Abstract
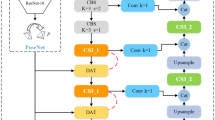
Significant advances have been made in human-centric video generation, yet the joint video-depth generation problem remains underexplored. Most existing monocular depth estimation methods may not generalize well to synthesized images or videos, and multi-view-based methods have difficulty controlling the human appearance and motion. In this work, we present IDOL (unIfied Dual-mOdal Latent diffusion) for high-quality human-centric joint video-depth generation. Our IDOL consists of two novel designs. First, to enable dual-modal generation and maximize the information exchange between video and depth generation, we propose a unified dual-modal U-Net, a parameter-sharing framework for joint video and depth denoising, wherein a modality label guides the denoising target, and cross-modal attention enables the mutual information flow. Second, to ensure a precise video-depth spatial alignment, we propose a motion consistency loss that enforces consistency between the video and depth feature motion fields, leading to harmonized outputs. Additionally, a cross-attention map consistency loss is applied to align the cross-attention map of the video denoising with that of the depth denoising, further facilitating spatial alignment. Extensive experiments on the TikTok and NTU120 datasets show our superior performance, significantly surpassing existing methods in terms of video FVD and depth accuracy.
Y. Zhai—Work done during an internship at Microsoft.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amit, T., Shaharbany, T., Nachmani, E., Wolf, L.: Segdiff: image segmentation with diffusion probabilistic models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.00390 (2021)
Atapour-Abarghouei, A., Breckon, T.P.: Real-time monocular depth estimation using synthetic data with domain adaptation via image style transfer. In: CVPR, pp. 2800–2810 (2018)
Bae, J., Moon, S., Im, S.: Deep digging into the generalization of self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In: AAAI, vol. 37, pp. 187–196 (2023)
Balaji, Y., Min, M.R., Bai, B., Chellappa, R., Graf, H.P.: Conditional GAN with discriminative filter generation for text-to-video synthesis. In: IJCAI, vol. 1, p. 2 (2019)
Baranchuk, D., Rubachev, I., Voynov, A., Khrulkov, V., Babenko, A.: Label-efficient semantic segmentation with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.03126 (2021)
Brock, A., Donahue, J., Simonyan, K.: Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.11096 (2018)
Cao, Z., Simon, T., Wei, S.E., Sheikh, Y.: Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: CVPR, pp. 7291–7299 (2017)
Chang, D., et al.: Magicdance: realistic human dance video generation with motions & facial expressions transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.12052 (2023)
Chen, S., Sun, P., Song, Y., Luo, P.: Diffusiondet: diffusion model for object detection. In: ICCV, pp. 19830–19843 (2023)
Chen, T., Li, L., Saxena, S., Hinton, G., Fleet, D.J.: A generalist framework for panoptic segmentation of images and videos. In: ICCV, pp. 909–919 (2023)
Chen, W., et al.: Control-a-video: Controllable text-to-video generation with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13840 (2023)
Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A.: Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. In: NeurIPS, vol. 34, pp. 8780–8794 (2021)
Esser, P., Chiu, J., Atighehchian, P., Granskog, J., Germanidis, A.: Structure and content-guided video synthesis with diffusion models. In: ICCV, pp. 7346–7356 (2023)
Fu, J., et al.: StyleGAN-human: a data-centric odyssey of human generation. In: ECCV, pp. 1–19 (2022)
Ge, Y., Zhang, R., Wang, X., Tang, X., Luo, P.: DeepFashion2: a versatile benchmark for detection, pose estimation, segmentation and re-identification of clothing images. In: CVPR, pp. 5337–5345 (2019)
Geyer, M., Bar-Tal, O., Bagon, S., Dekel, T.: TokenFlow: consistent diffusion features for consistent video editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10373 (2023)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 63(11), 139–144 (2020)
Gu, J., et al.: Nerfdiff: single-image view synthesis with nerf-guided distillation from 3D-aware diffusion, pp. 11808–11826 (2023)
Güler, R.A., Neverova, N., Kokkinos, I.: Densepose: dense human pose estimation in the wild. In: CVPR, pp. 7297–7306 (2018)
Guo, Y., et al.: Animatediff: animate your personalized text-to-image diffusion models without specific tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04725 (2023)
Ha, S., Kersner, M., Kim, B., Seo, S., Kim, D.: Marionette: few-shot face reenactment preserving identity of unseen targets. In: AAAI, vol. 34, pp. 10893–10900 (2020)
Hertz, A., Mokady, R., Tenenbaum, J., Aberman, K., Pritch, Y., Cohen-Or, D.: Prompt-to-prompt image editing with cross attention control. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.01626 (2022)
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter, S.: GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In: NeurIPS, vol. 30 (2017)
Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: NeurIPS, vol. 33, pp. 6840–6851 (2020)
Hu, L., Gao, X., Zhang, P., Sun, K., Zhang, B., Bo, L.: Animate anyone: consistent and controllable image-to-video synthesis for character animation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.17117 (2023)
Hu, Z., Xu, D.: Videocontrolnet: a motion-guided video-to-video translation framework by using diffusion model with controlnet. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14073 (2023)
Jafarian, Y., Park, H.S.: Learning high fidelity depths of dressed humans by watching social media dance videos. In: CVPR, pp. 12753–12762 (2021)
Ji, Y., et al.: DDP: diffusion model for dense visual prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17559 (2023)
Ju, X., Zeng, A., Zhao, C., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Xu, Q.: HumanSD: a native skeleton-guided diffusion model for human image generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.04269 (2023)
Karras, J., Holynski, A., Wang, T.C., Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.: Dreampose: fashion image-to-video synthesis via stable diffusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06025 (2023)
Khachatryan, L., et al.: Text2video-zero: text-to-image diffusion models are zero-shot video generators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.13439 (2023)
Kirillov, A., et al.: Segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643 (2023)
Li, Y., et al.: GLIGEN: open-set grounded text-to-image generation. In: CVPR, pp. 22511–22521 (2023)
Lin, K., Wang, L., Liu, Z.: End-to-end human pose and mesh reconstruction with transformers. In: CVPR, pp. 1954–1963 (2021)
Lin, T.Y., et al.: Microsoft coco: common objects in context. In: ECCV, pp. 740–755 (2014)
Liu, J., Shahroudy, A., Perez, M., Wang, G., Duan, L.Y., Kot, A.C.: NTU RGB+ D 120: a large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding. IEEE TPAMI 42(10), 2684–2701 (2019)
Liu, S., et al.: Grounding DINO: marrying DINO with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.05499 (2023)
Liu, X., et al.: Hyperhuman: hyper-realistic human generation with latent structural diffusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08579 (2023)
Luan, T., et al.: Spectrum AUC difference (SAUCD): human-aligned 3D shape evaluation. In: CVPR, pp. 20155–20164 (2024)
Luan, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Zhou, Z., Qiao, Y.: PC-HMR: pose calibration for 3D human mesh recovery from 2d images/videos. In: AAAI (2021)
Luan, T., et al.: High fidelity 3D hand shape reconstruction via scalable graph frequency decomposition. In: CVPR, pp. 16795–16804 (2023)
Ma, Y., et al.: Follow your pose: pose-guided text-to-video generation using pose-free videos. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.01186 (2023)
Mallya, A., Wang, T.C., Liu, M.Y.: Implicit warping for animation with image sets. In: NeurIPS, vol. 35, pp. 22438–22450 (2022)
Mokady, R., Hertz, A., Aberman, K., Pritch, Y., Cohen-Or, D.: Null-text inversion for editing real images using guided diffusion models. In: CVPR, pp. 6038–6047 (2023)
Mou, C., et al.: T2I-adapter: learning adapters to dig out more controllable ability for text-to-image diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.08453 (2023)
Nichol, A., Jun, H., Dhariwal, P., Mishkin, P., Chen, M.: Point-E: a system for generating 3D point clouds from complex prompts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.08751 (2022)
Nirkin, Y., Keller, Y., Hassner, T.: FSGAN: subject agnostic face swapping and reenactment. In: ICCV, pp. 7184–7193 (2019)
Poole, B., Jain, A., Barron, J.T., Mildenhall, B.: Dreamfusion: text-to-3D using 2D diffusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.14988 (2022)
Qi, C., et al.: Fatezero: fusing attentions for zero-shot text-based video editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09535 (2023)
Qian, S., et al.: Make a face: towards arbitrary high fidelity face manipulation. In: ICCV, pp. 10033–10042 (2019)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision, pp. 8748–8763 (2021)
Raj, A., et al.: Dreambooth3D: subject-driven text-to-3D generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.13508 (2023)
Ranftl, R., Bochkovskiy, A., Koltun, V.: Vision transformers for dense prediction. In: ICCV, pp. 12179–12188 (2021)
Ranftl, R., Lasinger, K., Hafner, D., Schindler, K., Koltun, V.: Towards robust monocular depth estimation: mixing datasets for zero-shot cross-dataset transfer. IEEE TPAMI 44(3), 1623–1637 (2020)
Reda, F., Kontkanen, J., Tabellion, E., Sun, D., Pantofaru, C., Curless, B.: FILM: frame interpolation for large motion. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13667, pp. 250–266. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20071-7_15
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., Ommer, B.: High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: CVPR, pp. 10684–10695 (2022)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: MICCAI, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Ruan, L., et al.: MM-diffusion: learning multi-modal diffusion models for joint audio and video generation. In: CVPR, pp. 10219–10228 (2023)
Saxena, S., Kar, A., Norouzi, M., Fleet, D.J.: Monocular depth estimation using diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.14816 (2023)
Schuhmann, C., et al.: Laion-400m: open dataset of clip-filtered 400 million image-text pairs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.02114 (2021)
Shahroudy, A., Liu, J., Ng, T.T., Wang, G.: NTU RGB+ D: a large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis. In: CVPR, pp. 1010–1019 (2016)
Siarohin, A., Lathuilière, S., Tulyakov, S., Ricci, E., Sebe, N.: Animating arbitrary objects via deep motion transfer. In: CVPR (2019)
Siarohin, A., Woodford, O.J., Ren, J., Chai, M., Tulyakov, S.: Motion representations for articulated animation. In: CVPR (2021)
Stan, G.B.M., et al.: LDM3D: latent diffusion model for 3D. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10853 (2023)
Tang, H., Wang, W., Xu, D., Yan, Y., Sebe, N.: GestureGAN for hand gesture-to-gesture translation in the wild. In: ACM MM, pp. 774–782 (2018)
Tumanyan, N., Geyer, M., Bagon, S., Dekel, T.: Plug-and-play diffusion features for text-driven image-to-image translation. In: CVPR, pp. 1921–1930 (2023)
Unterthiner, T., Van Steenkiste, S., Kurach, K., Marinier, R., Michalski, M., Gelly, S.: Towards accurate generative models of video: a new metric & challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.01717 (2018)
Wang, T., et al.: Disco: disentangled control for referring human dance generation in real world. In: CVPR (2024)
Watson, D., Chan, W., Martin-Brualla, R., Ho, J., Tagliasacchi, A., Norouzi, M.: Novel view synthesis with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04628 (2022)
Wiles, O., Koepke, A., Zisserman, A.: X2Face: a network for controlling face generation using images, audio, and pose codes. In: ECCV, pp. 670–686 (2018)
Wolleb, J., Sandkühler, R., Bieder, F., Valmaggia, P., Cattin, P.C.: Diffusion models for implicit image segmentation ensembles. In: International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, pp. 1336–1348. PMLR (2022)
Wu, J., Fang, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Xu, Y.: Medsegdiff: medical image segmentation with diffusion probabilistic model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.00611 (2022)
Wynn, J., Turmukhambetov, D.: Diffusionerf: regularizing neural radiance fields with denoising diffusion models. In: CVPR, pp. 4180–4189 (2023)
Xu, Z., et al.: Magicanimate: temporally consistent human image animation using diffusion model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.16498 (2023)
Yang, L., Kang, B., Huang, Z., Xu, X., Feng, J., Zhao, H.: Depth anything: unleashing the power of large-scale unlabeled data. In: CVPR (2024)
Yang, Z., Zeng, A., Yuan, C., Li, Y.: Effective whole-body pose estimation with two-stages distillation. In: ICCV, pp. 4210–4220 (2023)
Zakharov, E., Shysheya, A., Burkov, E., Lempitsky, V.: Few-shot adversarial learning of realistic neural talking head models. In: ICCV, pp. 9459–9468 (2019)
Zhang, L., Rao, A., Agrawala, M.: Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In: ICCV, pp. 3836–3847 (2023)
Zhao, J., Zhang, H.: Thin-plate spline motion model for image animation. In: CVPR (2022)
Zhao, S., Fu, H., Gong, M., Tao, D.: Geometry-aware symmetric domain adaptation for monocular depth estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 9788–9798 (2019)
Zheng, C., Cham, T.J., Cai, J.: T2Net: synthetic-to-realistic translation for solving single-image depth estimation tasks. In: ECCV, pp. 767–783 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) under Contract No. HR001120C0124. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhai, Y. et al. (2025). IDOL: Unified Dual-Modal Latent Diffusion for Human-Centric Joint Video-Depth Generation. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15073. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72633-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72633-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72632-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72633-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)