Abstract
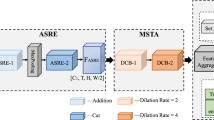
Gait recognition is a biometric technology that distinguishes individuals by their walking patterns. However, previous methods face challenges when accurately extracting identity features because they often become entangled with non-identity clues. To address this challenge, we propose CLTD, a causality-inspired discriminative feature learning module designed to effectively eliminate the influence of confounders in triple domains, i.e., spatial, temporal, and spectral. Specifically, we utilize the Cross Pixel-wise Attention Generator (CPAG) to generate attention distributions for factual and counterfactual features in spatial and temporal domains. Then, we introduce the Fourier Projection Head (FPH) to project spatial features into the spectral space, which preserves essential information while reducing computational costs. Additionally, we employ an optimization method with contrastive learning to enforce semantic consistency constraints across sequences from the same subject. Our approach has demonstrated significant performance improvements on challenging datasets, proving its effectiveness. Moreover, it can be seamlessly integrated into existing gait recognition methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, E.D., et al.: CEBaB: estimating the causal effects of real-world concepts on NLP model behavior. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 35, pp. 17582–17596 (2022)
Chai, T., Li, A., Zhang, S., Li, Z., Wang, Y.: Lagrange motion analysis and view embeddings for improved gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 20249–20258 (2022)
Chao, H., He, Y., Zhang, J., Feng, J.: GaitSet: regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 8126–8133 (2019)
Chen, J., Gao, Z., Wu, X., Luo, J.: Meta-causal learning for single domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7683–7692 (2023)
Ding, S., Feng, F., He, X., Liao, Y., Shi, J., Zhang, Y.: Causal incremental graph convolution for recommender system retraining. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth \(16\times 16\) words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Dou, H., Zhang, P., Su, W., Yu, Y., Li, X.: MetaGait: learning to learn an omni sample adaptive representation for gait recognition. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13665, pp. 357–374. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20065-6_21
Dou, H., Zhang, P., Su, W., Yu, Y., Lin, Y., Li, X.: GaitGCI: generative counterfactual intervention for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5578–5588 (2023)
Fan, C., Liang, J., Shen, C., Hou, S., Huang, Y., Yu, S.: OpenGait: revisiting gait recognition towards better practicality. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9707–9716 (2023)
Fan, C., et al.: GaitPart: temporal part-based model for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14225–14233 (2020)
Fu, Y., Meng, S., Hou, S., Hu, X., Huang, Y.: GPGait: generalized pose-based gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 19595–19604 (2023)
Guo, H., Ji, Q.: Physics-augmented autoencoder for 3D skeleton-based gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 19627–19638 (2023)
Guo, T., Liu, H., Chen, Z., Liu, M., Wang, T., Ding, R.: Contrastive learning from extremely augmented skeleton sequences for self-supervised action recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 762–770 (2022)
Gutmann, M., Hyvärinen, A.: Noise-contrastive estimation: a new estimation principle for unnormalized statistical models. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 297–304. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings (2010)
Han, J., Bhanu, B.: Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(2), 316–322 (2005)
Hermans, A., Beyer, L., Leibe, B.: In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737 (2017)
Hou, R., Chang, H., Ma, B., Huang, R., Shan, S.: BiCnet-TKS: learning efficient spatial-temporal representation for video person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2014–2023 (2021)
Hou, S., Cao, C., Liu, X., Huang, Y.: Gait lateral network: learning discriminative and compact representations for gait recognition. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12354, pp. 382–398. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_22
Huang, X., Wang, X., He, B., He, S., Liu, W., Feng, B.: Star: spatio-temporal augmented relation network for gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Biometrics Behav. Identity Sci. 5(1), 115–125 (2022)
Huang, X., et al.: Condition-adaptive graph convolution learning for skeleton-based gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2023)
Huang, X., et al.: Context-sensitive temporal feature learning for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12909–12918 (2021)
Huang, Z., et al.: 3D local convolutional neural networks for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14920–14929 (2021)
Huang, Z., Wang, X., Huang, L., Huang, C., Wei, Y., Liu, W.: CCNet: criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 603–612 (2019)
Lee, B.K., Kim, J., Ro, Y.M.: Mitigating adversarial vulnerability through causal parameter estimation by adversarial double machine learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4499–4509 (2023)
Lee, S., Bae, J., Kim, H.Y.: Decompose, adjust, compose: effective normalization by playing with frequency for domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11776–11785 (2023)
Li, C., et al.: Embedding Fourier for ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement. In: ICLR (2023)
Li, X., Makihara, Y., Xu, C., Yagi, Y., Ren, M.: Gait recognition via semi-supervised disentangled representation learning to identity and covariate features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13309–13319 (2020)
Li, X., et al.: Causally-aware intraoperative imputation for overall survival time prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15681–15690 (2023)
Lin, B., Zhang, S., Yu, X.: Gait recognition via effective global-local feature representation and local temporal aggregation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14648–14656 (2021)
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., Black, M.J.: SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(6) (2015)
Ma, K., Fu, Y., Zheng, D., Cao, C., Hu, X., Huang, Y.: Dynamic aggregated network for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22076–22085 (2023)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11) (2008)
Mao, X., Liu, Y., Liu, F., Li, Q., Shen, W., Wang, Y.: Intriguing findings of frequency selection for image deblurring. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1905–1913 (2023)
Miao, J., Chen, C., Liu, F., Wei, H., Heng, P.A.: CauSSL: causality-inspired semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21426–21437 (2023)
van den Oord, A., Li, Y., Vinyals, O.: Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748 (2018)
Paszke, A., et al.: PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Pearl, J., Glymour, M., Jewell, N.P.: Causal Inference in Statistics: A Primer. Wiley, Hoboken (2016)
Quan, S., Hirano, M., Yamakawa, Y.: Semantic information in contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5686–5696 (2023)
Rao, H., Miao, C.: TranSG: transformer-based skeleton graph prototype contrastive learning with structure-trajectory prompted reconstruction for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22118–22128 (2023)
Sarkar, S., Phillips, P.J., Liu, Z., Vega, I.R., Grother, P., Bowyer, K.W.: The humanid gait challenge problem: data sets, performance, and analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(2), 162–177 (2005)
Shen, C., Yu, S., Wang, J., Huang, G.Q., Wang, L.: A comprehensive survey on deep gait recognition: algorithms, datasets and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.13732 (2022)
Shiraga, K., Makihara, Y., Muramatsu, D., Echigo, T., Yagi, Y.: GEINet: view-invariant gait recognition using a convolutional neural network. In: 2016 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2016)
Takemura, N., Makihara, Y., Muramatsu, D., Echigo, T., Yagi, Y.: Multi-view large population gait dataset and its performance evaluation for cross-view gait recognition. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 10, 1–14 (2018)
Tang, K., Niu, Y., Huang, J., Shi, J., Zhang, H.: Unbiased scene graph generation from biased training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3716–3725 (2020)
Teepe, T., Gilg, J., Herzog, F., Hörmann, S., Rigoll, G.: Towards a deeper understanding of skeleton-based gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1569–1577 (2022)
Teepe, T., Khan, A., Gilg, J., Herzog, F., Hörmann, S., Rigoll, G.: GaitGraph: graph convolutional network for skeleton-based gait recognition. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2314–2318. IEEE (2021)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Wang, J., et al.: Causal intervention for sparse-view gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 77–85 (2023)
Wang, L., Liu, B., Liang, F., Wang, B.: Hierarchical spatio-temporal representation learning for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 19639–19649 (2023)
Wang, M., et al.: DyGait: exploiting dynamic representations for high-performance gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 13424–13433 (2023)
Yang, X., Zhang, H., Qi, G., Cai, J.: Causal attention for vision-language tasks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9847–9857 (2021)
Yang, Z., Lin, M., Zhong, X., Wu, Y., Wang, Z.: Good is bad: causality inspired cloth-debiasing for cloth-changing person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1472–1481 (2023)
Yu, S., Tan, D., Tan, T.: A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In: 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2006), vol. 4, pp. 441–444. IEEE (2006)
Zhang, C., Chen, X.P., Han, G.Q., Liu, X.J.: Spatial transformer network on skeleton-based gait recognition. Expert Syst. e13244 (2023)
Zhang, Q.: Probabilistic reasoning based on dynamic causality trees/diagrams. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 46(3), 209–220 (1994)
Zhao, Z., Wang, D., Zhao, X.: Movement enhancement toward multi-scale video feature representation for temporal action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13555–13564 (2023)
Zheng, J., et al.: Gait recognition in the wild with multi-hop temporal switch. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 6136–6145 (2022)
Zheng, J., Liu, X., Liu, W., He, L., Yan, C., Mei, T.: Gait recognition in the wild with dense 3D representations and a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 20228–20237 (2022)
Zhou, M., Huang, J., Guo, C.L., Li, C.: Fourmer: an efficient global modeling paradigm for image restoration. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 42589–42601. PMLR (2023)
Zhu, Z., et al.: Gait recognition in the wild: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14789–14799 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under project 2023YFF0905401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiong, H., Feng, B., Wang, X., Liu, W. (2025). Causality-Inspired Discriminative Feature Learning in Triple Domains for Gait Recognition. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15112. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72949-2_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72949-2_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72948-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72949-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)