Abstract
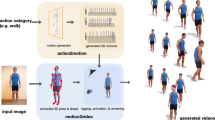
We propose a new framework for creating and easily manipulating 3D models of arbitrary objects using casually captured videos. Our core ingredient is a novel hierarchy deformation model, which captures motions of objects with a tree-structured bones. Our hierarchy system decomposes motions based on the granularity and reveals the correlations between parts without exploiting any prior structural knowledge. We further propose to regularize the bones to be positioned at the basis of motions, centers of parts, sufficiently covering related surfaces of the part. This is achieved by our bone occupancy function, which identifies whether a given 3D point is placed within the bone. Coupling the proposed components, our framework offers several clear advantages: (1) Users can obtain animatable 3D models of the arbitrary objects in improved quality from their casual videos, (2) users can manipulate 3D models in an intuitive manner with minimal costs, and (3) users can interactively add or delete control points as necessary. The experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our framework on diverse instances, in reconstruction quality, interpretability and easier manipulation. Our code is available at https://github.com/subin6/HSNB.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alldieck, T., Magnor, M., Bhatnagar, B.L., Theobalt, C., Pons-Moll, G.: Learning to reconstruct people in clothing from a single RGB camera. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1175–1186 (2019)
Alldieck, T., Magnor, M., Xu, W., Theobalt, C., Pons-Moll, G.: Detailed human avatars from monocular video. In: 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 98–109. IEEE (2018)
Alldieck, T., Magnor, M., Xu, W., Theobalt, C., Pons-Moll, G.: Video based reconstruction of 3d people models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8387–8397 (2018)
Anguelov, D., Srinivasan, P., Koller, D., Thrun, S., Rodgers, J., Davis, J.: Scape: shape completion and animation of people. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers, pp. 408–416 (2005)
Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: A morphable model for the synthesis of 3d faces. In: Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries, vol. 2, pp. 157–164 (2023)
Bozic, A., Zollhofer, M., Theobalt, C., Nießner, M.: Deepdeform: learning non-rigid RGB-D reconstruction with semi-supervised data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7002–7012 (2020)
Cao, A., Johnson, J.: Hexplane: a fast representation for dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 130–141 (2023)
Collet, A., et al.: High-quality streamable free-viewpoint video. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 34(4), 1–13 (2015)
Dou, M., et al.: Fusion4d: real-time performance capture of challenging scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 35(4), 1–13 (2016)
Fridovich-Keil, S., Meanti, G., Warburg, F.R., Recht, B., Kanazawa, A.: K-planes: explicit radiance fields in space, time, and appearance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12479–12488 (2023)
Gao, C., Saraf, A., Kopf, J., Huang, J.B.: Dynamic view synthesis from dynamic monocular video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5712–5721 (2021)
Genova, K., Cole, F., Sud, A., Sarna, A., Funkhouser, T.: Local deep implicit functions for 3d shape. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4857–4866 (2020)
Genova, K., Cole, F., Vlasic, D., Sarna, A., Freeman, W.T., Funkhouser, T.: Learning shape templates with structured implicit functions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7154–7164 (2019)
Hertz, A., Perel, O., Giryes, R., Sorkine-Hornung, O., Cohen-Or, D.: Spaghetti: editing implicit shapes through part aware generation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 41(4), 1–20 (2022)
Innmann, M., Zollhöfer, M., Nießner, M., Theobalt, C., Stamminger, M.: VolumeDeform: real-time volumetric non-rigid reconstruction. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 362–379. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_22
Kirillov, A., Wu, Y., He, K., Girshick, R.: Pointrend: image segmentation as rendering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9799–9808 (2020)
Kuai, T., Karthikeyan, A., Kant, Y., Mirzaei, A., Gilitschenski, I.: Camm: building category-agnostic and animatable 3d models from monocular videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6586–6596 (2023)
Li, R., et al.: TAVA: template-free animatable volumetric actors. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13692, pp. 419–436. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19824-3_25
Li, T., et al.: Neural 3d video synthesis from multi-view video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5521–5531 (2022)
Li, Z., Niklaus, S., Snavely, N., Wang, O.: Neural scene flow fields for space-time view synthesis of dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6498–6508 (2021)
Lin, W., Zheng, C., Yong, J.H., Xu, F.: Occlusionfusion: occlusion-aware motion estimation for real-time dynamic 3d reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1736–1745 (2022)
Liu, L., Habermann, M., Rudnev, V., Sarkar, K., Gu, J., Theobalt, C.: Neural actor: neural free-view synthesis of human actors with pose control. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 40(6), 1–16 (2021)
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., Black, M.J.: SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. In: Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries, Volume 2, pp. 851–866 (2023)
Lorensen, W.E., Cline, H.E.: Marching cubes: a high resolution 3d surface construction algorithm. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. (1987)
Mildenhall, B., Srinivasan, P.P., Tancik, M., Barron, J.T., Ramamoorthi, R., Ng, R.: NeRF: representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 65(1), 99–106 (2021)
Neverova, N., Novotny, D., Szafraniec, M., Khalidov, V., Labatut, P., Vedaldi, A.: Continuous surface embeddings. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 17258–17270 (2020)
Noguchi, A., Iqbal, U., Tremblay, J., Harada, T., Gallo, O.: Watch it move: unsupervised discovery of 3d joints for re-posing of articulated objects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3677–3687 (2022)
Park, K., et al.: Nerfies: deformable neural radiance fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5865–5874 (2021)
Park, K., et al.: Hypernerf: a higher-dimensional representation for topologically varying neural radiance fields. ACM Trans. Graph. 40(6) (2021)
Paschalidou, D., Katharopoulos, A., Geiger, A., Fidler, S.: Neural parts: learning expressive 3d shape abstractions with invertible neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3204–3215 (2021)
Pavlakos, G., et al.: Expressive body capture: 3d hands, face, and body from a single image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10975–10985 (2019)
Peng, S., et al.: Animatable neural radiance fields for modeling dynamic human bodies. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14314–14323 (2021)
Peng, S., et al.: Neural body: implicit neural representations with structured latent codes for novel view synthesis of dynamic humans. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9054–9063 (2021)
Pumarola, A., Corona, E., Pons-Moll, G., Moreno-Noguer, F.: D-NeRF: neural radiance fields for dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10318–10327 (2021)
Su, S.Y., Yu, F., Zollhöfer, M., Rhodin, H.: A-NeRF: articulated neural radiance fields for learning human shape, appearance, and pose. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 12278–12291 (2021)
Tertikas, K., et al.: Partnerf: generating part-aware editable 3d shapes without 3d supervision. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09554 (2023)
Tretschk, E., Tewari, A., Golyanik, V., Zollhöfer, M., Lassner, C., Theobalt, C.: Non-rigid neural radiance fields: reconstruction and novel view synthesis of a dynamic scene from monocular video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12959–12970 (2021)
Tu, T., Li, M.F., Lin, C.H., Cheng, Y.C., Sun, M., Yang, M.H.: Dreamo: articulated 3d reconstruction from a single casual video. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.02617 (2023)
Vlasic, D., Baran, I., Matusik, W., Popović, J.: Articulated mesh animation from multi-view silhouettes. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Papers, pp. 1–9 (2008)
Wang, X., et al.: Animatabledreamer: text-guided non-rigid 3d model generation and reconstruction with canonical score distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.03795 (2023)
Wang, Y., Dong, Y., Sun, F., Yang, X.: Root pose decomposition towards generic non-rigid 3d reconstruction with monocular videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13890–13900 (2023)
Weng, C.Y., Curless, B., Srinivasan, P.P., Barron, J.T., Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.: Humannerf: free-viewpoint rendering of moving people from monocular video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern Recognition, pp. 16210–16220 (2022)
Wu, Y., Chen, Z., Liu, S., Ren, Z., Wang, S.: Casa: category-agnostic skeletal animal reconstruction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 28559–28574 (2022)
Xian, W., Huang, J.B., Kopf, J., Kim, C.: Space-time neural irradiance fields for free-viewpoint video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9421–9431 (2021)
Xiang, D., Joo, H., Sheikh, Y.: Monocular total capture: Posing face, body, and hands in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10965–10974 (2019)
Xu, Z., Zhou, Y., Kalogerakis, E., Landreth, C., Singh, K.: Rignet: neural rigging for articulated characters. ACM Trans. Graph. 39 (2020)
Yang, G., Ramanan, D.: Volumetric correspondence networks for optical flow. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32 (2019)
Yang, G., et al.: Lasr: learning articulated shape reconstruction from a monocular video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15980–15989 (2021)
Yang, G., et al.: ViSER: video-specific surface embeddings for articulated 3D shape reconstruction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 19326–19338 (2021)
Yang, G., Vo, M., Neverova, N., Ramanan, D., Vedaldi, A., Joo, H.: Banmo: building animatable 3d neural models from many casual videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2863–2873 (2022)
Yang, G., Wang, C., Reddy, N.D., Ramanan, D.: Reconstructing animatable categories from videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16995–17005 (2023)
Yariv, L., Gu, J., Kasten, Y., Lipman, Y.: Volume rendering of neural implicit surfaces. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 4805–4815 (2021)
Zollhöfer, M., et al.: Real-time non-rigid reconstruction using an RGB-D camera. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 33(4), 1–12 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. 2022-0-00124), the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF- 2022R1A2C2004509), and Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (Artificial Intelligence Graduate School Program, Yonsei University, under Grant 2020-0-01361).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (mp4 43825 KB)
Supplementary material 3 (mp4 22160 KB)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jeon, S., Cho, I., Kim, M., Cho, W.O., Kim, S.J. (2025). Hierarchically Structured Neural Bones for Reconstructing Animatable Objects from Casual Videos. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15068. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72684-2_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72684-2_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72683-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72684-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)