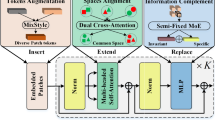
Abstract
Generalizable Face anti-spoofing (FAS) approaches have recently garnered considerable attention due to their robustness in unseen scenarios. Some recent methods incorporate vision-language models into FAS, leveraging their impressive pre-trained performance to improve the generalization. However, these methods only utilize coarse-grained or single-element prompts for fine-tuning FAS tasks, without fully exploring the potential of language supervision, leading to unsatisfactory generalization ability. To address these concerns, we propose a novel framework called TF-FAS, which aims to thoroughly explore and harness twofold-element fine-grained semantic guidance to enhance generalization. Specifically, the Content Element Decoupling Module (CEDM) is proposed to comprehensively explore the semantic elements related to content. It is subsequently employed to supervise the decoupling of categorical features from content-related features, thereby enhancing the generalization abilities. Moreover, recognizing the subtle differences within the data of each class in FAS, we present a Fine-Grained Categorical Element Module (FCEM) to explore fine-grained categorical element guidance, then adaptively integrate them to facilitate the distribution modeling for each class. Comprehensive experiments and analysis demonstrate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art competitors. Code: https://github.com/xudongww/TF-FAS
X. Wang and K.-Y. Zhang—Equal contributions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achiam, J., et al.: GPT-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774 (2023)
Agarwal, A., Singh, R., Vatsa, M.: Face anti-spoofing using Haralick features. In: International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), pp. 1–6 (2016)
Alexey, D.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010.11929 (2020)
Anjos, A., Marcel, S.: Counter-measures to photo attacks in face recognition: a public database and a baseline. In: International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), pp. 1–7 (2011)
Belghazi, M.I., et al.: MINE: mutual information neural estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04062 (2018)
Boulkenafet, Z., Komulainen, J., Hadid, A.: Face anti-spoofing based on color texture analysis. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2636–2640 (2015)
Boulkenafet, Z., Komulainen, J., Hadid, A.: Face antispoofing using speeded-up robust features and Fisher vector encoding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. (SPL) 24, 41–145 (2016)
Boulkenafet, Z., Komulainen, J., Li, L., Feng, X., Hadid, A.: OULU-NPU: a mobile face presentation attack database with real-world variations. In: IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 612–618 (2017)
Cai, R., et al.: Rehearsal-free domain continual face anti-spoofing: generalize more and forget less. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 8037–8048 (2023)
Cai, R., et al.: S-adapter: generalizing vision transformer for face anti-spoofing with statistical tokens. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) (2024)
Chen, Z., et al.: Generalizable representation learning for mixture domain face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 1132–1139 (2021)
Cheng, F., Wang, X., Lei, J., Crandall, D., Bansal, M., Bertasius, G.: VINDLU: a recipe for effective video-and-language pretraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10739–10750 (2023)
Cheng, P., Hao, W., Dai, S., Liu, J., Gan, Z., Carin, L.: CLUB: a contrastive log-ratio upper bound of mutual information. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 1779–1788 (2020)
Chingovska, I., Anjos, A., Marcel, S.: On the effectiveness of local binary patterns in face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference of Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), pp. 1–7 (2012)
Cui, Q., et al.: Contrastive vision-language pre-training with limited resources. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13696, pp. 236–253. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20059-5_14
Dai, H., et al.: AugGPT: leveraging chatGPT for text data augmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13007 (2023)
Du, Z., Li, J., Zuo, L., Zhu, L., Lu, K.: Energy-based domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), pp. 1749–1757 (2022)
Erdogmus, N., Marcel, S.: Spoofing 2D face recognition systems with 3D masks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference of Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), pp. 1–8 (2013)
Fang, H., Liu, A., Jiang, N., Lu, Q., Zhao, G., Wan, J.: VL-FAS: domain generalization via vision-language model for face anti-spoofing. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4770–4774 (2024)
Fei, J., Wang, T., Zhang, J., He, Z., Wang, C., Zheng, F.: Transferable decoding with visual entities for zero-shot image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3136–3146 (2023)
de Freitas Pereira, T., Anjos, A., De Martino, J.M., Marcel, S.: LBP-top based countermeasure against face spoofing attacks. In: Computer Vision-ACCV 2012 Workshops: ACCV 2012 International Workshops (ACCV), pp. 121–132 (2013)
George, A., Marcel, S.: On the effectiveness of vision transformers for zero-shot face anti-spoofing. In: International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), pp. 1–8 (2021)
Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W.B., Zhang, M., Balduzzi, D., Li, W.: Deep reconstruction-classification networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9908, pp. 597–613. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_36
Goyal, S., Kumar, A., Garg, S., Kolter, Z., Raghunathan, A.: Finetune like you pretrain: improved finetuning of zero-shot vision models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 19338–19347 (2023)
Hu, L., Kan, M., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Duplex generative adversarial network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1498–1507 (2018)
Hu, X., et al.: Scaling up vision-language pre-training for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 17980–17989 (2022)
Huang, H.P., et al.: Adaptive transformers for robust few-shot cross-domain face anti-spoofing. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13673, pp. 37–54. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19778-9_3
Jia, C., et al.: Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 4904–4916 (2021)
Jia, Y., Zhang, J., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Single-side domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8484–8493 (2020)
Jia, Y., Zhang, J., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Unified unsupervised and semi-supervised domain adaptation network for cross-scenario face anti-spoofing. Pattern Recognit. (PR) 115, 107888 (2021)
Khosla, P., et al.: Supervised contrastive learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), pp. 18661–18673 (2020)
Kim, G., Eum, S., Suhr, J.K., Kim, D.I., Park, K.R., Kim, J.: Face liveness detection based on texture and frequency analyses. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 67–72 (2012)
Kim, S., Yu, S., Kim, K., Ban, Y., Lee, S.: Face liveness detection using variable focusing. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 1–6 (2013)
Kim, Y.E., Lee, S.W.: Domain generalization with pseudo-domain label for face anti-spoofing. In: Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), pp. 431–442 (2021)
Komulainen, J., Hadid, A., Pietikäinen, M.: Context based face anti-spoofing. In: International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), pp. 1–8 (2013)
Le, B.M., Woo, S.S.: Gradient alignment for cross-domain face anti-spoofing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.18817 (2024)
Li, H., Li, W., Cao, H., Wang, S., Huang, F., Kot, A.C.: Unsupervised domain adaptation for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 13, 1794–1809 (2018)
Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.: BLIP: bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 12888–12900 (2022)
Li, P., Liu, G., He, J., Zhao, Z., Zhong, S.: Masked vision and language pre-training with unimodal and multimodal contrastive losses for medical visual question answering. In: Greenspan, H., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2023. LNCS, vol. 14220, pp. 374–383. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43907-0_36
Li, P., Liu, G., Tan, L., Liao, J., Zhong, S.: Self-supervised vision-language pretraining for medial visual question answering. In: International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1–5 (2023)
Liao, C.H., Chen, W.C., Liu, H.T., Yeh, Y.R., Hu, M.C., Chen, C.S.: Domain invariant vision transformer learning for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). pp. 6098–6107 (2023)
Liu, A., et al.: FM-ViT: flexible modal vision transformers for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 18, 4775–4786 (2023)
Liu, H., Li, C., Wu, Q., Lee, Y.J.: Visual instruction tuning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2024)
Liu, M., Mu, J., Yu, Z., Ruan, K., Shu, B., Yang, J.: Adversarial learning and decomposition-based domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. Pattern Recognit. Lett. (PRL) 155, 171–177 (2022)
Liu, S., Lu, S., Xu, H., Yang, J., Ding, S., Ma, L.: Feature generation and hypothesis verification for reliable face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 1782–1791 (2022)
Liu, S., et al.: Adaptive normalized representation learning for generalizable face anti-spoofing. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), pp. 1469–1477 (2021)
Liu, S., et al.: Dual reweighting domain generalization for face presentation attack detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.16128 (2021)
Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Dai, W., Gou, M., Huang, C.T., Xiong, H.: Source-free domain adaptation with contrastive domain alignment and self-supervised exploration for face anti-spoofing. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13672, pp. 511–528. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19775-8_30
Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Dai, W., Gou, M., Huang, C.T., Xiong, H.: Source-free domain adaptation with domain generalized pretraining for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach.Intell. (TPAMI) 46, 5430–5448 (2024)
Liu, Y., et al.: Towards unsupervised domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2023)
Mu, L., et al: TEG-DG: textually guided domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.18420 (2023)
Nag, S., Zhu, X., Song, Y.Z., Xiang, T.: Zero-shot temporal action detection via vision-language prompting. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13663, pp. 681–697. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20062-5_39
Niu, X., Yu, Z., Han, H., Li, X., Shan, S., Zhao, G.: Video-based remote physiological measurement via cross-verified feature disentangling. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12347, pp. 295–310. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_18
Panwar, A., Singh, P., Saha, S., Paudel, D.P., Van Gool, L.: Unsupervised compound domain adaptation for face anti-spoofing. In: IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 1–8 (2021)
Parelli, M., et al.: Clip-guided vision-language pre-training for question answering in 3D scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5606–5611 (2023)
Patel, K., Han, H., Jain, A.K., Ott, G.: Live face video vs. spoof face video: use of moiré patterns to detect replay video attacks. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 98–105 (2015)
Pramanick, S., et al.: EgoVLPv2: egocentric video-language pre-training with fusion in the backbone. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5285–5297 (2023)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 8748–8763 (2021)
Sarhan, M.H., Navab, N., Eslami, A., Albarqouni, S.: Fairness by learning orthogonal disentangled representations. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12374, pp. 746–761. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58526-6_44
Schwartz, W.R., Rocha, A., Pedrini, H.: Face spoofing detection through partial least squares and low-level descriptors. In: International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), pp. 1–8 (2011)
Shao, R., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.C.: Multi-adversarial discriminative deep domain generalization for face presentation attack detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
Shao, R., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.C.: Multi-adversarial discriminative deep domain generalization for face presentation attack detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10023–10031 (2019)
Shao, R., Lan, X., Yuen, P.C.: Regularized fine-grained meta face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 11974–11981 (2020)
Shu, M., et al.: Test-time prompt tuning for zero-shot generalization in vision-language models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), pp. 14274–14289 (2022)
Singh, A.K., Joshi, P., Nandi, G.C.: Face liveness detection through face structure analysis. Int. J. Appl. Pattern Recognit. (IJAPR) 1, 338–360 (2014)
Smith, D.F., Wiliem, A., Lovell, B.C.: Face recognition on consumer devices: reflections on replay attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 10, 736–745 (2015)
Srivatsan, K., Naseer, M., Nandakumar, K.: Flip: cross-domain face anti-spoofing with language guidance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 19685–19696 (2023)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7167–7176 (2017)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2017)
Wang, C.Y., Lu, Y.D., Yang, S.T., Lai, S.H.: PatchNet: a simple face anti-spoofing framework via fine-grained patch recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 20281–20290 (2022)
Wang, G., Han, H., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Improving cross-database face presentation attack detection via adversarial domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 1–8 (2019)
Wang, G., Han, H., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Cross-domain face presentation attack detection via multi-domain disentangled representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6678–6687 (2020)
Wang, G., Han, H., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Unsupervised adversarial domain adaptation for cross-domain face presentation attack detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 16, 56–69 (2020)
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Bian, Y., Cai, Y., Wang, C., Pu, S.: Self-domain adaptation for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 2746–2754 (2021)
Wang, J., et al.: All in one: exploring unified video-language pre-training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6598–6608 (2023)
Wang, M., Xing, J., Liu, Y.: ActionCLIP: a new paradigm for video action recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08472 (2021)
Wang, W., Liu, P., Zheng, H., Ying, R., Wen, F.: Domain generalization for face anti-spoofing via negative data augmentation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 18, 2333–2344 (2023)
Wang, W., et al.: Image as a foreign language: Beit pretraining for all vision and vision-language tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.10442 (2022)
Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Wu, L., Han, H., Ma, Y., Li, Z.: Improving face anti-spoofing via advanced multi-perspective feature learning. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 19, 1–18 (2023)
Wang, Z., et al.: Domain generalization via shuffled style assembly for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4123–4133 (2022)
Wen, D., Han, H., Jain, A.K.: Face spoof detection with image distortion analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 10, 746–761 (2015)
Wu, W., Sun, Z., Ouyang, W.: Revisiting classifier: transferring vision-language models for video recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)), pp. 2847–2855 (2023)
Xie, J., Zheng, S.: Zero-shot object detection through vision-language embedding alignment. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), pp. 1–15 (2022)
Yan, Z., Zhang, Y., Fan, Y., Wu, B.: UCF: uncovering common features for generalizable deepfake detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 22412–22423 (2023)
Yang, J., Lei, Z., Liao, S., Li, S.Z.: Face liveness detection with component dependent descriptor. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 1–6 (2013)
Yin, W., Ming, Y., Tian, L.: A face anti-spoofing method based on optical flow field. In: International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), pp. 1333–1337 (2016)
Yu, Z., Li, X., Niu, X., Shi, J., Zhao, G.: Face anti-spoofing with human material perception. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12352, pp. 557–575. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58571-6_33
Yu, Z., Li, X., Shi, J., Xia, Z., Zhao, G.: Revisiting pixel-wise supervision for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. Identity Sci. (T-BIOM) 3:285–295 (2021)
Yu, Z., Wan, J., Qin, Y., Li, X., Li, S.Z., Zhao, G.: NAS-FAS: static-dynamic central difference network search for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 43, 3005–3023 (2020)
Yue, H., et al.: Cyclically disentangled feature translation for face anti-spoofing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.03651 (2022)
Zeng, Y., Zhang, X., Li, H.: Multi-grained vision language pre-training: aligning texts with visual concepts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.08276 (2021)
Zhang, K.-Y., et al.: Face anti-spoofing via disentangled representation learning. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12364, pp. 641–657. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58529-7_38
Zhang, Y., et al.: CelebA-spoof: large-scale face anti-spoofing dataset with rich annotations. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12357, pp. 70–85. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_5
Zhang, Z., Yan, J., Liu, S., Lei, Z., Yi, D., Li, S.Z.: A face antispoofing database with diverse attacks. In: International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 26–31 (2012)
Zhang, Z., Yi, D., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Face liveness detection by learning multispectral reflectance distributions. In: IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 436–441 (2011)
Zheng, G., Liu, Y., Dai, W., Li, C., Zou, J., Xiong, H.: Towards unified representation of invariant-specific features in missing modality face anti-spoofing. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2024)
Zheng, T., et al.: MFAE: masked frequency autoencoders for domain generalization face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. (TIFS) 19, 4058–4069 (2024)
Zheng, T., Yu, Q., Chen, Z., Wang, J.: FAMIM: a novel frequency-domain augmentation masked image model framework for domain generalizable face anti-spoofing. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4470–4474 (2024)
Zheng, Z., Ma, M., Wang, K., Qin, Z., Yue, X., You, Y.: Preventing zero-shot transfer degradation in continual learning of vision-language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.06628 (2023)
Zhong, Y., et al.: RegionCLIP: region-based language-image pretraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 16793–16803 (2022)
Zhou, K., Yang, J., Loy, C.C., Liu, Z.: Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 130, 2337–2348 (2022)
Zhou, Q., Zhang, K.Y., Yao, T., Lu, X., Ding, S., Ma, L.: Test-time domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 175–187 (2024)
Zhou, Q., et al.: Instance-aware domain generalization for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 20453–20463 (2023)
Zhou, Q., Zhang, K.Y., Yao, T., Yi, R., Ding, S., Ma, L.: Adaptive mixture of experts learning for generalizable face anti-spoofing. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), pp. 6009–6018 (2022)
Zhou, Q., et al.: Generative domain adaptation for face anti-spoofing. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13665, pp. 335–356. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20065-6_20
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2022ZD0118201), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 62025603), the National Natural Science Foundation of Chine a (No. U21B2037, No. U22B2051, No. U23A20383, No. 62176222, No. 62176223, No. 62176226, No. 62072386, No. 62072387, No. 62072389, No. 62002305 and No. 62272401), and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (No. 2022J06001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, X. et al. (2025). TF-FAS: Twofold-Element Fine-Grained Semantic Guidance for Generalizable Face Anti-spoofing. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15065. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72667-5_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72667-5_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72666-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72667-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)