Abstract
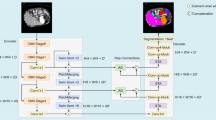
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) has achieved remarkable successes in the realm of natural image segmentation, but its deployment in the medical imaging sphere has encountered challenges. Specifically, the model struggles with medical images that feature low contrast, faint boundaries, intricate morphologies, and small-sized objects. To address these challenges and enhance SAM’s performance in the medical domain, we introduce a comprehensive modification. Firstly, we incorporate a frozen Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) branch as an image encoder, which synergizes with SAM’s original Vision Transformer (ViT) encoder through a novel variational attention fusion module. This integration bolsters the model’s capability to capture local spatial information, which is often paramount in medical imagery. Moreover, to further optimize SAM for medical imaging, we introduce feature and position adapters within the ViT branch, refining the encoder’s representations. We see that compared to current prompting strategies to fine-tune SAM for ultrasound medical segmentation, the use of text descriptions that serve as text prompts for SAM helps significantly improve the performance. Leveraging ChatGPT’s natural language understanding capabilities, we generate prompts that offer contextual information and guidance to SAM, enabling it to better understand the nuances of ultrasound medical images and improve its segmentation accuracy. Our method, in its entirety, represents a significant stride towards making universal image segmentation models more adaptable and efficient in the medical domain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dhabyani, W., Gomaa, M., Khaled, H., Aly, F.: Deep learning approaches for data augmentation and classification of breast masses using ultrasound images. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 10(5), 1–11 (2019)
Alemi, A.A., Fischer, I., Dillon, J.V., Murphy, K.: Deep variational information bottleneck. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.00410 (2016)
Byra, M., et al.: Breast mass segmentation in ultrasound with selective kernel U-Net convolutional neural network. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 61, 102027 (2020)
Cao, H., et al.: Swin-UNet: UNet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds.) Computer Vision, ECCV 2022 Workshops. LNCS, vol. 13803, pp. 205–218. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25066-8_9
Chen, G., Li, L., Dai, Y., Zhang, J., Yap, M.H.: AAU-Net: an adaptive attention U-Net for breast lesions segmentation in ultrasound images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42(5), 1289–1300 (2022)
Chen, J., et al.: TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Chen, L., Bentley, P., Mori, K., Misawa, K., Fujiwara, M., Rueckert, D.: DRINet for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(11), 2453–2462 (2018)
Degerli, A., Kiranyaz, S., Hamid, T., Mazhar, R., Gabbouj, M.: Early myocardial infarction detection over multi-view echocardiography. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 87, 105448 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105448
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16\(\times \)16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Ermis, B., Zappella, G., Wistuba, M., Rawal, A., Archambeau, C.: Continual learning with transformers for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3774–3781 (2022)
Feng, S., et al.: CPFNet: context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(10), 3008–3018 (2020)
Gao, P., et al.: CLIP-Adapter: better vision-language models with feature adapters. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 132(2), 581–595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01891-x
Gao, P., et al.: LLaMA-Adapter V2: parameter-efficient visual instruction model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.15010 (2023)
Gong, H., Chen, J., Chen, G., Li, H., Li, G., Chen, F.: Thyroid region prior guided attention for ultrasound segmentation of thyroid nodules. Comput. Biol. Med. 155, 106389 (2023)
Gowda, S.N.: Human activity recognition using combinatorial deep belief networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 1–6 (2017)
Gowda, S.N., Arnab, A., Huang, J.: Optimizing ViViT training: time and memory reduction for action recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04822 (2023)
Gowda, S.N., Gao, B., Clifton, D.: FE-Adapter: adapting image-based emotion classifiers to videos (2024)
Gowda, S.N., Rohrbach, M., Sevilla-Lara, L.: Smart frame selection for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 1451–1459 (2021)
Gowda, S.N., Yuan, C.: ColorNet: investigating the importance of color spaces for image classification. In: Jawahar, C.V., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K. (eds.) ACCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11364, pp. 581–596. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20870-7_36
Gu, R., et al.: CA-Net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(2), 699–711 (2020)
Gu, Z., et al.: CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(10), 2281–2292 (2019)
Hatamizadeh, A., et al.: UNETR: transformers for 3D medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 574–584 (2022)
He, A., Wang, K., Li, T., Du, C., Xia, S., Fu, H.: H2Former: an efficient hierarchical hybrid transformer for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42(9), 2763–2775 (2023)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
He, S., Bao, R., Li, J., Grant, P.E., Ou, Y.: Accuracy of segment-anything model (SAM) in medical image segmentation tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09324 (2023)
Houlsby, N., et al.: Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2790–2799. PMLR (2019)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Huang, X., Deng, Z., Li, D., Yuan, X.: MISSFormer: an effective medical image segmentation transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.07162 (2021)
Huang, Y., et al.: Segment anything model for medical images? arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14660 (2023)
Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114 (2013)
Kirillov, A., et al.: Segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643 (2023)
Smistad, E., et al.: Deep learning for segmentation using an open large-scale dataset in 2D echocardiography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(9), 2198–2210 (2019)
Lin, X., Xiang, Y., Zhang, L., Yang, X., Yan, Z., Yu, L.: SAMUS: adapting segment anything model for clinically-friendly and generalizable ultrasound image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.06824 (2023)
Liu, S., et al.: Grounding DINO: marrying DINO with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.05499 (2023)
Liu, X., Song, L., Liu, S., Zhang, Y.: A review of deep-learning-based medical image segmentation methods. Sustainability 13(3), 1224 (2021)
Luo, Z., Hu, Z., Xi, Y., Zhang, R., Ma, J.: I-Tuning: tuning frozen language models with image for lightweight image captioning. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), ICASSP 2023, pp. 1–5. IEEE (2023)
Ma, J., Wang, B.: Segment anything in medical images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12306 (2023)
Mei, X., et al.: RadImageNet: an open radiologic deep learning research dataset for effective transfer learning. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 4(5), e210315 (2022)
OpenAI: GPT-4 technical report (2023)
Pan, J., Lin, Z., Zhu, X., Shao, J., Li, H.: ST-Adapter: parameter-efficient image-to-video transfer learning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 26462–26477 (2022)
Pedraza, L., Vargas, C., Narváez, F., Durán, O., Muñoz, E., Romero, E.: An open access thyroid ultrasound image database. In: 10th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, vol. 9287, pp. 188–193. SPIE (2015)
Pfeiffer, J., et al.: AdapterHub: a framework for adapting transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.07779 (2020)
Pham, D.L., Xu, C., Prince, J.L.: Current methods in medical image segmentation. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2(1), 315–337 (2000)
Rasmy, L., Xiang, Y., Xie, Z., Tao, C., Zhi, D.: Med-BERT: pretrained contextualized embeddings on large-scale structured electronic health records for disease prediction. npj Dig. Med. 4(1), 86 (2021)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Roy, S., et al.: SAM.MD: zero-shot medical image segmentation capabilities of the segment anything model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05396 (2023)
Sung, Y.L., Cho, J., Bansal, M.: VL-Adapter: parameter-efficient transfer learning for vision-and-language tasks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5227–5237 (2022)
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Patel, V.M.: UNeXt: MLP-based rapid medical image segmentation network. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13435, pp. 23–33. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_3
Wang, Y., Mukherjee, S., Liu, X., Gao, J., Awadallah, A.H., Gao, J.: AdaMix: mixture-of-adapter for parameter-efficient tuning of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12410 (2022)
Wu, H., Chen, S., Chen, G., Wang, W., Lei, B., Wen, Z.: FAT-Net: feature adaptive transformers for automated skin lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 76, 102327 (2022)
Wu, J., et al.: Medical SAM Adapter: adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12620 (2023)
Wunderling, T., Golla, B., Poudel, P., Arens, C., Friebe, M., Hansen, C.: Comparison of thyroid segmentation techniques for 3D ultrasound. In: Medical Imaging 2017: Image Processing, vol. 10133, pp. 346–352. SPIE (2017)
Zhang, K., Liu, D.: Customized segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.13785 (2023)
Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Hu, Q.: TransFuse: fusing transformers and CNNs for medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 14–24. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_2
Zheng, S., et al.: Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6881–6890 (2021)
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Acknowledgements
DAC was supported by the Pandemic Sciences Institute at the University of Oxford; the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC); an NIHR Research Professorship; a Royal Academy of Engineering Research Chair; the Wellcome Trust funded VITAL project (grant 204904/Z/16/Z); the EPSRC (grant EP/W031744/1); and the InnoHK Hong Kong Centre for Cerebro-cardiovascular Engineering (COCHE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gowda, S.N., Clifton, D.A. (2025). CC-SAM: SAM with Cross-Feature Attention and Context for Ultrasound Image Segmentation. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15103. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72995-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72995-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-72994-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-72995-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)