Abstract
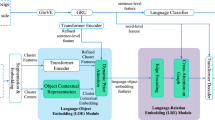
The existing works on object-level language grounding with 3D objects mostly focus on improving performance by utilizing the off-the-shelf pre-trained models to capture features, such as viewpoint selection or geometric priors. However, they have failed to consider exploring the cross-modal representation of language-vision alignment in the cross-domain field. To answer this problem, we propose a novel method called Domain Adaptation for Language Grounding (DA4LG) with 3D objects. Specifically, the proposed DA4LG consists of a visual adapter module with multi-task learning to realize vision-language alignment by comprehensive multimodal feature representation. Experimental results demonstrate that DA4LG competitively performs across visual and non-visual language descriptions, independent of the completeness of observation. DA4LG achieves state-of-the-art performance in the single-view setting and multi-view setting with the accuracy of \(83.8 \%\) and \(86.8 \%\) respectively in the language grounding benchmark SNARE. The simulation experiments show the well-practical and generalized performance of DA4LG compared to the existing methods. Our project is available at https://sites.google.com/view/da4lg.
P. Sun and Y. Song—Equal Contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achlioptas, P., Abdelreheem, A., Xia, F., Elhoseiny, M., Guibas, L.: ReferIt3D: neural listeners for fine-grained 3D object identification in real-world scenes. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12346, pp. 422–440. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_25
Achlioptas, P., Fan, J., Hawkins, R., Goodman, N., Guibas, L.J.: ShapeGlot: learning language for shape differentiation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8938–8947 (2019)
Ahn, M., et al.: Do as I can, not as I say: grounding language in robotic affordances. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.01691 (2022)
Akula, A., Gella, S., Wang, K., Zhu, S.C., Reddy, S.: Mind the context: the impact of contextualization in neural module networks for grounding visual referring expressions. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 6398–6416 (2021)
Bisk, Y., et al.: Experience grounds language. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 8718–8735 (2020)
Chang, A.X., et al.: ShapeNet: an information-rich 3D model repository. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03012 (2015)
Chen, D.Z., Chang, A.X., Nießner, M.: ScanRefer: 3D object localization in RGB-D scans using natural language. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12365, pp. 202–221. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58565-5_13
Chen, S., Guhur, P.L., Tapaswi, M., Schmid, C., Laptev, I.: Language conditioned spatial relation reasoning for 3D object grounding. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 35, pp. 20522–20535 (2022)
Corona, R., Zhu, S., Klein, D., Darrell, T.: Voxel-informed language grounding. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp. 54–60 (2022)
Csurka, G.: Domain adaptation for visual applications: a comprehensive survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.05374 (2017)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Devillers, B., Choksi, B., Bielawski, R., Vanrullen, R.: Does language help generalization in vision models? In: Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, pp. 171–182 (2021)
Diao, S., Xu, R., Su, H., Jiang, Y., Song, Y., Zhang, T.: Taming pre-trained language models with N-gram representations for low-resource domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 3336–3349 (2021)
Diao, S., Xu, T., Xu, R., Wang, J., Zhang, T.: Mixture-of-domain-adapters: decoupling and injecting domain knowledge to pre-trained language models’ memories. In: Rogers, A., Boyd-Graber, J., Okazaki, N. (eds.) Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 5113–5129. Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, Canada, July 2023. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.acl-long.280
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2020)
Language models and linguistic theories beyond words. Nat. Mach. Intell. 5(7), 677–678 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-023-00703-8
Gong, Y., Yue, Y., Ji, W., Zhou, G.: Cross-domain few-shot learning based on pseudo-Siamese neural network. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 1427 (2023)
Guo, Z., et al.: ViewRefer: grasp the multi-view knowledge for 3D visual grounding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15372–15383 (2023)
Gururangan, S., et al.: Don’t stop pretraining: adapt language models to domains and tasks. In: Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 8342–8360 (2020)
Hao, Y., Dong, L., Wei, F., Xu, K.: Visualizing and understanding the effectiveness of BERT. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp. 4143–4152 (2019)
Harnad, S.: The symbol grounding problem. Physica D 42(1–3), 335–346 (1990)
Hu, E.J., et al.: LoRA: low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
Huang, S., Chen, Y., Jia, J., Wang, L.: Multi-view transformer for 3D visual grounding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15524–15533 (2022)
Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., Hoi, S.: BLIP-2: bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In: ICML (2023)
Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.: BLIP: bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 12888–12900. PMLR (2022)
Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., Lee, S.: ViLBERT: pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Malik, B., Kashyap, A.R., Kan, M.Y., Poria, S.: UDApter-efficient domain adaptation using adapters. In: Proceedings of the 17th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 2241–2255 (2023)
Mitra, C., Anwar, A., Corona, R., Klein, D., Thomason, J.: Comparative multi-view language grounding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.06694 (2023)
Miyanishi, T., Azuma, D., Kurita, S., Kawanabe, M.: Cross3DVG: baseline and dataset for cross-dataset 3D visual grounding on different RGB-D scans. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13876 (2023)
OpenAI: GPT-4 technical report (2023)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8748–8763. PMLR (2021)
Radford, A., et al.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog (2019)
Roh, J., Desingh, K., Farhadi, A., Fox, D.: LanguageRefer: spatial-language model for 3D visual grounding. In: Conference on Robot Learning, pp. 1046–1056. PMLR (2022)
Schumann, R., Riezler, S.: Analyzing generalization of vision and language navigation to unseen outdoor areas. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 7519–7532 (2022)
Shrivastava, A., et al.: VISITRON: visual semantics-aligned interactively trained object-navigator. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022, pp. 1984–1994 (2022)
Song, Y., Sun, P., Fang, P., Yang, L., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y.: Human-in-the-loop robotic grasping using BERT scene representation. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 2992–3006 (2022)
Song, Y., et al.: Learning 6-DoF fine-grained grasp detection based on part affordance grounding (2024). https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11564
Song, Y., et al.: Scene-driven multimodal knowledge graph construction for embodied AI (2023)
Štefánik, M., Novotnỳ, V., Groverová, N., Sojka, P.: AdaptOr: objective-centric adaptation framework for language models. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, pp. 261–269 (2022)
Sun, W., Khan, H., Guenon des Mesnards, N., Rubino, M., Arkoudas, K.: Unfreeze with care: space-efficient fine-tuning of semantic parsing models. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 999–1007 (2022)
Tai, W., Kung, H., Dong, X.L., Comiter, M., Kuo, C.F.: exBERT: extending pre-trained models with domain-specific vocabulary under constrained training resources. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 1433–1439 (2020)
Thomason, J., Shridhar, M., Bisk, Y., Paxton, C., Zettlemoyer, L.: Language grounding with 3D objects. In: Conference on Robot Learning, pp. 1691–1701. PMLR (2022)
Todorov, E., Erez, T., Tassa, Y.: MuJoCo: a physics engine for model-based control. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5026–5033. IEEE (2012)
Wang, Z., Liang, J., He, R., Xu, N., Wang, Z., Tan, T.: Improving zero-shot generalization for CLIP with synthesized prompts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3032–3042 (2023)
Yagubbayli, F., Wang, Y., Tonioni, A., Tombari, F.: LegoFormer: transformers for block-by-block multi-view 3D reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.12102 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Gong, Z., Chang, A.X.: Multi3DRefer: grounding text description to multiple 3D objects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15225–15236 (2023)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF under Grant Number GZC20232292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, P. et al. (2025). Multi-task Domain Adaptation for Language Grounding with 3D Objects. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15092. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72754-2_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72754-2_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72753-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72754-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)