Abstract
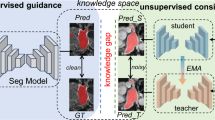
Despite the recent success of domain generalization in medical image segmentation, voxel-wise annotation for all source domains remains a huge burden. Semi-supervised domain generalization has been proposed very recently to combat this challenge by leveraging limited labeled data along with abundant unlabeled data collected from multiple medical institutions, depending on precisely harnessing unlabeled data while improving generalization simultaneously. In this work, we observe that domain shifts between medical institutions cause disparate feature statistics, which significantly deteriorates pseudo-label quality due to an unexpected normalization process. Nevertheless, this phenomenon could be exploited to facilitate unseen domain generalization. Therefore, we propose 1) multiple statistics-individual branches to mitigate the impact of domain shifts for reliable pseudo-labels and 2) one statistics-aggregated branch for domain-invariant feature learning. Furthermore, to simulate unseen domains with statistics difference, we approach this from two aspects, i.e., a perturbation with histogram matching at image level and a random batch normalization selection strategy at feature level, producing diverse statistics to expand the training distribution. Evaluation results on three medical image datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method compared with recent SOTA methods. The code is available at https://github.com/qiumuyang/SIAB.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, W., et al.: Semi-supervised learning for network-based cardiac MR image segmentation. In: Descoteaux, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10434, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8_29
Bai, Y., Chen, D., Li, Q., Shen, W., Wang, Y.: Bidirectional copy-paste for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11514–11524 (2023)
Bernard, O., et al.: Deep learning techniques for automatic mri cardiac multi-structures segmentation and diagnosis: is the problem solved? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(11), 2514–2525 (2018)
Cai, H., Li, S., Qi, L., Yu, Q., Shi, Y., Gao, Y.: Orthogonal annotation benefits barely-supervised medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3302–3311 (2023)
Campello, V.M., et al.: Multi-centre, multi-vendor and multi-disease cardiac segmentation: the m &ms challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(12), 3543–3554 (2021)
Chen, J., et al.: Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Chen, X., Yuan, Y., Zeng, G., Wang, J.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross pseudo supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2613–2622 (2021)
Cheplygina, V., de Bruijne, M., Pluim, J.P.: Not-so-supervised: a survey of semi-supervised, multi-instance, and transfer learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 54, 280–296 (2019)
Dou, Q., Coelho de Castro, D., Kamnitsas, K., Glocker, B.: Domain generalization via model-agnostic learning of semantic features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32 (2019)
Guo, J., Qi, L., Shi, Y.: Domaindrop: suppressing domain-sensitive channels for domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 19114–19124 (2023)
Hu, S., Liao, Z., Zhang, J., Xia, Y.: Domain and content adaptive convolution based multi-source domain generalization for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42(1), 233–244 (2022)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 448–456. PMLR (2015)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on Challenges in Representation Learning, ICML, vol. 3, p. 896. Atlanta (2013)
Li, D., Yang, Y., Song, Y.Z., Hospedales, T.: Learning to generalize: meta-learning for domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Li, X., Yu, L., Chen, H., Fu, C.W., Xing, L., Heng, P.A.: Transformation-consistent self-ensembling model for semisupervised medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(2), 523–534 (2020)
Liu, Q., Chen, C., Qin, J., Dou, Q., Heng, P.A.: Feddg: federated domain generalization on medical image segmentation via episodic learning in continuous frequency space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1013–1023 (2021)
Liu, Q., Dou, Q., Heng, P.-A.: Shape-aware meta-learning for generalizing prostate MRI segmentation to unseen domains. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12262, pp. 475–485. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59713-9_46
Liu, X., Thermos, S., O’Neil, A., Tsaftaris, S.A.: Semi-supervised meta-learning with disentanglement for domain-generalised medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 307–317. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_29
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2019)
Luo, X., Chen, J., Song, T., Wang, G.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation through dual-task consistency. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 8801–8809 (2021)
Lyu, J., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Lin, L., Cheng, P., Tang, X.: Aadg: automatic augmentation for domain generalization on retinal image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 41(12), 3699–3711 (2022)
Miao, J., Chen, C., Liu, F., Wei, H., Heng, P.A.: Caussl: causality-inspired semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21426–21437 (2023)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Nam, H., Kim, H.E.: Batch-instance normalization for adaptively style-invariant neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 31 (2018)
Pizer, S.M., et al.: Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vision Graph. Image Process. 39(3), 355–368 (1987)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Seo, S., Suh, Y., Kim, D., Kim, G., Han, J., Han, B.: Learning to optimize domain specific normalization for domain generalization. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12367, pp. 68–83. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58542-6_5
Shi, Y., et al.: Inconsistency-aware uncertainty estimation for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 41(3), 608–620 (2021)
Sohn, K., et al.: Fixmatch: simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 596–608 (2020)
Su, Z., Yao, K., Yang, X., Huang, K., Wang, Q., Sun, J.: Rethinking data augmentation for single-source domain generalization in medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 37, pp. 2366–2374 (2023)
Tajbakhsh, N., Jeyaseelan, L., Li, Q., Chiang, J.N., Wu, Z., Ding, X.: Embracing imperfect datasets: a review of deep learning solutions for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 63, 101693 (2020)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, J., et al.: Generalizing to unseen domains: a survey on domain generalization. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 35, 8052–8072 (2022)
Wang, S., Yu, L., Li, K., Yang, X., Fu, C.W., Heng, P.A.: Dofe: domain-oriented feature embedding for generalizable fundus image segmentation on unseen datasets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(12), 4237–4248 (2020)
Wang, X., Zhang, J., Qi, L., Shi, Y.: Generalizable decision boundaries: dualistic meta-learning for open set domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 11564–11573 (2023)
Wang, Y., Xiao, B., Bi, X., Li, W., Gao, X.: Mcf: mutual correction framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15651–15660 (2023)
Wu, Y., Wu, Z., Wu, Q., Ge, Z., Cai, J.: Exploring smoothness and class-separation for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, pp. 34–43. Springer, Heidelberg (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_4
Wu, Y., Xu, M., Ge, Z., Cai, J., Zhang, L.: Semi-supervised left atrium segmentation with mutual consistency training. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 297–306. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_28
Yang, L., Qi, L., Feng, L., Zhang, W., Shi, Y.: Revisiting weak-to-strong consistency in semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7236–7246 (2023)
Yao, H., Hu, X., Li, X.: Enhancing pseudo label quality for semi-supervised domain-generalized medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 3099–3107 (2022)
Yu, L., Wang, S., Li, X., Fu, C.-W., Heng, P.-A.: Uncertainty-aware self-ensembling model for semi-supervised 3D left atrium segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 605–613. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_67
Yuan, J., Liu, Y., Shen, C., Wang, Z., Li, H.: A simple baseline for semi-supervised semantic segmentation with strong data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8229–8238 (2021)
Zhou, K., Loy, C.C., Liu, Z.: Semi-supervised domain generalization with stochastic stylematch. Int. J. Comput. Vision 1–11 (2023)
Zhou, Z., Qi, L., Shi, Y.: Generalizable medical image segmentation via random amplitude mixup and domain-specific image restoration. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 420–436. Springer, Heidelberg (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19803-8_25
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the NSFC Project (62222604, 62206052, 62192783), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation Project (BK20210224), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024M750424), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (020214380120), the State Key Laboratory Funds for Key Project (ZZKT2024A14), and Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2023MF037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qiu, M., Zhang, J., Qi, L., Yu, Q., Shi, Y., Gao, Y. (2025). The Devil Is in the Statistics: Mitigating and Exploiting Statistics Difference for Generalizable Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15112. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72949-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72949-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72948-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72949-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)