Abstract
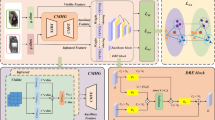
Unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification (USL-VI-ReID) is a promising yet highly challenging retrieval task. The key challenges in USL-VI-ReID are to accurately generate pseudo-labels and establish pseudo-label correspondences across modalities without relying on any prior annotations. Recently, clustered pseudo-label methods have gained more attention in USL-VI-ReID. However, most existing methods don’t fully exploit the intra-class nuances, as they simply utilize a single memory that represents an identity to establish cross-modality correspondences, resulting in noisy cross-modality correspondences. To address the problem, we propose a Multi-Memory Matching (MMM) framework for USL-VI-ReID. We first design a simple yet effective Cross-Modality Clustering (CMC) module to generate the pseudo-labels through clustering together both two modality samples. To associate cross-modality clustered pseudo-labels, we design a Multi-Memory Learning and Matching (MMLM) module, ensuring that optimization explicitly focuses on the nuances of individual perspectives and establishes reliable cross-modality correspondences. Finally, we design a Soft Cluster-level Alignment (SCA) loss to narrow the modality gap while mitigating the effect of noisy pseudo-labels through a soft many-to-many alignment strategy. Extensive experiments on the public SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets demonstrate the reliability of the established cross-modality correspondences and the effectiveness of MMM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arpit, D., et al.: A closer look at memorization in deep networks. In: ICML, pp. 233–242 (2017)
Chen, H., Lagadec, B., Brémond, F.: ICE: inter-instance contrastive encoding for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 14940–14949 (2021)
Chen, Y., Wan, L., Li, Z., Jing, Q., Sun, Z.: Neural feature search for RGB-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 587–597 (2021)
Chen, Z., Zhang, Z., Tan, X., Qu, Y., Xie, Y.: Unveiling the power of clip in unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ACM MM, pp. 3667–3675 (2023)
Cheng, D., Huang, X., Wang, N., He, L., Li, Z., Gao, X.: Unsupervised visible-infrared person reid by collaborative learning with neighbor-guided label refinement. ArXiv:2305.12711 (2023)
Cho, Y., Kim, W.J., Hong, S., Yoon, S.: Part-based pseudo label refinement for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 7298–7308 (2022)
Dai, Z., Wang, G., Yuan, W., Zhu, S., Tan, P.: Cluster contrast for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ACCV, pp. 319–337 (2022)
Ester, M., Kriegel, H., Sander, J., Xu, X.: A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In: KDD, pp. 226–231 (1996)
Feng, J., Wu, A., Zheng, W.: Shape-erased feature learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 22752–22761 (2023)
Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Shi, H., Huang, T.S.: Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 6111–6120 (2019)
Ge, Y., Chen, D., Li, H.: Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In: ICLR (2020)
Ge, Y., Zhu, F., Chen, D., Zhao, R., Li, H.: Self-paced contrastive learning with hybrid memory for domain adaptive object re-id. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Gong, Y., Huang, L., Chen, L.: Person re-identification method based on color attack and joint defence. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 4312–4321. IEEE (2022)
Gong, Y., Zhong, Z., Luo, Z., Qu, Y., Ji, R., Jiang, M.: Cross-modality perturbation synergy attack for person re-identification. CoRR abs/2401.10090 (2024)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M.J., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.: A kernel two-sample test. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 723–773 (2012)
He, L., Wang, N., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Gao, X., et al.: Efficient bilateral cross-modality cluster matching for unsupervised visible-infrared person reid. ArXiv:2305.12673 (2023)
Hubert, L., Arabie, P.: Comparing partitions. J. Classificat. 2, 193–218 (1985)
Shi, J., et al.: Progressive contrastive learning with multi-prototype for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. arXiv:2402.19026 (2024)
Kim, M., Kim, S., Park, J., Park, S., Sohn, K.: Partmix: regularization strategy to learn part discovery for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 18621–18632 (2023)
Li, H., Ye, M., Zhang, M., Du, B.: All in one framework for multimodal re-identification in the wild. In: CVPR. pp. 17459–17469 (2024)
Liang, W., Wang, G., Lai, J., Xie, X.: Homogeneous-to-heterogeneous: Unsupervised learning for RGB-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 6392–6407 (2021)
Lin, L., Liu, H., Liang, J., Li, Z., Feng, J., Han, H.: Consensus-agent deep reinforcement learning for face aging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2024)
Lin, L., Wang, T., Liu, H., Zhu, C., Chen, J.: Toward quantifiable face age transformation under attribute unbias. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2024)
Lin, Y., Xie, L., Wu, Y., Yan, C., Tian, Q.: Unsupervised person re-identification via softened similarity learning. In: CVPR, pp. 3387–3396 (2020)
Nguyen, D.T., Hong, H.G., Kim, K., Park, K.R.: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3), 605 (2017)
Pang, Z., Wang, C., Zhao, L., Liu, Y., Sharma, G.: Cross-modality hierarchical clustering and refinement for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1–1 (2023)
Pang, Z., Zhao, L., Liu, Q., Wang, C.: Camera invariant feature learning for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 25, 6171–6182 (2022)
Park, H., Lee, S., Lee, J., Ham, B.: Learning by aligning: visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In: ICCV, pp. 12026–12035 (2021)
Shi, J., Yin, X., Zhang, D., Qu, Y.: Visible embraces infrared: cross-modality person re-identification with single-modality supervision. In: 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC), pp. 4781–4787. IEEE (2023)
Shi, J., et al.: Dual pseudo-labels interactive self-training for semi-supervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 11218–11228 (2023)
Sun, H., et al.: Not all pixels are matched: dense contrastive learning for cross-modality person re-identification. In: ACM MM, pp. 5333–5341 (2022)
Tan, L., Dai, P., Ji, R., Wu, Y.: Dynamic prototype mask for occluded person re-identification. In: ACM MM, pp. 531–540 (2022)
Tan, L., Xia, J., Liu, W., Dai, P., Wu, Y., Cao, L.: Occluded person re-identification via saliency-guided patch transfer. In: AAAI, vol. 38, pp. 5070–5078 (2024)
Tang, Y., et al.: Align before search: aligning ads image to text for accurate cross-modal sponsored search (2023)
Tang, Y., et al.: Context-i2w: mapping images to context-dependent words for accurate zero-shot composed image retrieval. In: AAAI, vol. 38, pp. 5180–5188 (2024)
Wang, D., Zhang, S.: Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. In: CVPR, pp. 10978–10987 (2020)
Wang, G., et al.: Cross-modality paired-images generation and augmentation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. Neural Netw. 128, 294–304 (2020)
Wang, J., et al.: Optimal transport for label-efficient visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13684, pp. 93–109. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20053-3_6
Wang, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, P., Lu, H., Tu, Z., Lu, H.: Top-reid: multi-spectral object re-identification with token permutation. In: AAAI, vol. 38, pp. 5758–5766 (2024)
Wei, Z., Yang, X., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Syncretic modality collaborative learning for visible infrared person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 225–234 (2021)
Wu, A., Zheng, W., Yu, H., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 5390–5399 (2017)
Wu, Y., et al.: Multi-centroid representation network for domain adaptive person re-id. In: AAAI, pp. 2750–2758 (2022)
Wu, Z., Ye, M.: Unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification via progressive graph matching and alternate learning. In: CVPR, pp. 9548–9558 (2023)
Yang, B., Chen, J., Ma, X., Ye, M.: Translation, association and augmentation: learning cross-modality re-identification from single-modality annotation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 5099–5113 (2023)
Yang, B., Chen, J., Ye, M.: Towards grand unified representation learning for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 11069–11079 (2023)
Yang, B., Chen, J., Ye, M.: Shallow-deep collaborative learning for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 16870–16879 (2024)
Yang, B., Ye, M., Chen, J., Wu, Z.: Augmented dual-contrastive aggregation learning for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ACM MM, pp. 2843–2851 (2022)
Yang, M., Huang, Z., Hu, P., Li, T., Lv, J., Peng, X.: Learning with twin noisy labels for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 14288–14297 (2022)
Yang, M., Huang, Z., Peng, X.: Robust object re-identification with coupled noisy labels. IJCV 1–19 (2024)
Ye, M., Ruan, W., Du, B., Shou, M.Z.: Channel augmented joint learning for visible-infrared recognition. In: ICCV, pp. 13547–13556 (2021)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.H.: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2872–2893 (2022)
Ye, M., Wang, Z., Lan, X., Yuen, P.C.: Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: IJCAI, pp. 1092–1099 (2018)
Yin, X., et al.: Robust pseudo-label learning with neighbor relation for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. CoRR abs/2405.05613 (2024)
Zhai, Y., Ye, Q., Lu, S., Jia, M., Ji, R., Tian, Y.: Multiple expert brainstorming for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: ECCV, vol. 12352, pp. 594–611 (2020)
Zhang, G., Zhang, H., Lin, W., Chandran, A.K., Jing, X.: Camera contrast learning for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(8), 4096–4107 (2023)
Zhang, P., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Tu, Z., Lu, H.: Magic tokens: Select diverse tokens for multi-modal object re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 17117–17126 (2024)
Zhang, Q., Lai, C., Liu, J., Huang, N., Han, J.: FMCNet: feature-level modality compensation for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 7339–7348 (2022)
Zhang, Y., Wang, H.: Diverse embedding expansion network and low-light cross-modality benchmark for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 2153–2162 (2023)
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, H.: Towards a unified middle modality learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ACM MM, pp. 788–796 (2021)
Zhang, Z., Xie, Y., Li, D., Zhang, W., Tian, Q.: Learning to align via wasserstein for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 7104–7116 (2020)
Zou, C., Chen, Z., Cui, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, C.: Discrepant and multi-instance proxies for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV, pp. 11058–11068 (2023)
Zuo, J., et al..: Ufinebench: Towards text-based person retrieval with ultra-fine granularity. In: CVPR, pp. 22010–22019 (2024)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62176224, 62222602, 62106075, 62176092, 62306165), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (23ZR1420400), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2023NSCQ-JQX0007), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2023M731957), CCF-Lenovo Blue Ocean Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shi, J. et al. (2025). Multi-memory Matching for Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15076. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72649-1_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72649-1_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72648-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72649-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)