Abstract
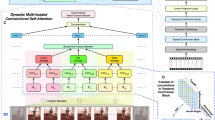
Human Pose Forecasting is a major problem in human intention comprehension that can be addressed through learning the historical poses via deep methods. However, existing methods often lack the modeling of the person’s role in the event in multi-person scenes. This leads to limited performance in complicated scenes with variant interactions happening at the same time. In this paper, we introduce the Interaction-Aware Pose Forecasting Transformer (IAFormer) framework to better learn the interaction features. With the key insight that the event often involves only part of the people in the scene, we designed the Interaction Perceptron Module (IPM) to evaluate the human-to-event interaction level. With the interaction evaluation, the human-independent features are extracted with the attention mechanism for interaction-aware forecasting. In addition, an Interaction Prior Learning Module (IPLM) is presented to learn and accumulate prior knowledge of high-frequency interactions, encouraging semantic pose forecasting rather than simple trajectory pose forecasting. We conduct experiments using datasets such as CMU-Mocap, UMPM, CHI3D, Human3.6M, and synthesized crowd datasets. The results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches considering scenarios with varying numbers of people. Code is available at https://github.com/ArcticPole/ IAFormer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Aa, N., Luo, X., Giezeman, G.J., Tan, R.T., Veltkamp, R.C.: Umpm benchmark: a multi-person dataset with synchronized video and motion capture data for evaluation of articulated human motion and interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 1264–1269 (2011)
Adeli, V., et al.: Tripod: Human trajectory and pose dynamics forecasting in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13390–13400 (2021)
Butepage, J., Black, M.J., Kragic, D., Kjellstrom, H.: Deep representation learning for human motion prediction and classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6158–6166 (2017)
Chiu, H.k., Adeli, E., Wang, B., Huang, D.A., Niebles, J.C.: Action-agnostic human pose forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 1423–1432 (2019)
CMU-Graphics-Lab: CMU graphics lab motion capture database (2003). http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/
Cui, Q., Sun, H.: Towards accurate 3d human motion prediction from incomplete observations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4801–4810 (2021)
Cui, Q., Sun, H., Yang, F.: Learning dynamic relationships for 3d human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6519–6527 (2020)
Dang, L., Nie, Y., Long, C., Zhang, Q., Li, G.: MSR-GCN: multi-scale residual graph convolution networks for human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 11467–11476 (2021)
Diller, C., Funkhouser, T., Dai, A.: Forecasting characteristic 3d poses of human actions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15914–15923 (2022)
Ding, Y., Mao, R., Du, G., Zhang, L.: Clothes-eraser: clothing-aware controllable disentanglement for clothes-changing person re-identification. In: Signal, Image and Video Processing, , pp. 1–12 (2024)
Ding, Y., Wang, A., Zhang, L.: Multidimensional semantic disentanglement network for clothes-changing person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 1025–1033 (2024)
Ding, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, A., Gong, T., Zhang, L.: Disentangled body features for clothing change person re-identification. Multimedia Tools Appl. 1–22 (2024)
Fieraru, M., Zanfir, M., Oneata, E., Popa, A.I., Olaru, V., Sminchisescu, C.: Three-dimensional reconstruction of human interactions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7214–7223 (2020)
Fragkiadaki, K., Levine, S., Felsen, P., Malik, J.: Recurrent network models for human dynamics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4346–4354 (2015)
Guo, W., Bie, X., Alameda-Pineda, X., Moreno-Noguer, F.: Multi-person extreme motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13053–13064 (2022)
Ionescu, C., Papava, D., Olaru, V., Sminchisescu, C.: Human3. 6m: large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(7), 1325–1339 (2013)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907 (2016)
Li, M., Chen, S., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Tian, Q.: Dynamic multiscale graph neural networks for 3d skeleton based human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 214–223 (2020)
Ma, T., Nie, Y., Long, C., Zhang, Q., Li, G.: Progressively generating better initial guesses towards next stages for high-quality human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6437–6446 (2022)
Mao, W., Liu, M., Salzmann, M.: History repeats itself: human motion prediction via motion attention. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 474–489 (2020)
Mao, W., Liu, M., Salzmann, M., Li, H.: Learning trajectory dependencies for human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9489–9497 (2019)
Martinez, J., Black, M.J., Romero, J.: On human motion prediction using recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2891–2900 (2017)
Mehta, D., et al.: Single-shot multi-person 3d pose estimation from monocular RGB. In: International Conference on 3D Vision, pp. 120–130 (2018)
Paszke, A., et al.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (2019)
Peng, X., Mao, S., Wu, Z.: Trajectory-aware body interaction transformer for multi-person pose forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 17121–17130 (2023)
Shen, F., Xie, Y., Zhu, J., Zhu, X., Zeng, H.: Git: graph interactive transformer for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 1039–1051 (2023)
Shen, F., Zhu, J., Zhu, X., Xie, Y., Huang, J.: Exploring spatial significance via hybrid pyramidal graph network for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(7), 8793–8804 (2021)
Shu, X., Zhang, L., Qi, G.J., Liu, W., Tang, J.: Spatiotemporal co-attention recurrent neural networks for human-skeleton motion prediction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 3300–3315 (2021)
Sofianos, T., Sampieri, A., Franco, L., Galasso, F.: Space-time-separable graph convolutional network for pose forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 11209–11218 (2021)
Van Den Oord, A., Vinyals, O., et al.: Neural discrete representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Von Marcard, T., Henschel, R., Black, M.J., Rosenhahn, B., Pons-Moll, G.: Recovering accurate 3d human pose in the wild using imus and a moving camera. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 601–617 (2018)
Wang, J., Xu, H., Narasimhan, M., Wang, X.: Multi-person 3d motion prediction with multi-range transformers. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 6036–6049 (2021)
Wu, Z., Pan, S., Chen, F., Long, G., Zhang, C., Philip, S.Y.: A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(1), 4–24 (2020)
Xiao, P., Wang, C., Lin, Z., Hao, Y., Chen, G., Xie, L.: Knowledge-based clustering federated learning for fault diagnosis in robotic assembly. Knowl.-Based Syst. 294, 111792 (2024)
Xu, C., Tan, R.T., Tan, Y., Chen, S., Wang, X., Wang, Y.: Auxiliary tasks benefit 3d skeleton-based human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9509–9520 (2023)
Xu, Q., et al.: Joint-relation transformer for multi-person motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9816–9826 (2023)
Zhang, H., Shen, C., Li, Y., Cao, Y., Liu, Y., Yan, Y.: Exploiting temporal consistency for real-time video depth estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1725–1734 (2019)
Zheng, W., Xu, C., Xu, X., Liu, W., He, S.: Ciri: curricular inactivation for residue-aware one-shot video inpainting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13012–13022 (2023)
Zhong, C., Hu, L., Zhang, Z., Ye, Y., Xia, S.: Spatio-temporal gating-adjacency gcn for human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6447–6456 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by China National Key R&D Program (Grant No. 2023YFE0202700), Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangzhou City (No.2023B01J0022), Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Outstanding Youth Team Project (No.2024B1515040010), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62302170), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No.2024A1515010187), Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No.2024A04J3750).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiao, P., Xie, Y., Xu, X., Chen, W., Zhang, H. (2025). Multi-person Pose Forecasting with Individual Interaction Perceptron and Prior Learning. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15076. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72649-1_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72649-1_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72648-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72649-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)