: Poor long-term survival in patients with moderate aortic stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 74(15), 1851–1863 (2019)
Stutz, D., Roy, A.G., Matejovicova, T., et al.: Conformal prediction under ambiguous ground truth. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09302 (2023)
Vaseli, H., Gu, A.N., Ahmadi Amiri, S.N., et al.: ProtoASNet: dynamic prototypes for inherently interpretable and uncertainty-aware aortic stenosis classification in echocardiography. In: Greenspan, H., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2023. LNCS, vol. 14225, pp. 368–378. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43987-2_36
Vovk, V.: Conditional validity of inductive conformal predictors. In: Asian Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 475–490. PMLR (2012)
Vovk, V., Gammerman, A., Shafer, G.: Algorithmic Learning in a Random World, vol. 29. Springer, New York (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/b106715
Wessler, B.S., Huang, Z., Long, G.M., Jr., Pacifici, S., et al.: Automated detection of aortic stenosis using machine learning. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 36(4), 411–420 (2023)
Wieslander, H., Harrison, P.J., Skogberg, G., Jackson, S., et al.: Deep learning with conformal prediction for hierarchical analysis of large-scale whole-slide tissue images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(2), 371–380 (2020)
Ye, X., Li, X., Liu, T., Sun, Y., et al.: Active negative loss functions for learning with noisy labels. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 36 (2024)
Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Chen, D.Z.: RR-CP: reliable-region-based conformal prediction for trustworthy medical image classification. In: Sudre, C.H., Baumgartner, C.F., Dalca, A., Mehta, R., Qin, C., Wells, W.M. (eds.) UNSURE 2023. LNCS, vol. 14291, pp. 12–21. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44336-7_2
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the UBC Advanced Research Computing Center (ARC), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gu, A.N., Tsang, M., Vaseli, H., Tsang, T., Abolmaesumi, P. (2024). Reliable Multi-view Learning with Conformal Prediction for Aortic Stenosis Classification in Echocardiography. In: Linguraru, M.G., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2024. MICCAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15001. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72378-0_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72378-0_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72377-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72378-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)