Abstract
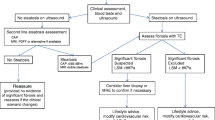
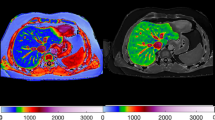
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its progressive form of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) pose a major public health problem that affects more than 30% of the global population. Since NAFLD is asymptomatic in the early stages, sufferers often remain untreated until the onset of NASH, which can lead to fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis of the liver. This condition is traditionally diagnosed via liver biopsy, which is invasive and associated with significant risks for the patient and susceptibility to sampling errors. These limitations underscore the necessity for non-invasive tools to assess disease severity. We explore the potential of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences in the UK Biobank (UKBB) to classify individuals as having either a healthy liver, NAFLD, or progressive NAFLD-associated advanced fibrosis. For the classification inputs, we utilize proton density fat fraction (PDFF) and native spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) maps, as well as serum biomarker data for assessing the sub-cohorts. The best models achieve near-perfect performance on identifying healthy individuals and NAFLD with AUCs of 0.99 and 0.98 respectively, while individuals with advanced fibrosis are under-diagnosed with an AUC of 0.67 at best. While segmentation decreases model performance, when classifying on full images, we make use of non-liver-related features, which is sub-optimal if we want to detect liver-related imaging biomarkers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
This research has been conducted using data from UK Biobank, a major biomedical database which can be found in https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/. This research has been conducted using the UK Biobank Resource under Application Number 53639.
References
Younossi, Z.M., Koenig, A.B., Abdelatif, D., Fazel, Y., Henry, L., Wymer, M.: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 64(1), 73–84 (2016)
Toshimitsu, K., et al.: Dietary habits and nutrient intake in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nutrition 23(1), 46–52 (2007)
Miao, L., Targher, G., Byrne, C.D., Cao, Y.-Y., Zheng, M.-H.: Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. (2024)
Ward, Z.J., et al.: Projected US state-level prevalence of adult obesity and severe obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 381(25), 2440–2450 (2019)
Friedman, S.L.: Liver fibrosis-from bench to bedside. J. Hepatol. 38, 38–53 (2003)
Kinner, S., Reeder, S.B., Yokoo, T.: Quantitative imaging biomarkers of NAFLD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 61, 1337–1347 (2016)
Langner, T., Strand, R., Ahlström, H., Kullberg, J.: Large-scale biometry with interpretable neural network regression on UK biobank body MRI. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 17752 (2020)
Caussy, C., Reeder, S.B., Sirlin, C.B., Loomba, R.: Noninvasive, quantitative assessment of liver fat by MRI-PDFF as an endpoint in Nash trials. Hepatology 68(2), 763–772 (2018)
Nauffal, V., et al.: Noninvasive assessment of organ-specific and shared pathways in multi-organ fibrosis using T1 mapping. Natu. Med., 1–12 (2024)
Taylor, A.J., Salerno, M., Dharmakumar, R., Jerosch-Herold, M.: T1 mapping: basic techniques and clinical applications. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 9(1), 67–81 (2016)
Mojtahed, A., et al.: Reference range of liver corrected t1 values in a population at low risk for fatty liver disease-a UK biobank sub-study, with an appendix of interesting cases. Abdom. Radiol. 44, 72–84 (2019)
Li, X., Liu, H., Wang, R., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Li, C.: Gadoxetate-disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for liver fibrosis staging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Radiol. 75(4), 319-e11 (2020)
Wojciechowska, M., Malacrino, S., Garcia Martin, N., Fehri, H., Rittscher, J.: Early detection of liver fibrosis using graph convolutional networks. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12908, pp. 217–226. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87237-3_21
Gao, Z., Liu, Y., Wu, F., Shi, N., Shi, Y., Zhuang, X.: A reliable and interpretable framework of multi-view learning for liver fibrosis staging. In: Greenspan, H., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2023. LNCS, vol. 14224, pp. 178–188. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43904-9_18
Hydes, T.J., et al.: The impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis on adverse clinical outcomes and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study using the UK biobank. BMC Med. 21(1), 185 (2023)
Angulo, P., et al.: The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 45(4), 846–854 (2007)
Shah, A.G.: Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7(10), 1104–1112 (2009)
Sterling, R.K., et al.: Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 43(6), 1317–1325 (2006)
Paik, J., Golabi, P., Younoszai, Z., Mishra, A., Trimble, G., Younossi, Z.M.: Chronic kidney disease is independently associated with increased mortality in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 39(2), 342–352 (2019)
Glover, G.H., Schneider, E.: Three-point Dixon technique for true water/fat decomposition with B0 inhomogeneity correction. Magn. Reson. Med. 18(2), 371–383 (1991)
Piechnik, S.K.: Shortened modified look-locker inversion recovery (ShMOLLI) for clinical myocardial T1-mapping at 1.5 and 3 T within a 9 heartbeat breathhold. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 12(1), 69 (2010)
Falk, T., et al.: U-Net: deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat. Methods 16(1), 67–70 (2019)
Macdonald, J.A., Zhu, Z., Konkel, B., Mazurowski, M.A., Wiggins, W.F., Bashir, M.R.: Duke liver dataset: a publicly available liver MRI dataset with liver segmentation masks and series labels. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 5(5), e220275 (2023)
Hectors, S.J., et al.: Fully automated prediction of liver fibrosis using deep learning analysis of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Eur. Radiol. 31, 3805–3814 (2021)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Al-Belmpeisi, R. et al. (2025). Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis from MRI in UK Biobank. In: Xu, X., Cui, Z., Rekik, I., Ouyang, X., Sun, K. (eds) Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15242. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73290-4_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73290-4_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73292-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73290-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)