Abstract
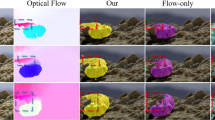
Multi-modal test-time adaptation (MM-TTA) is proposed to adapt models to an unlabeled target domain by leveraging the complementary multi-modal inputs in an online manner. Previous MM-TTA methods for 3D segmentation rely on predictions of cross-modal information in each input frame, while they ignore the fact that predictions of geometric neighborhoods within consecutive frames are highly correlated, leading to unstable predictions across time. To fulfill this gap, we propose ReLiable Spatial-temporal Voxels (Latte), an MM-TTA method that leverages reliable cross-modal spatial-temporal correspondences for multi-modal 3D segmentation. Motivated by the fact that reliable predictions should be consistent with their spatial-temporal correspondences, Latte aggregates consecutive frames in a slide window manner and constructs Spatial-Temporal (ST) voxels to capture temporally local prediction consistency for each modality. After filtering out ST voxels with high ST entropy, Latte conducts cross-modal learning for each point and pixel by attending to those with reliable and consistent predictions among both spatial and temporal neighborhoods. Experimental results show that Latte achieves state-of-the-art performance on three different MM-TTA benchmarks compared to previous MM-TTA or TTA methods. Visit our project site https://sites.google.com/view/eccv24-latte.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behley, J., et al.: Semantickitti: a dataset for semantic scene understanding of lidar sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9297–9307 (2019)
Caesar, H., et al.: nuscenes: a multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11621–11631 (2020)
Cao, H., Xu, Y., Yang, J., Yin, P., Yuan, S., Xie, L.: Mopa: multi-modal prior aided domain adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11839 (2023)
Cao, H., Xu, Y., Yang, J., Yin, P., Yuan, S., Xie, L.: Multi-modal continual test-time adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 18809–18819, October 2023
Chen, R., et al.: Clip2scene: towards label-efficient 3d scene understanding by clip. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7020–7030 (2023)
Choy, C., Gwak, J., Savarese, S.: 4d spatio-temporal convnets: minkowski convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3075–3084 (2019)
Fan, H., Yang, Y., Kankanhalli, M.: Point 4d transformer networks for spatio-temporal modeling in point cloud videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14204–14213 (2021)
Fan, H., Yu, X., Ding, Y., Yang, Y., Kankanhalli, M.: Pstnet: point spatio-temporal convolution on point cloud sequences. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.13713 (2022)
Feng, D., et al.: Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(3), 1341–1360 (2020)
Geyer, J., et al.: A2d2: audi autonomous driving dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.06320 (2020)
Gong, T., Jeong, J., Kim, T., Kim, Y., Shin, J., Lee, S.J.: Robust continual test-time adaptation: Instance-aware bn and prediction-balanced memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.05117 (2022)
Goyal, S., Sun, M., Raghunathan, A., Kolter, J.Z.: Test time adaptation via conjugate pseudo-labels. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2022)
Graham, B.: Sparse 3d convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.02890 (2015)
Guo, Y., Wang, H., Hu, Q., Liu, H., Liu, L., Bennamoun, M.: Deep learning for 3d point clouds: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(12), 4338–4364 (2020)
Huang, S., Gojcic, Z., Huang, J., Wieser, A., Schindler, K.: Dynamic 3d scene analysis by point cloud accumulation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 674–690. Springer (2022)
Jaritz, M., Vu, T.H., De Charette, R., Wirbel, É., Pérez, P.: Cross-modal learning for domain adaptation in 3d semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(2), 1533–1544 (2022)
Ji, X., Yuan, S., Yin, P., Xie, L.: Lio-gvm: an accurate, tightly-coupled lidar-inertial odometry with gaussian voxel map. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. (2024)
Li, M., Zhang, Y., Xie, Y., Gao, Z., Li, C., Zhang, Z., Qu, Y.: Cross-domain and cross-modal knowledge distillation in domain adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 3829–3837 (2022)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Do we really need to access the source data? source hypothesis transfer for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6028–6039. PMLR (2020)
Liu, W., et al.: Adversarial unsupervised domain adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation with multi-modal learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 176, 211–221 (2021)
Liu, Y., Kothari, P., Van Delft, B., Bellot-Gurlet, B., Mordan, T., Alahi, A.: Ttt++: when does self-supervised test-time training fail or thrive? Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 21808–21820 (2021)
Niu, S., et al.: Efficient test-time model adaptation without forgetting. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 16888–16905. PMLR (2022)
Niu, S., et al.: Towards stable test-time adaptation in dynamic wild world. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.12400 (2023)
Peng, D., Lei, Y., Li, W., Zhang, P., Guo, Y.: Sparse-to-dense feature matching: Intra and inter domain cross-modal learning in domain adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7108–7117 (2021)
Piergiovanni, A., Casser, V., Ryoo, M.S., Angelova, A.: 4d-net for learned multi-modal alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15435–15445 (2021)
Qi, C.R., Su, H., Mo, K., Guibas, L.J.: Pointnet: deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 652–660 (2017)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8748–8763. PMLR (2021)
Saltori, C., et al.: Gipso: geometrically informed propagation for online adaptation in 3d lidar segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 567–585. Springer (2022)
Shin, I., et al.: Mm-tta: multi-modal test-time adaptation for 3d semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16928–16937 (2022)
Simons, C., Raychaudhuri, D.S., Ahmed, S.M., You, S., Karydis, K., Roy-Chowdhury, A.K.: Summit: Source-free adaptation of uni-modal models to multi-modal targets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1239–1249, October 2023
Song, J., Lee, J., Kweon, I.S., Choi, S.: Ecotta: memory-efficient continual test-time adaptation via self-distilled regularization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11920–11929 (2023)
Su, Y., Xu, X., Li, T., Jia, K.: Revisiting realistic test-time training: sequential inference and adaptation by anchored clustering regularized self-training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.10856 (2023)
Tang, H., et al.: Searching efficient 3d architectures with sparse point-voxel convolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 685–702. Springer (2020)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (2017)
Vedula, S., Baker, S., Rander, P., Collins, R., Kanade, T.: Three-dimensional scene flow. In: Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 2, pp. 722–729. IEEE (1999)
Vizzo, I., Guadagnino, T., Mersch, B., Wiesmann, L., Behley, J., Stachniss, C.: Kiss-icp: in defense of point-to-point icp-simple, accurate, and robust registration if done the right way. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 8(2), 1029–1036 (2023)
Vogel, C., Schindler, K., Roth, S.: 3d scene flow estimation with a rigid motion prior. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1291–1298. IEEE (2011)
Vogel, C., Schindler, K., Roth, S.: Piecewise rigid scene flow. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1377–1384 (2013)
Wang, D., Shelhamer, E., Liu, S., Olshausen, B., Darrell, T.: Tent: fully test-time adaptation by entropy minimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021). https://openreview.net/forum?id=uXl3bZLkr3c
Wang, J.K., Wibisono, A.: Towards understanding gd with hard and conjugate pseudo-labels for test-time adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.10019 (2022)
Wang, Q., Fink, O., Van Gool, L., Dai, D.: Continual test-time domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7201–7211 (2022)
Wyner, A.: Recent results in the shannon theory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 20(1), 2–10 (1974)
Xie, E., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Alvarez, J.M., Luo, P.: Segformer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 12077–12090 (2021)
Xing, B., Ying, X., Wang, R., Yang, J., Chen, T.: Cross-modal contrastive learning for domain adaptation in 3d semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 37, pp. 2974–2982 (2023)
Xu, J., et al.: Int: towards infinite-frames 3d detection with an efficient framework. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 193–209. Springer (2022)
Yin, P., et al.: Outram: one-shot global localization via triangulated scene graph and global outlier pruning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.08914 (2023)
Yuan, L., Xie, B., Li, S.: Robust test-time adaptation in dynamic scenarios. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15922–15932 (2023)
Zhang, M., Levine, S., Finn, C.: Memo: Test time robustness via adaptation and augmentation. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 38629–38642 (2022)
Acknowledgment
This research is supported by the National Research Foundation, Singapore, under the NRF Medium Sized Centre for Advanced Robotics Technology Innovation (CARTIN). Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the views of National Research Foundation, Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cao, H. et al. (2025). Reliable Spatial-Temporal Voxels For Multi-modal Test-Time Adaptation. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15086. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73390-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73390-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73389-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73390-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)