Abstract
When developing Computer Aided Detection (CAD) systems for Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), the complexity arising from the volumetric nature of the modality poses significant technical challenges for obtaining large-scale accurate annotations. Without access to large-scale annotations, the resulting model may not generalize to different domains. Given the costly nature of obtaining DBT annotations, how to effectively increase the amount of data used for training DBT CAD systems remains an open challenge.
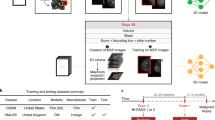
In this paper, we present SelectiveKD, a semi-supervised learning framework for building cancer detection models for DBT, which only requires a limited number of annotated slices to reach high performance. We achieve this by utilizing unlabeled slices available in a DBT stack through a knowledge distillation framework in which the teacher model provides a supervisory signal to the student model for all slices in the DBT volume. Our framework mitigates the potential noise in the supervisory signal from a sub-optimal teacher by implementing a selective dataset expansion strategy using pseudo labels.
We evaluate our approach with a large-scale real-world dataset of over 10,000 DBT exams collected from multiple device manufacturers and locations. The resulting SelectiveKD process effectively utilizes unannotated slices from a DBT stack, leading to significantly improved cancer classification performance (AUC) and generalization performance.
L. Dillard, H. Lee and W. Lee–These authors contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andharia, D., Shah, H., Prajapati, A.D., Bhansali, A.D., Shah, A., Desai, D.: Digital breast tomosynthesis(DBT) vs 2D mammography and impact of combined use: a meta-analysis. In: medRxiv (2023)
Bahl, M., Gaffney, S., McCarthy, A.M., Lowry, K.P., Dang, P.A., Lehman, C.D.: Breast cancer characteristics associated with 2d digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis for screening-detected and interval cancers. Radiology 287(1), 49–57 (2018)
Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Goodfellow, I., Papernot, N., Oliver, A., Raffel, C.A.: MixMatch: a holistic approach to semi-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32 (2019)
Chen, Y., Mancini, M., Zhu, X., Akata, Z.: Semi-supervised and unsupervised deep visual learning: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 46, 1327–1347 (2022)
Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Li, W., Gong, S.: Semi-supervised learning under class distribution mismatch. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 3569–3576 (2020)
Chikarmane, S.A., Cochon, L.R., Khorasani, R., Sahu, S., Giess, C.S.: Screening mammography performance metrics of 2D digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis in women with a personal history of breast cancer. Am. J. Roentgenol. 217, 587–594 (2021)
DeLong, E.R., DeLong, D.M., Clarke-Pearson, D.L.: Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44, 837–845 (1988)
Dhamija, E., Gulati, M., Deo, S., Gogia, A., Hari, S.: Digital breast tomosynthesis: an overview. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 12(2), 315–329 (2021)
Goldberg, J.E., et al.: New horizons: artificial intelligence for digital breast tomosynthesis. Radiographics 43(1), e220060 (2022)
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network (2015)
Huang, L., Chen, Y., He, X.: Spectral-spatial masked transformer with supervised and contrastive learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–18 (2023)
Ko, M.J., et al.: Accuracy of digital breast tomosynthesis for detecting breast cancer in the diagnostic setting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Radiol. 22(8), 1240 (2021)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on Challenges in Representation Learning, ICML, Atlanta, vol. 3, p. 896 (2013)
Lee, W., Lee, H., Lee, H., Park, E.K., Nam, H., Kooi, T.: Transformer-based deep neural network for breast cancer classification on digital breast tomosynthesis images. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 5(3), e220159 (2023)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: SGDR: stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.03983 (2016)
Nguyen, T., et al.: Overview of digital breast tomosynthesis: clinical cases, benefits, and disadvantages. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 96(9), 843–859 (2015)
Shahan, C.L.: An overview of digital breast tomosynthesis. W. Va. Med. J. 2016, 996 (2016)
Shen, Y., Shi, L., Zhao, J., Dong, Y., Wang, L.: Fully convolutional spectral-spatial fusion network integrating supervised contrastive learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Rem. Sens. 16, 9077–9088 (2023)
Shoshan, Y., et al.: Artificial intelligence for reducing workload in breast cancer screening with digital breast tomosynthesis. Radiology 303(1), 69–77 (2022)
Singh, P., et al.: Shifting to machine supervision: annotation-efficient semi and self-supervised learning for automatic medical image segmentation and classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.10319 (2023)
Tamé, I.d.A., Sirotkin, K., Carballeira, P., Escudero-Viñolo, M.: Self-supervised curricular deep learning for chest X-ray image classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10687 (2023)
Tardy, M., Mateus, D.: Trainable summarization to improve breast tomosynthesis classification. In: de Bruijne, M. (ed.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12907, pp. 140–149. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_14
Xie, Q., Luong, M.T., Hovy, E., Le, Q.V.: Self-training with noisy student improves imageNet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10687–10698 (2020)
Zhang, J., Yang, J., Yu, J., Fan, J.: Semisupervised image classification by mutual learning of multiple self-supervised models. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 37(5), 3117–3141 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dillard, L., Lee, H., Lee, W., Kim, T.S., Diba, A., Kooi, T. (2025). SelectiveKD: A Semi-supervised Framework for Cancer Detection in DBT Through Knowledge Distillation and Pseudo-labeling. In: Ali, S., van der Sommen, F., Papież, B.W., Ghatwary, N., Jin, Y., Kolenbrander, I. (eds) Cancer Prevention, Detection, and Intervention. CaPTion 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15199. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73376-5_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73376-5_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73375-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73376-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)