Abstract
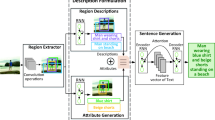
Region-level captioning is challenged by the caption degeneration issue, which refers to that pre-trained multimodal models tend to predict the most frequent captions but miss the less frequent ones. In this study, we propose a controllable region-level captioning (ControlCap) approach, which introduces control words to a multimodal model to address the caption degeneration issue. In specific, ControlCap leverages a discriminative module to generate control words within the caption space to partition it to multiple sub-spaces. The multimodal model is constrained to generate captions within a few sub-spaces containing the control words, which increases the opportunity of hitting less frequent captions, alleviating the caption degeneration issue. Furthermore, interactive control words can be given by either a human or an expert model, which enables captioning beyond the training caption space, enhancing the model’s generalization ability. Extensive experiments on Visual Genome and RefCOCOg datasets show that ControlCap respectively improves the CIDEr score by 21.6 and 2.2, outperforming the state-of-the-arts by significant margins. Code is available at https://github.com/callsys/ControlCap.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Introducing ChatGPT (2022). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Alayrac, J., et al.: Flamingo: a visual language model for few-shot learning. In: NeurIPS (2022)
Brown, T.B., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Carlsson, F., Öhman, J., Liu, F., Verlinden, S., Nivre, J., Sahlgren, M.: Fine-grained controllable text generation using non-residual prompting. In: ACL, pp. 6837–6857 (2022)
Chen, J., et al.: MiniGPT-V2: large language model as a unified interface for vision-language multi-task learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.09478 (2023)
Chen, K., Zhang, Z., Zeng, W., Zhang, R., Zhu, F., Zhao, R.: Shikra: unleashing multimodal llm’s referential dialogue magic. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.15195 (2023)
Chung, H.W., et al.: Scaling instruction-finetuned language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.11416 (2022)
Dai, W., et al.: InstructBLIP: towards general-purpose vision-language models with instruction tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06500 (2023)
Dathathri, S., et al.: Plug and play language models: a simple approach to controlled text generation. In: ICLR (2020)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Devlin, J., Chang, M., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Burstein, J., Doran, C., Solorio, T. (eds.) NAACL, pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Ding, N., Deng, C., Tan, M., Du, Q., Ge, Z., Wu, Q.: Image captioning with controllable and adaptive length levels. IEEE TPAMI 764–779 (2024)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16\(\times \)16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: ICLR (2021)
Fan, A., Lewis, M., Dauphin, Y.N.: Hierarchical neural story generation. In: Gurevych, I., Miyao, Y. (eds.) ACL, pp. 889–898 (2018)
Fang, Y., et al.: EVA: exploring the limits of masked visual representation learning at scale. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 19358–19369 (2023)
Guo, Q., et al.: RegionGPT: towards region understanding vision language model (2024)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.: Mask R-CNN. In: IEEE ICCV, pp. 2961–2969 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1735–1780 (1997)
Hu, Y., Hua, H., Yang, Z., Shi, W., Smith, N.A., Luo, J.: PromptCap: prompt-guided image captioning for VQA with GPT-3. In: IEEE ICCV, pp. 2963–2975 (2023)
Huang, X., et al.: Segment and caption anything (2024). https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00869
Huang, X., et al.: Tag2Text: guiding vision-language model via image tagging. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.05657 (2023)
Johnson, J., Karpathy, A., Fei-Fei, L.: DenseCap: fully convolutional localization networks for dense captioning. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 4565–4574 (2016)
Karatzas, D., et al.: ICDAR 2015 competition on robust reading. In: IEEE ICDAR, pp. 1156–1160 (2015)
Kirillov, A., et al.: Segment anything. In: IEEE ICCV, pp. 4015–4026 (2023)
Krishna, R., et al.: Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. IJCV 32–73 (2017)
Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., Hoi, S.C.H.: BLIP-2: bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In: ICML, pp. 19730–19742 (2023)
Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.C.H.: BLIP: bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In: ICML, pp. 12888–12900 (2022)
Li, P., Zhang, H., Liu, X., Shi, S.: Rigid formats controlled text generation. In: ACL (2020)
Li, X., Thickstun, J., Gulrajani, I., Liang, P., Hashimoto, T.B.: Diffusion-LM improves controllable text generation. In: NeurIPS (2022)
Li, X., Jiang, S., Han, J.: Learning object context for dense captioning. In: AAAI, pp. 8650–8657 (2019)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Liu, H., Li, C., Wu, Q., Lee, Y.J.: Visual instruction tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08485 (2023)
Liu, R., Jia, C., Wei, J., Xu, G., Wang, L., Vosoughi, S.: Mitigating political bias in language models through reinforced calibration. In: AAAI, pp. 14857–14866 (2021)
Liu, S., Zhang, L., Yang, X., Su, H., Zhu, J.: Query2Label: a simple transformer way to multi-label classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.10834 (2021)
Long, Y., et al.: CapDet: Unifying dense captioning and open-world detection pretraining. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 15233–15243 (2023)
Peng, Z., et al.: Kosmos-2: grounding multimodal large language models to the world. In: ICLR (2024)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: ICML, pp. 8748–8763 (2021)
Rasheed, H., et al.: GLaMM: pixel grounding large multimodal model. In: IEEE CVPR (2024)
Ridnik, T., et al.: Asymmetric loss for multi-label classification. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 82–91 (2021)
Shao, S., et al.: Objects365: a large-scale, high-quality dataset for object detection. In: IEEE ICCV, pp. 8430–8439 (2019)
Shao, Z., Han, J., Debattista, K., Pang, Y.: DCMSTRD: end-to-end dense captioning via multi-scale transformer decoding. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 1–13 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2024.3369863
Shao, Z., Han, J., Marnerides, D., Debattista, K.: Region-object relation-aware dense captioning via transformer. IEEE TNNLS (2022)
Song, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, W., Liu, T.: Bob: BERT over BERT for training persona-based dialogue models from limited personalized data. In: ACL, pp. 167–177 (2021)
Sun, Z., et al.: Alpha-clip: a clip model focusing on wherever you want. In: IEEE CVPR (2024)
Touvron, H., et al.: LLaMA: open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971 (2023)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Wang, T., et al.: Caption anything: interactive image description with diverse multimodal controls. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.02677 (2023)
Wang, W., et al.: The all-seeing project: towards panoptic visual recognition and understanding of the open world. In: ICLR (2024)
Wu, J., et al.: GRiT: a generative region-to-text transformer for object understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.00280 (2022)
Yang, L., Tang, K., Yang, J., Li, L.J.: Dense captioning with joint inference and visual context. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 2193–2202 (2017)
Yin, G., Sheng, L., Liu, B., Yu, N., Wang, X., Shao, J.: Context and attribute grounded dense captioning. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 6241–6250 (2019)
Yu, L., Poirson, P., Yang, S., Berg, A.C., Berg, T.L.: Modeling context in referring expressions. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9906, pp. 69–85. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_5
Yu, L., Tan, H., Bansal, M., Berg, T.L.: A joint speaker-listener-reinforcer model for referring expressions. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 7282–7290 (2017)
Yu, Q., et al.: CapsFusion: rethinking image-text data at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.20550 (2023)
Yuan, Y., et al.: Osprey: pixel understanding with visual instruction tuning. In: IEEE CVPR (2024)
Zhang, H., Song, H., Li, S., Zhou, M., Song, D.: A survey of controllable text generation using transformer-based pre-trained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.05337 (2022)
Zhang, S., et al.: GPT4RoI: Instruction tuning large language model on region-of-interest. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.03601 (2023)
Zhang, S., et al.: OPT: open pre-trained transformer language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.01068 (2022)
Zhang, Y., et al.: Recognize anything: a strong image tagging model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.03514 (2023)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (E2ET1104, E3ET6201X2), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant 62225208 and 62171431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, Y. et al. (2025). ControlCap: Controllable Region-Level Captioning. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15096. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72920-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72920-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72919-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72920-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)