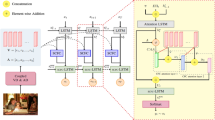
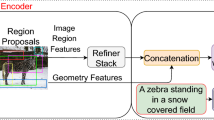
Abstract
Effectively aligning with human judgment when evaluating machine-generated image captions represents a complex yet intriguing challenge. Existing evaluation metrics like CIDEr or CLIP-Score fall short in this regard as they do not take into account the corresponding image or lack the capability of encoding fine-grained details and penalizing hallucinations. To overcome these issues, in this paper, we propose BRIDGE, a new learnable and reference-free image captioning metric that employs a novel module to map visual features into dense vectors and integrates them into multi-modal pseudo-captions which are built during the evaluation process. This approach results in a multimodal metric that properly incorporates information from the input image without relying on reference captions, bridging the gap between human judgment and machine-generated image captions. Experiments spanning several datasets demonstrate that our proposal achieves state-of-the-art results compared to existing reference-free evaluation scores. Our source code and trained models are publicly available at: https://github.com/aimagelab/bridge-score.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aditya, S., Yang, Y., Baral, C., Fermuller, C., Aloimonos, Y.: From images to sentences through scene description graphs using commonsense reasoning and knowledge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.03292 (2015)
Anderson, P., Fernando, B., Johnson, M., Gould, S.: SPICE: semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9909, pp. 382–398. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46454-1_24
Anderson, P., et al.: Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: CVPR (2018)
Banerjee, S., Lavie, A.: METEOR: an automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In: ACL Workshops (2005)
Barraco, M., Sarto, S., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: With a little help from your own past: prototypical memory networks for image captioning. In: ICCV (2023)
Bird, S., Klein, E., Loper, E.: Natural Language Processing with Python: Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit. Inc, O’Reilly Media (2009)
Caffagni, D., et al.: The revolution of multimodal large language models: a survey. In: ACL Findings (2024)
Chan, D., Petryk, S., Gonzalez, J.E., Darrell, T., Canny, J.: CLAIR: evaluating image captions with large language models. In: EMNLP (2023)
Chen, J., Li, D.Z.X.S.X., Zhang, Z.L.P., Xiong, R.K.V.C.Y., Elhoseiny, M.: MiniGPT-v2: large language model as a unified interface for vision-language multi-task learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.09478 (2023)
Chen, Y.-C., et al.: UNITER: UNiversal Image-TExt representation learning. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12375, pp. 104–120. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58577-8_7
Chiang, W.L., et al.: Vicuna: an open-source chatbot impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality (2023)
Chung, H.W., et al.: Scaling instruction-finetuned language models. JMLR 25(70), 1–53 (2024)
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: SMArT: training shallow memory-aware transformers for robotic explainability. In: ICRA (2020)
Cornia, M., Stefanini, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning. In: CVPR (2020)
Dai, W., et al.: InstructBLIP: towards general-purpose vision-language models with instruction tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06500 (2023)
Dong, H., Li, J., Wu, B., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, H.: Benchmarking and improving detail image caption. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.19092 (2024)
Herdade, S., Kappeler, A., Boakye, K., Soares, J.: Image captioning: transforming objects into words. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Hessel, J., Holtzman, A., Forbes, M., Bras, R.L., Choi, Y.: CLIPScore: a reference-free evaluation metric for image captioning. In: EMNLP (2021)
Hodosh, M., Young, P., Hockenmaier, J.: Framing image description as a ranking task: data, models and evaluation metrics. JAIR 47, 853–899 (2013)
Huang, L., Wang, W., Chen, J., Wei, X.Y.: Attention on attention for image captioning. In: ICCV (2019)
Jiang, M., Hu, J., Huang, Q., Zhang, L., Diesner, J., Gao, J.: REO-Relevance, extraness, omission: a fine-grained evaluation for image captioning. In: EMNLP (2019)
Jiang, M., et al.: TIGEr: text-to-image grounding for image caption evaluation. In: EMNLP (2019)
Karpathy, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In: CVPR (2015)
Kim, J.H., Kim, Y., Lee, J., Yoo, K.M., Lee, S.W.: Mutual information divergence: a unified metric for multimodal generative models. In: NeurIPS (2022)
Laurençon, H., et al.: OBELICS: an open web-scale filtered dataset of interleaved image-text documents. In: NeurIPS (2023)
Lee, H., Yoon, S., Dernoncourt, F., Bui, T., Jung, K.: UMIC: an unreferenced metric for image captioning via contrastive learning. In: ACL (2021)
Lee, H., Yoon, S., Dernoncourt, F., Kim, D.S., Bui, T., Jung, K.: ViLBERTScore: evaluating image caption using vision-and-language BERT. In: EMNLP Workshops (2020)
Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., Hoi, S.: BLIP-2: bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In: ICML (2023)
Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.: BLIP: bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In: ICML (2022)
Li, X., et al.: What if we recaption billions of web images with LLaMA-3? arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.08478 (2024)
Li, X., et al.: Oscar: object-semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12375, pp. 121–137. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58577-8_8
Li, Y., Pan, Y., Yao, T., Mei, T.: Comprehending and ordering semantics for image captioning. In: CVPR (2022)
Lin, C.Y.: Rouge: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: ACL Workshops (2004)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Liu, H., Li, C., Li, Y., Lee, Y.J.: Improved baselines with visual instruction tuning. In: CVPR (2024)
Liu, H., Li, C., Wu, Q., Lee, Y.J.: Visual instruction tuning. In: NeurIPS (2023)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. In: ICLR (2019)
Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., Lee, S.: ViLBERT: pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Oord, A.V.d., Li, Y., Vinyals, O.: Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748 (2018)
Pan, Y., Yao, T., Li, Y., Mei, T.: X-Linear attention networks for image captioning. In: CVPR (2020)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.J.: BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: ACL (2002)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: ICML (2021)
Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., Sutskever, I.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 1(8), 9 (2019)
Ramos, R., Martins, B., Elliott, D., Kementchedjhieva, Y.: SmallCap: lightweight image captioning prompted with retrieval augmentation. In: CVPR (2023)
Rashtchian, C., Young, P., Hodosh, M., Hockenmaier, J.: Collecting image annotations using amazon’s mechanical Turk. In: NAACL Workshops (2010)
Saito, K., et al.: Pic2Word: mapping pictures to words for zero-shot composed image retrieval. In: CVPR (2023)
Sarto, S., Barraco, M., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: Positive-augmented contrastive learning for image and video captioning evaluation. In: CVPR (2023)
Sarto, S., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: Retrieval-augmented transformer for image captioning. In: CBMI (2022)
Shekhar, R., et al.: FOIL it! find one mismatch between image and language caption. In: ACL (2017)
Shi, Y., et al.: EMScore: evaluating video captioning via coarse-grained and fine-grained embedding matching. In: CVPR (2022)
Tewel, Y., Shalev, Y., Schwartz, I., Wolf, L.: Zerocap: zero-shot image-to-text generation for visual-semantic arithmetic. In: CVPR (2022)
Touvron, H., et al.: LLaMA: open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971 (2023)
Touvron, H., et al.: Llama 2: open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288 (2023)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Vedantam, R., Lawrence Zitnick, C., Parikh, D.: CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation. In: CVPR (2015)
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., Erhan, D.: Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: CVPR (2015)
Wang, S., Yao, Z., Wang, R., Wu, Z., Chen, X.: FAIEr: fidelity and adequacy ensured image caption evaluation. In: CVPR (2021)
Xu, K., et al.: Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: ICML (2015)
Yang, X., Tang, K., Zhang, H., Cai, J.: Auto-encoding scene graphs for image captioning. In: CVPR (2019)
Yi, Y., Deng, H., Hu, J.: Improving image captioning evaluation by considerg inter refinerences variance. In: ACL (2020)
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., Hockenmaier, J.: From image descriptions to visual denotations: new similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. TACL 2, 67–78 (2014)
Zhang, P., et al.: VinVL: revisiting visual representations in vision-language models. In: CVPR (2021)
Zhang, T., Kishore, V., Wu, F., Weinberger, K.Q., Artzi, Y.: BERTScore: evaluating text generation with BERT. In: ICLR (2020)
Zhu, W., Wang, X.E., Yan, A., Eckstein, M., Wang, W.Y.: ImaginE: an imagination-based automatic evaluation metric for natural language generation. In: EACL (2023)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the CINECA award under the ISCRA initiative, for the availability of high-performance computing resources. This work has been conducted under a research grant co-funded by Leonardo S.p.A. and supported by the PNRR-M4C2 (PE00000013) project “FAIR - Future Artificial Intelligence Research” and by the PRIN project “MUSMA” (CUP G53D23002930006 - M4C2 I1.1), both funded by EU - Next-Generation EU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sarto, S., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R. (2025). BRIDGE: Bridging Gaps in Image Captioning Evaluation with Stronger Visual Cues. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15136. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73229-4_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73229-4_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73228-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73229-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)