Abstract
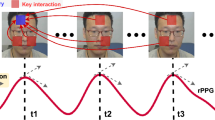
Scene representation networks, or implicit neural representations (INR) have seen a range of success in numerous image and video applications. However, being universal function fitters, they fit all variations in videos without any selectivity. This is particularly a problem for tasks such as remote plethysmography, the extraction of heart rate information from face videos. As a result of low native signal to noise ratio, previous signal processing techniques suffer from poor performance, while previous learning-based methods have improved performance but suffer from hallucinations that mitigate generalizability. Directly applying prior INRs cannot remedy this signal strength deficit, since they fit to both the signal as well as interfering factors. In this work, we introduce an INR framework that increases this plethysmograph signal strength. Specifically, we leverage architectures to have selective representation capabilities. We are able to decompose the face video into a blood plethysmograph component, and a face appearance component. By inferring the plethysmograph signal from this blood component, we show state-of-the-art performance on out-of-distribution samples without sacrificing performance for in-distribution samples. We implement our framework on a custom-built multiresolution hash encoding backbone to enable practical dataset-scale representations through a 50x speed-up over traditional INRs. We also present a dataset of optically challenging out-of-distribution scenes to test generalization to real-world scenarios. Code and data may be found at https://implicitppg.github.io/.
P. Chari and A. B. Harish—Contributed Equally.
A. B. Harish and A. Armouti—Work done when at UCLA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Baselines are configured, where possible, using the toolbox from [23].
References
Al Masri, A., Jasra, S.K.: The forensic biometric analysis of emotions from facial expressions, and physiological processes from the heart and skin. J. Emerg. Forensic Sci. Res. 1(1), 61–77 (2016)
Association CT: Physical activity monitoring for heart rate, ANSI/CTA-2065 (2018)
Ba, Y., Wang, Z., Karinca, K.D., Bozkurt, O.D., Kadambi, A.: Overcoming difficulty in obtaining dark-skinned subjects for remote-PPG by synthetic augmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.06007 (2021)
Balakrishnan, G., Durand, F., Guttag, J.: Detecting pulse from head motions in video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3430–3437 (2013)
Chari, P., Ba, Y., Athreya, S., Kadambi, A.: MIME: minority inclusion for majority group enhancement of AI performance. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13673, pp. 326–343. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19778-9_19
Chari, P., et al.: Diverse R-PPG: camera-based heart rate estimation for diverse subject skin-tones and scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.12769 (2020)
Chen, H., He, B., Wang, H., Ren, Y., Lim, S.N., Shrivastava, A.: NeRV: Neural representations for videos. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 21557–21568 (2021)
Chen, W., McDuff, D.: DeepPhys: video-based physiological measurement using convolutional attention networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 349–365 (2018)
Chen, Z., et al.: VideoINR: learning video implicit neural representation for continuous space-time super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2047–2057 (2022)
Chen, Z., Zheng, T., Cai, C., Luo, J.: MoVi-Fi: motion-robust vital signs waveform recovery via deep interpreted RF sensing. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, pp. 392–405 (2021)
De Haan, G., Jeanne, V.: Robust pulse rate from chrominance-based RPPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(10), 2878–2886 (2013)
Del Regno, K., et al.: Thermal imaging and radar for remote sleep monitoring of breathing and apnea. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.11936 (2024)
Gao, C., Saraf, A., Kopf, J., Huang, J.B.: Dynamic view synthesis from dynamic monocular video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5712–5721 (2021)
Hurter, C., McDuff, D.: Cardiolens: remote physiological monitoring in a mixed reality environment. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2017 Emerging Technologies, pp. 1–2 (2017)
Jiang, C., et al.: Local implicit grid representations for 3D scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6001–6010 (2020)
Kadambi, A.: Achieving fairness in medical devices. Science 372(6537), 30–31 (2021)
Lee, E., Chen, E., Lee, C.-Y.: Meta-rPPG: remote heart rate estimation using a transductive meta-learner. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12372, pp. 392–409. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58583-9_24
Li, R., Tancik, M., Kanazawa, A.: NerfAcc: a general nerf acceleration toolbox. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04847 (2022)
Li, Z., Niklaus, S., Snavely, N., Wang, O.: Neural scene flow fields for space-time view synthesis of dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6498–6508 (2021)
Lindell, D.B., Van Veen, D., Park, J.J., Wetzstein, G.: Bacon: band-limited coordinate networks for multiscale scene representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16252–16262 (2022)
Liu, X., Fromm, J., Patel, S., McDuff, D.: Multi-task temporal shift attention networks for on-device contactless vitals measurement. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 19400–19411 (2020)
Liu, X., Hill, B., Jiang, Z., Patel, S., McDuff, D.: EfficientPhys: enabling simple, fast and accurate camera-based cardiac measurement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 5008–5017 (2023)
Liu, X., et al.: Deep physiological sensing toolbox. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.00716 (2022)
Magdalena Nowara, E., Marks, T.K., Mansour, H., Veeraraghavan, A.: SparsePPG: towards driver monitoring using camera-based vital signs estimation in near-infrared. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 1272–1281 (2018)
Mai, L., Liu, F.: Motion-adjustable neural implicit video representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10738–10747 (2022)
Maity, A.K., Wang, J., Sabharwal, A., Nayar, S.K.: RobustPPG: camera-based robust heart rate estimation using motion cancellation. Biomed. Opt. Express 13(10), 5447–5467 (2022)
Martel, J.N., Lindell, D.B., Lin, C.Z., Chan, E.R., Monteiro, M., Wetzstein, G.: Acorn: adaptive coordinate networks for neural scene representation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.02788 (2021)
Mehta, I., Gharbi, M., Barnes, C., Shechtman, E., Ramamoorthi, R., Chandraker, M.: Modulated periodic activations for generalizable local functional representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14214–14223 (2021)
Mildenhall, B., Hedman, P., Martin-Brualla, R., Srinivasan, P.P., Barron, J.T.: NeRF in the dark: high dynamic range view synthesis from noisy raw images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16190–16199 (2022)
Mildenhall, B., Srinivasan, P.P., Tancik, M., Barron, J.T., Ramamoorthi, R., Ng, R.: NeRF: representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 65(1), 99–106 (2021)
Monitors, C.: Heart rate meters, and alarms. ANSI/AAMI Standard EC13 (2002)
Müller, T., Evans, A., Schied, C., Keller, A.: Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. 41(4), 102:1–102:15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3528223.3530127
Nelson, B.W., Allen, N.B.: Accuracy of consumer wearable heart rate measurement during an ecologically valid 24-hour period: intraindividual validation study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 7(3), e10828 (2019)
Nießner, M., Zollhöfer, M., Izadi, S., Stamminger, M.: Real-time 3D reconstruction at scale using voxel hashing. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 32(6), 1–11 (2013)
Niu, X., Shan, S., Han, H., Chen, X.: RhythmNet: end-to-end heart rate estimation from face via spatial-temporal representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 2409–2423 (2019)
Nowara, E.M., McDuff, D., Veeraraghavan, A.: A meta-analysis of the impact of skin tone and gender on non-contact photoplethysmography measurements. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 284–285 (2020)
Nowara, E.M., Sabharwal, A., Veeraraghavan, A.: PPGSecure: biometric presentation attack detection using photopletysmograms. In: 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), pp. 56–62. IEEE (2017)
Owhadi, H., Scovel, C., Sullivan, T.J., McKerns, M., Ortiz, M.: Optimal uncertainty quantification. SIAM Rev. 55(2), 271–345 (2013)
Park, J.J., Florence, P., Straub, J., Newcombe, R., Lovegrove, S.: DeepSDF: learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 165–174 (2019)
Peters, H., Ba, Y., Kadambi, A.: pCON: polarimetric coordinate networks for neural scene representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2023)
Poh, M.Z., McDuff, D.J., Picard, R.W.: Non-contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using video imaging and blind source separation. Opt. Express 18(10), 10762–10774 (2010)
Ramaswamy, V.V., Kim, S.S., Russakovsky, O.: Fair attribute classification through latent space de-biasing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9301–9310 (2021)
Schulz, P., Scheuvens, L., Fettweis, G.: A new perspective on maximal-ratio combining. In: 2023 IEEE 34th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2023)
Sitzmann, V., Martel, J., Bergman, A., Lindell, D., Wetzstein, G.: Implicit neural representations with periodic activation functions. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 7462–7473 (2020)
Song, R., Chen, H., Cheng, J., Li, C., Liu, Y., Chen, X.: PulseGAN: learning to generate realistic pulse waveforms in remote photoplethysmography. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(5), 1373–1384 (2021)
Tancik, M., et al.: Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 7537–7547 (2020)
Teschner, M., Heidelberger, B., Müller, M., Pomerantes, D., Gross, M.H.: Optimized spatial hashing for collision detection of deformable objects. In: VMV, vol. 3, pp. 47–54 (2003)
Verkruysse, W., Svaasand, L.O., Nelson, J.S.: Remote plethysmographic imaging using ambient light. Opt. Express 16(26), 21434–21445 (2008)
Vilesov, A., et al.: Blending camera and 77 GHz radar sensing for equitable, robust plethysmography. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 41(4), 1–14 (2022)
Wadhwa, N., Rubinstein, M., Durand, F., Freeman, W.T.: Phase-based video motion processing. ACM Tran. Graph. (TOG) 32(4), 1–10 (2013)
Wang, W., Den Brinker, A.C., Stuijk, S., De Haan, G.: Algorithmic principles of remote PPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(7), 1479–1491 (2016)
Wang, Z., et al.: Towards fairness in visual recognition: Effective strategies for bias mitigation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8919–8928 (2020)
Wang, Z., et al.: Synthetic generation of face videos with plethysmograph physiology. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 20587–20596 (2022)
Wang, Z., et al.: Alto: alternating latent topologies for implicit 3D reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.04096 (2022)
Wu, H.Y., Rubinstein, M., Shih, E., Guttag, J., Durand, F., Freeman, W.: Eulerian video magnification for revealing subtle changes in the world. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 31(4), 1–8 (2012)
Xu, T., White, J., Kalkan, S., Gunes, H.: Investigating bias and fairness in facial expression recognition. In: Bartoli, A., Fusiello, A. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12540, pp. 506–523. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65414-6_35
Yu, Z., Li, X., Zhao, G.: Remote photoplethysmograph signal measurement from facial videos using spatio-temporal networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.02419 (2019)
Yu, Z., Shen, Y., Shi, J., Zhao, H., Torr, P.H., Zhao, G.: PhysFormer: facial video-based physiological measurement with temporal difference transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4186–4196 (2022)
Zhao, E.Q., et al.: Making thermal imaging more equitable and accurate: resolving solar loading biases. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08832 (2023)
Zheng, T., Chen, Z., Zhang, S., Cai, C., Luo, J.: MoRe-Fi: motion-robust and fine-grained respiration monitoring via deep-learning UWB radar. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, pp. 111–124 (2021)
Zhi, S., Laidlow, T., Leutenegger, S., Davison, A.J.: In-place scene labelling and understanding with implicit scene representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15838–15847 (2021)
Acknowledgements
We thank the Visual Machines Group (VMG) at UCLA for feedback and support. A.K. was supported by a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER award, IIS-2046737, Army Young Investigator Program Award, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Young Faculty Award, and a Cisco Research Award. P.C. was partially supported by a Cisco Research Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chari, P. et al. (2025). Implicit Neural Models to Extract Heart Rate from Video. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15141. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73010-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73010-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73009-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73010-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)