Abstract
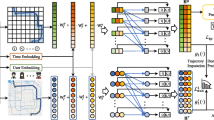
Human trajectory prediction is a practical task of predicting the future positions of pedestrians on the road, which typically covers all temporal ranges from short-term to long-term within a trajectory. However, existing works attempt to address the entire trajectory prediction with a singular, uniform training paradigm, neglecting the distinction between short-term and long-term dynamics in human trajectories. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a novel Progressive Pretext Task learning (PPT) framework, which progressively enhances the model’s capacity of capturing short-term dynamics and long-term dependencies for the final entire trajectory prediction. Specifically, we elaborately design three stages of training tasks in the PPT framework. In the first stage, the model learns to comprehend the short-term dynamics through a stepwise next-position prediction task. In the second stage, the model is further enhanced to understand long-term dependencies through a destination prediction task. In the final stage, the model aims to address the entire future trajectory task by taking full advantage of the knowledge from previous stages. To alleviate the knowledge forgetting, we further apply a cross-task knowledge distillation. Additionally, we design a Transformer-based trajectory predictor, which is able to achieve highly efficient two-step reasoning by integrating a destination-driven prediction strategy and a group of learnable prompt embeddings. Extensive experiments on popular benchmarks have demonstrated that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with high efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/PPT.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, I., Jeon, H.-G.: A set of control points conditioned pedestrian trajectory prediction. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 37(5), 6155–6165 (2023)
Bae, I., Oh, J., Jeon, H.G.: Eigentrajectory: low-rank descriptors for multi-modal trajectory forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (2023)
Bae, I., Park, J.H., Jeon, H.G.: Non-probability sampling network for stochastic human trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6477–6487 (2022)
Cai, Z., Vasconcelos, N.: Cascade r-cnn: delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6154–6162 (2018)
Choi, C., Choi, J.H., Li, J., Malla, S.: Shared cross-modal trajectory prediction for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 244–253 (2021)
Foka, A.F., Trahanias, P.E.: Probabilistic autonomous robot navigation in dynamic environments with human motion prediction. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2, 79–94 (2010)
Fu, H., Zheng, W., Meng, X., Wang, X., Wang, C., Ma, H.: You do not need additional priors or regularizers in retinex-based low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 18125–18134 (2023)
Gidaris, S., Komodakis, N.: Object detection via a multi-region and semantic segmentation-aware cnn model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 1134–1142 (2015)
Giuliari, F., Hasan, I., Cristani, M., Galasso, F.: Transformer networks for trajectory forecasting. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 10335–10342. IEEE (2021)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27 (2014)
Gregor, K., Danihelka, I., Graves, A., Rezende, D., Wierstra, D.: Draw: a recurrent neural network for image generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1462–1471. PMLR (2015)
Gu, T., et al.: Stochastic trajectory prediction via motion indeterminacy diffusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 17113–17122 (2022)
Gupta, A., Johnson, J., Fei-Fei, L., Savarese, S., Alahi, A.: Social GAN: socially acceptable trajectories with generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2255–2264 (2018)
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Komodakis, N., Gidaris, S.: Attend refine repeat: active box proposal generation via in-out localization. In: BMVC (2016)
Kosaraju, V., Sadeghian, A., Martín-Martín, R., Reid, I., Rezatofighi, H., Savarese, S.: Social-bigat: multimodal trajectory forecasting using bicycle-GAN and graph attention networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32 (2019)
Leal-Taixé, L., Fenzi, M., Kuznetsova, A., Rosenhahn, B., Savarese, S.: Learning an image-based motion context for multiple people tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3542–3549 (2014)
Lee, M., Sohn, S.S., Moon, S., Yoon, S., Kapadia, M., Pavlovic, V.: MUSE-VAE: multi-scale VAE for environment-aware long term trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2221–2230 (2022)
Levinson, J., et al.: Towards fully autonomous driving: systems and algorithms. In: 2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pp. 163–168. IEEE (2011)
Li, L.L., et al.: End-to-end contextual perception and prediction with interaction transformer. In: 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5784–5791. IEEE (2020)
Liang, Z., Li, C., Zhou, S., Feng, R., Loy, C.C.: Iterative prompt learning for unsupervised backlit image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8094–8103 (2023)
Luo, Y., Cai, P., Bera, A., Hsu, D., Lee, W.S., Manocha, D.: Porca: modeling and planning for autonomous driving among many pedestrians. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 3(4), 3418–3425 (2018)
Ma, T., Nie, Y., Long, C., Zhang, Q., Li, G.: Progressively generating better initial guesses towards next stages for high-quality human motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6437–6446 (2022)
Mangalam, K., An, Y., Girase, H., Malik, J.: From goals, waypoints and paths to long term human trajectory forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15233–15242 (2021)
Mangalam, K., et al.: It is not the journey but the destination: endpoint conditioned trajectory prediction. In: ECCV 2020, Part II 16, pp. 759–776. Springer (2020)
Mao, W., Xu, C., Zhu, Q., Chen, S., Wang, Y.: Leapfrog diffusion model for stochastic trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5517–5526 (2023)
Mohamed, A., Qian, K., Elhoseiny, M., Claudel, C.: Social-stgcnn: a social spatio-temporal graph convolutional neural network for human trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14424–14432 (2020)
Najibi, M., Rastegari, M., Davis, L.S.: G-cnn: an iterative grid based object detector. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2369–2377 (2016)
Park, S.H., et al.: Diverse and admissible trajectory forecasting through multimodal context understanding. In: ECCV 2020, Part XI 16, pp. 282–298. Springer (2020)
Pellegrini, S., Ess, A., Schindler, K., Van Gool, L.: You’ll never walk alone: modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 261–268. IEEE (2009)
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
Robicquet, A., Sadeghian, A., Alahi, A., Savarese, S.: Learning social etiquette: human trajectory understanding in crowded scenes. In: ECCV 2016, Part VIII 14, pp. 549–565. Springer (2016)
Sadeghian, A., Kosaraju, V., Sadeghian, A., Hirose, N., Rezatofighi, H., Savarese, S.: Sophie: an attentive GAN for predicting paths compliant to social and physical constraints. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1349–1358 (2019)
Salzmann, T., Ivanovic, B., Chakravarty, P., Pavone, M.: Trajectron++: dynamically-feasible trajectory forecasting with heterogeneous data. In: ECCV 2020, Part XVIII 16, pp. 683–700. Springer (2020)
Shi, L., et al.: SGCN: sparse graph convolution network for pedestrian trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8994–9003 (2021)
Shi, L., Wang, L., Zhou, S., Hua, G.: Trajectory unified transformer for pedestrian trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9675–9684 (2023)
Song, H., Ding, W., Chen, Y., Shen, S., Wang, M.Y., Chen, Q.: Pip: planning-informed trajectory prediction for autonomous driving. In: ECCV 2020, Part XXI 16, pp. 598–614. Springer (2020)
Sun, J., Li, Y., Fang, H.S., Lu, C.: Three steps to multimodal trajectory prediction: modality clustering, classification and synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13250–13259 (2021)
Tang, J., Sun, J., Lin, X., Zheng, W.S., Hu, J.F., et al.: Temporal continual learning with prior compensation for human motion prediction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36 (2024)
Tang, Jianwei, Wang, Jieming, Hu, Jian-Fang.: Predicting human poses via recurrent attention network. Visual Intell. 1(1) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44267-023-00020-z
Tsao, L.-W., Wang, Y.-K., Lin, H.-S., Shuai, H.-H., Wong, L.-K., Cheng, W.-H.: Social-SSL: self-supervised cross-sequence representation learning based on transformers for multi-agent trajectory prediction. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022, Part XXII, pp. 234–250. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20047-2_14
Valera, M., Velastin, S.A.: Intelligent distributed surveillance systems: a review. IEE Proc. Vision Image Signal Process. 152(2), 192–204 (2005)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, Q., et al.: Learning deep transformer models for machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 57th Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL (2019)
Wong, C., et al.: View vertically: a hierarchical network for trajectory prediction via Fourier spectrums. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 682–700. Springer (2022)
Wong, C., Xia, B., Peng, Q., Yuan, W., You, X.: MSN: multi-style network for trajectory prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 24(9), 9751–9766 (2023)
Xie, J., et al.: Pedestrian trajectory prediction based on social interactions learning with random weights. IEEE Trans. Multimedia (2024)
Xu, C., Mao, W., Zhang, W., Chen, S.: Remember intentions: retrospective-memory-based trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6488–6497 (2022)
Xu, P., Hayet, J.-B., Karamouzas, I.: SocialVAE: human trajectory prediction using timewise latents. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022, Part IV, pp. 511–528. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19772-7_30
Xu, S., Wang, Y.-X., Gui, L.-Y.: Diverse human motion prediction guided by multi-level spatial-temporal anchors. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022, Part XXII, pp. 251–269. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20047-2_15
Yi, S., Li, H., Wang, X.: Understanding pedestrian behaviors from stationary crowd groups. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3488–3496 (2015)
Yu, C., Ma, X., Ren, J., Zhao, H., Yi, S.: Spatio-temporal graph transformer networks for pedestrian trajectory prediction. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020, Part XII, pp. 507–523. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_30
Yuan, Y., Kitani, K.: DLow: diversifying latent flows for diverse human motion prediction. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020, Part IX, pp. 346–364. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_20
Yuan, Y., Weng, X., Ou, Y., Kitani, K.M.: Agentformer: agent-aware transformers for socio-temporal multi-agent forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9813–9823 (2021)
Yue, J., Manocha, D., Wang, H.: Human trajectory prediction via neural social physics. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 376–394. Springer (2022)
Zhao, H., Wildes, R.P.: Where are you heading? dynamic trajectory prediction with expert goal examples. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7629–7638 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partially by the NSFC (U21A20-471, U22A2095, 62076260, 61772570), Guangdong Natural Science Funds Project (2023B1515040025), Guangdong NSF for Distinguished Young Scholar (2022B15-15020009), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Information Security Technology (2023B1212060026), and Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (202201011134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lin, X., Liang, T., Lai, J., Hu, JF. (2025). Progressive Pretext Task Learning for Human Trajectory Prediction. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15088. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73404-5_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73404-5_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73403-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73404-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)