Abstract
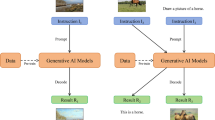
In this paper, we introduce Auto-GAS, the first training-free Generative Architecture Search (GAS) framework enabled by an auto-discovered proxy. Generative models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are now widely used in many real-time applications. Previous GAS methods use differentiable or evolutionary search to find optimal GAN generators for fast inference and memory efficiency. However, the high computational overhead of these training-based GAS techniques limits their adoption. To improve search efficiency, we explore training-free GAS but find existing zero-cost proxies designed for classification tasks underperform on generation benchmarks. To address this challenge, we develop a custom proxy search framework tailored for GAS tasks to enhance predictive power. Specifically, we construct an information-aware proxy that takes feature statistics as inputs and utilizes advanced transform, encoding, reduction, and augment operations to represent candidate proxies. Then, we employ an evolutionary algorithm to perform crossover and mutation on superior candidates within the population based on correlation evaluation. Finally, we perform generator search without training using the optimized proxy. Thus, Auto-GAS enables automated proxy discovery for GAS while significantly accelerating the search before training stage. Extensive experiments on image generation and image-to-image translation tasks demonstrate that Auto-GAS strikes superior accuracy-speed tradeoffs over state-of-the-art methods. Remarkably, Auto-GAS achieves competitive scores with 110\(\times \) faster search than GAN Compression. Code at: https://github.com/lliai/Auto-GAS.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfattah, M.S., Mehrotra, A., Dudziak, Ł., Lane, N.D.: Zero-cost proxies for lightweight NAS. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.08134 (2021)
Akhauri, Y., Munoz, J.P., Jain, N., Iyer, R.: EZNAS: evolving zero-cost proxies for neural architecture scoring. In: Oh, A.H., Agarwal, A., Belgrave, D., Cho, K. (eds.) NeurIPS (2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=lSqaDG4dvdt
Alemi, A.A., Fischer, I., Dillon, J.V., Murphy, K.: Deep variational information bottleneck. In: ICLR (2017)
Baker, B., Gupta, O., Naik, N., Raskar, R.: Designing neural network architectures using reinforcement learning. In: ICLR (2017)
Brock, A., Donahue, J., Simonyan, K.: Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. In: ICLR (2019)
Cavagnero, N., Robbiano, L., Pistilli, F., Caputo, B., Averta, G.: Entropic score metric: decoupling topology and size in training-free NAS. In: ICCV workshop (2023)
Chen, K., Yang, L., Chen, Y., Chen, K., Xu, Y., Li, L.: GP-NAS-ensemble: a model for the NAS performance prediction. In: CVPRW (2022)
Coates, A., Ng, A., Lee, H.: An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In: Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (2011)
Cordts, M., et al.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: CVPR (2016)
Dong, P., Li, L., Wei, Z.: Diswot: student architecture search for distillation without training. In: CVPR (2023)
Dong, P., Li, L., Wei, Z., Niu, X., Tian, Z., Pan, H.: EMQ: evolving training-free proxies for automated mixed precision quantization. In: ICCV (2023)
Dong, P., et al.: RD-NAS: enhancing one-shot supernet ranking ability via ranking distillation from zero-cost proxies. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.09850 (2023)
Dong, P., et al.: Prior-guided one-shot neural architecture search. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.13329 (2022)
Dong, P., et al.: Progressive meta-pooling learning for lightweight image classification model. In: ICASSP (2023)
Duan, Y., et al.: Transnas-bench-101: improving transferability and generalizability of cross-task neural architecture search. In: CVPR, pp. 5251–5260 (2021)
Elsken, T., Metzen, J.H., Hutter, F.: Neural architecture search: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.05377 (2018)
Gao, C., Chen, Y., Liu, S., Tan, Z., Yan, S.: Adversarialnas: adversarial neural architecture search for GANs. In: CVPR (2020)
Gong, X., Chang, S., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z.: AutoGAN: neural architecture search for generative adversarial networks. In: ICCV (2019)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: NeurIPS (2014)
Gulrajani, I., Ahmed, F., Arjovsky, M., Dumoulin, V., Courville, A.C.: Improved training of wasserstein GANs. In: NeurIPS (2017)
He, H., Wang, H., Lee, G.H., Tian, Y.: ProbGAN: towards probabilistic GAN with theoretical guarantees. In: ICLR (2018)
Hu, Y., Wang, X., Li, L., Gu, Q.: Improving one-shot NAS with shrinking-and-expanding supernet. Pattern Recogn. (2021)
Isola, P., Zhu, J., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.632
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 (2017)
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aila, T.: A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2019)
Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Lee, H., Hinton, G.E.: Similarity of neural network representations revisited. In: ICML (2019)
Krizhevsky, A., Nair, V., Hinton, G.: The cifar-10 dataset (2014). http://www.cs.toronto.edu/kriz/cifar.html
Lee, N., Ajanthan, T., Torr, P.H.: Snip: single-shot network pruning based on connection sensitivity. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.02340 (2018)
Li, G., Yang, Y., Bhardwaj, K., Marculescu, R.: Zico: zero-shot NAS via inverse coefficient of variation on gradients. In: The Eleventh ICLR (2023). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rwo-ls5GqGn
Li, H., Fu, T., Dai, J., Li, H., Huang, G., Zhu, X.: Autoloss-zero: searching loss functions from scratch for generic tasks. In: CVPR (2022)
Li, L.: Self-regulated feature learning via teacher-free feature distillation. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13686, pp. 347–363. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19809-0_20
Li, L., et al.: Detkds: knowledge distillation search for object detectors. In: ICML (2024)
Li, L., Dong, P., Li, A., Wei, Z., Yang, Y.: Kd-zero: evolving knowledge distiller for any teacher-student pairs. In: NeuIPS (2024)
Li, L., Dong, P., Wei, Z., Yang, Y.: Automated knowledge distillation via Monte Carlo tree search. In: ICCV (2023)
Li, L., Jin, Z.: Shadow knowledge distillation: bridging offline and online knowledge transfer. In: NeuIPS (2022)
Li, L., Sun, H., Dong, P., Wei, Z., Shao, S.: Auto-das: automated proxy discovery for training-free distillation-aware architecture search. In: ECCV (2024)
Li, L., Wang, Y., Yao, A., Qian, Y., Zhou, X., He, K.: Explicit connection distillation. In: ICLR (2020)
Li, M., Lin, J., Ding, Y., Liu, Z., Zhu, J.Y., Han, S.: GAN compression: efficient architectures for interactive conditional GANs. In: CVPR (2020)
Lin, M., et al.: Zen-NAS: a zero-shot NAS for high-performance image recognition. In: ICCV (2021)
Lin, Q., Fang, Z., Chen, Y., Tan, K.C., Li, Y.: Evolutionary architectural search for generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. (2022)
Liu, H., Simonyan, K., Yang, Y.: DARTS: differentiable architecture search. In: 7th ICLR, ICLR 2019, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019, abs/1806.09055 (2019)
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Deng, J., Soatto, S.: Dynamically grown generative adversarial networks. In: AAAI (2021)
Liu, Y., Yu, S., Lin, T.: Hessian regularization of deep neural networks: a novel approach based on stochastic estimators of hessian trace. Neurocomputing 536, 13–20 (2023)
Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Cai, X., Yuan, X.: E2GAN: end-to-end generative adversarial network for multivariate time series imputation. In: 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 3094–3100. AAAI Press Palo Alto, CA, USA (2019)
Mellor, J., Turner, J., Storkey, A., Crowley, E.J.: Neural architecture search without training. In: ICML (2021)
Miyato, T., Kataoka, T., Koyama, M., Yoshida, Y.: Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv abs/1802.05957 (2018)
Odena, A., Olah, C., Shlens, J.: Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs. In: ICML. PMLR (2017)
Park, T., Liu, M.Y., Wang, T.C., Zhu, J.Y.: Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In: CVPR (2019)
Qin, J., Wu, J., Xiao, X., Li, L., Wang, X.: Activation modulation and recalibration scheme for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. In: AAAI (2022)
Radford, A., Metz, L., Chintala, S.: Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. CoRR abs/1511.06434 (2016)
Real, E., Liang, C., So, D.R., Le, Q.V.: Automl-zero: evolving machine learning algorithms from scratch (2020)
Shao, S., Dai, X., Yin, S., Li, L., Chen, H., Hu, Y.: Catch-up distillation: You only need to train once for accelerating sampling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10769 (2023)
Shu, H., et al.: Co-evolutionary compression for unpaired image translation. In: ICCV (2019)
Shwartz-Ziv, R., Tishby, N.: Opening the black box of deep neural networks via information. arXiv:1703.00810 (2017)
Shwartz-Ziv, R., Tishby, N.: Opening the black box of deep neural networks via information. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1703.00810 (2017)
Tan, M., Le, Q.: Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: ICML (2019)
Tanaka, H., Kunin, D., Yamins, D.L., Ganguli, S.: Pruning neural networks without any data by iteratively conserving synaptic flow. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Tanaka, H., Kunin, D., Yamins, D.L., Ganguli, S.: Pruning neural networks without any data by iteratively conserving synaptic flow. NeurIPS 33, 6377–6389 (2020)
Tian, Y., Shen, L., Su, G., Li, Z., Liu, W.: AlphaGAN: fully differentiable architecture search for generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.09134 (2020)
Tian, Y., et al.: Off-policy reinforcement learning for efficient and effective GAN architecture search. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12352, pp. 175–192. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58571-6_11
Tishby, N., Zaslavsky, N.: Deep learning and the information bottleneck principle. In: ITW, pp. 1–5. IEEE (2015)
Wang, C., Zhang, G., Grosse, R.: Picking winning tickets before training by preserving gradient flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07376 (2020)
Wang, C., Xu, C., Yao, X., Tao, D.: Evolutionary generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 23(6), 921–934 (2019)
Wang, H., Huan, J.: AGAN: towards automated design of generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.11080 (2019)
Wang, W., Sun, Y., Halgamuge, S.: Improving MMD-GAN training with repulsive loss function. In: ICLR (2019)
Wei, Z., et al.: Convformer: closing the gap between CNN and vision transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.07738 (2022)
Wolchover, N., Reading, L.: New theory cracks open the black box of deep learning. Quanta Mag. (2017)
Xiaolong, L., Lujun, L., Chao, L., Yao, A.: Norm: knowledge distillation via n-to-one representation matching. In: ICLR (2023)
Ying, G., He, X., Gao, B., Han, B., Chu, X.: Eagan: efficient two-stage evolutionary architecture search for GANs. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13676, pp. 37–53. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19787-1_3
Yu, A., Grauman, K.: Fine-grained visual comparisons with local learning. In: CVPR (2014)
Zhang, M., Li, H., Pan, S., Chang, X., Su, S.: Overcoming multi-model forgetting in one-shot NAS with diversity maximization. In: CVPR, pp. 7809–7818 (2020)
Zhong, Z., et al.: BlockQNN: efficient block-wise neural network architecture generation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2020)
Zhu, C., Li, L., Wu, Y., Sun, Z.: Saswot: real-time semantic segmentation architecture search without training. In: AAAI (2024)
Zimian Wei, Z., et al.: Auto-prox: training-free vision transformer architecture search via automatic proxy discovery. In: AAAI (2024)
Zoph, B., Vasudevan, V., Shlens, J., Le, Q.V.: Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In: CVPR (2018)
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by Theme-based Research Scheme (T45-205/21-N) from Hong Kong RGC, and Generative AI Research and Development Centre from InnoHK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, L. et al. (2025). Auto-GAS: Automated Proxy Discovery for Training-Free Generative Architecture Search. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15063. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72652-1_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72652-1_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72651-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72652-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)