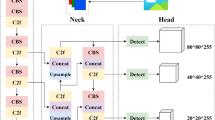
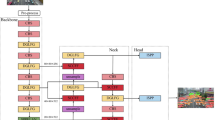
Abstract
Object detection in aerial images is a longstanding yet challenging task. Despite the significant advancements in recent years, most works still show unsatisfactory performance due to the scale variation of objects. A standard strategy to address this problem is multi-scale training, aiming to learn scale-invariant feature representations. Albeit achieving inspiring improvements, such a multi-scale strategy is impractical for real application as inference time increases considerably. Besides, the original images are resized to different scales and subsequently trained separately, lacking information interaction across different scales. This paper presents a novel method called multi-scale cross distillation (MSCD) to address the issues mentioned above. MSCD combines the merits of multi-scale training and knowledge distillation, enabling single-scale inference to achieve comparable or superior performance than multi-scale inference. Specifically, we first construct a parallel multi-branch architecture, in which each branch shares the same parameters yet takes images with different scales as input. Furthermore, we design an adaptive cross-scale distillation module that adaptively integrates the knowledge of different branches into one. Thus, the detectors trained with MSCD only require single-scale inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of MSCD. Without bells and whistles, MSCD can facilitate prevalent two-stage detectors to outperform corresponding single-scale models by \(\sim \)5 and \(\sim \)7 mAP improvement on DOTA and DIOR-R datasets, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
It is worth noting that the RPN only predicts foreground and background, which does not make predictions for all categories. Thus, for each prediction of RPN, \(y_i^{m, R}=[c_i^{m, R}, b_i^{m, R}]\in \mathbb {R}^{2+5}\).
- 2.
In this paper, we use the gray font to indicate that variables do not participate in gradient back-propagation.
- 3.
When conducting multi-scale training and testing, the original images are first resized to three scales, i.e., (0.5, 1.0, 1.5), which are then cropped to 1,024 \(\times \) 1,024 patches with a stride of 524.
References
Ahn, S., Hu, S.X., Damianou, A., Lawrence, N.D., Dai, Z.: Variational information distillation for knowledge transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9155–9163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00938
Blaschke, T.: Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 65(1), 2–16 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2009.06.004
Blaschke, T., et al.: Geographic object-based image analysis - towards a new paradigm. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 87, 180–191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.09.014
Burochin, J.P., Vallet, B., Brédif, M., Mallet, C., Brosset, T., Paparoditis, N.: Detecting blind building façades from highly overlapping wide angle aerial imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 96, 193–209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.07.011
Cai, Z., Vasconcelos, N.: Cascade R-CNN: delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6154–6162 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00644
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12346, pp. 213–229. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Chen, R., Ai, H., Shang, C., Chen, L., Zhuang, Z.: Learning lightweight pedestrian detector with hierarchical knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 1645–1649 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803079
Cheng, G., et al.: Anchor-free oriented proposal generator for object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3183022
Cheng, G., et al.: Dual-aligned oriented detector. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3149780
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20, 273–297 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022627411411
Dai, X., et al.: General instance distillation for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7838–7847 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00775
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 886–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177
Ding, J., Xue, N., Long, Y., Xia, G.S., Lu, Q.: Learning ROI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2844–2853 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00296
Ding, J., et al.: Object detection in aerial images: a large-scale benchmark and challenges. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(11), 7778–7796 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3117983
Duan, K., Bai, S., Xie, L., Qi, H., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Centernet: keypoint triplets for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6568–6577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00667
Fei-Fei, L., Perona, P.: A Bayesian hierarchical model for learning natural scene categories. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 524–531 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.16
Guo, Q., et al.: Online knowledge distillation via collaborative learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11017–11026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01103
Han, J., Ding, J., Li, J., Xia, G.S.: Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3062048
Han, J., Ding, J., Xue, N., Xia, G.S.: Redet: a rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2785–2794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00281
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hei, L., Jia, D.: Cornernet: detecting objects as paired keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision 128, 642–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01204-1
Heo, B., Kim, J., Yun, S., Park, H., Kwak, N., Choi, J.Y.: A comprehensive overhaul of feature distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1921–1930 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00201
Hinton, G., Salakhutdinov, R.: Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786), 504–507 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127647
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv e-prints (2015)
Hou, Y., Ma, Z., Liu, C., Loy, C.C.: Learning lightweight lane detection CNNs by self attention distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1013–1021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00110
Kim, K., Ji, B., Yoon, D., Hwang, S.: Self-knowledge distillation with progressive refinement of targets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6547–6556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00650
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105. Curran Associates Inc, Red Hook (2012)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Leitloff, J., Hinz, S., Stilla, U.: Vehicle detection in very high resolution satellite images of city areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 48(7), 2795–2806 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2010.2043109
Li, F., Zhang, H., Liu, S., Guo, J., Ni, L.M., Zhang, L.: DN-DETR: accelerate DETR training by introducing query denoising. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13609–13617 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01325
Li, Q., Jin, S., Yan, J.: Mimicking very efficient network for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7341–7349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.776
Li, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, N., Zhang, Z.X.: Scale-aware trident networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6053–6062 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00615
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 936–944 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(2), 318–327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826
Liu, S., et al.: DAB-DETR: dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for DETR. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2022)
Liu, S., Qi, L., Qin, H., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8759–8768 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00913
Liu, W., et al.: SSD: single shot MultiBox detector. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
Liu, W., Zhang, T., Huang, S., Li, K.: A hybrid optimization framework for UAV reconnaissance mission planning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 173, 108653 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2022.108653
Lowe, D.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision 60, 91–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Ma, J., et al.: Arbitrary-oriented scene text detection via rotation proposals. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 20(11), 3111–3122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2018.2818020
Ma, T., Tian, W., Xie, Y.: Multi-level knowledge distillation for low-resolution object detection and facial expression recognition. Knowl.-Based Syst. 240, 108136 (2022)
Nguyen, C.H., Nguyen, T.C., Tang, T.N., Phan, N.L.H.: Improving object detection by label assignment distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 1322–1331 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV51458.2022.00139
Osco, L.P., et al.: A CNN approach to simultaneously count plants and detect plantation-rows from UAV imagery. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 174, 1–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.01.024
Park, W., Kim, D., Lu, Y., Cho, M.: Relational knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3962–3971 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00409
Qi, L., et al.: Multi-scale aligned distillation for low-resolution detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14438–14448 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01421
Qian, W., Yang, X., Peng, S., Yan, J., Guo, Y.: Learning modulated loss for rotated object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 2458–2466 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i3.16347
Qian, W., Yang, X., Peng, S., Zhang, X., Yan, J.: RSDet++: point-based modulated loss for more accurate rotated object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(11), 7869–7879 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3186070
Qiao, S., Chen, L.C., Yuille, A.: Detectors: detecting objects with recursive feature pyramid and switchable atrous convolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10208–10219 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01008
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 779–788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolo9000: better, faster, stronger. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6517–6525 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.690
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Salvoldi, M., Cohen-Zada, A.L., Karnieli, A.: Using the venus super-spectral camera for detecting moving vehicles. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 192, 33–48 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.08.005
Singh, B., Davis, L.S.: An analysis of scale invariance in object detection - snip. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3578–3587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00377
Singh, B., Najibi, M., Davis, L.S.: Sniper: Efficient multi-scale training. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31 (2018). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/file/166cee72e93a992007a89b39eb29628b-Paper.pdf
Wang, T., Yuan, L., Zhang, X., Feng, J.: Distilling object detectors with fine-grained feature imitation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4928–4937 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00507
Xia, G.S., et al.: DOTA: a large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3974–3983 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00418
Xie, X., Cheng, G., Wang, J., Yao, X., Han, J.: Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3500–3509 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00350
Xu, G., Liu, Z., Li, X., Loy, C.C.: Knowledge distillation meets self-supervision. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 588–604 (2020)
Xu, Y., et al.: Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(4), 1452–1459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2974745
Yang, X., Yan, J., Feng, Z., He, T.: R3DET: refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 3163–3171 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i4.16426
Yang, X., Hou, L., Zhou, Y., Wang, W., Yan, J.: Dense label encoding for boundary discontinuity free rotation detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15814–15824 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01556
Yang, X., Yan, J.: Arbitrary-oriented object detection with circular smooth label. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12353, pp. 677–694. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58598-3_40
Yang, X., Yan, J., Ming, Q., Wang, W., Zhang, X., Tian, Q.: Rethinking rotated object detection with gaussian Wasserstein distance loss. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 139, pp. 11830–11841 (2021). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/yang21l.html
Yang, X., et al.: Learning high-precision bounding box for rotated object detection via kullback-leibler divergence. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 18381–18394 (2021). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/file/98f13708210194c475687be6106a3b84-Paper.pdf
Yang, X., et al.: The KFIoU Loss for Rotated Object Detection. arXiv e-prints arXiv:2201.12558 (2022)
Yang, Z., Liu, S., Hu, H., Wang, L., Lin, S.: Reppoints: point set representation for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9656–9665 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00975
Yang, Z., et al.: Focal and global knowledge distillation for detectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4633–4642 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00460
Yu, Y., Da, F.: Phase-shifting coder: predicting accurate orientation in oriented object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13354–13363 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01283
Zhang, H., et al.: DINO: DETR with Improved DeNoising Anchor Boxes for End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv e-prints (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.03605
Zhang, L., Ma, K.: Structured knowledge distillation for accurate and efficient object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(12), 15706–15724 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3300470
Zhang, T., et al.: Balance learning for ship detection from synthetic aperture radar remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 182, 190–207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.10.010
Zhang, Y., Xiang, T., Hospedales, T.M., Lu, H.: Deep mutual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4320–4328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00454
Zhao, F., Xia, L., Kylling, A., Li, R., Shang, H., Xu, M.: Detection flying aircraft from landsat 8 oli data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 141, 176–184 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.05.001
Zheng, Z., et al.: Localization distillation for object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(8), 10070–10083 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3248583
Zhou, Y., et al.: Mmrotate: a rotated object detection benchmark using pytorch. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 7331–7334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3503161.3548541
Zhu, J., et al.: Complementary relation contrastive distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9256–9265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00914
Zhu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., Li, B., Wang, X., Dai, J.: Deformable DETR: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
Zhu, Y., et al.: Scalekd: distilling scale-aware knowledge in small object detector. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 19723–19733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01889
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 12302252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, K., Wang, Z., Li, Z., Teng, X., Li, Y. (2025). Multi-Scale Cross Distillation for Object Detection in Aerial Images. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15107. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72967-6_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72967-6_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72966-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72967-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)