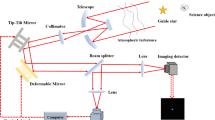
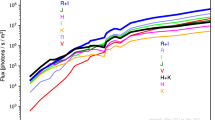
Abstract
Adaptive optics (AO) compile a variety of techniques that produce high-quality images in ground-based telescopes. Most commonly used AO techniques require the use of laser guide stars, which introduce errors due to the limited width and low altitude of these artificial stars, resulting in issues such as anisoplanatism and cone-effect problems. This study proposes an alternative AO system that aims to eliminate these issues. In contrast with similar techniques such as the Projected Pupil Plane Pattern (PPPP), that uses two pictures, Wavefronts Obtained from Measurements from Beam-profiles through Atmospheric Turbulence (WOMBAT) requires only one picture, reducing the complexity of the system. Even with only one image, WOMBAT manages to achieve similar results to PPPP in wavefront correction, offering potential advancements in ground-based telescope imaging quality.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bharmal, N.A., Myers, R.M., Yang, H.: PPPP: an on-sky experiment for zero-cone effect LGS alternative. In: Close, L.M., Schreiber, L., Schmidt, D. (eds.) Adaptive Optics Systems VI. Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 10703, p. 1070362, July 2018. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2313166
Buscher, D.F., Love, G.D., Myers, R.M.: Laser beacon wave-front sensing without focal anisoplanatism. Opt. Lett. 27(3), 149–151 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.27.000149
Casas, J.M., et al.: Multi-frequency point source detection with fully convolutional networks: performance in realistic microwave sky simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 658, A110 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202141874
Chan, S.H., Chimitt, N.: Computational imaging through atmospheric turbulence. Found. Trends\(\text{\textregistered} \) Comput. Graph. Vis. 15(4), 253–508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1561/0600000103
Davies, R., Kasper, M.: Adaptive optics for astronomy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 50, 305–351 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-astro-081811-125447
Hippler, S., et al.: Single conjugate adaptive optics for the ELT instrument METIS. Exp. Astron. 47, 65–105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-018-9609-y
Iglesias Álvarez, S., et al.: One-dimensional convolutional neural networks for detecting transiting exoplanets. Axioms 12(4), 348 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12040348
Lakshminarayanan, V., Fleck, A.: Zernike polynomials: a guide. J. Mod. Opt. 58, 1678–1678 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2011.633763
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Pérez, S., et al.: Enhancing open-loop wavefront prediction in adaptive optics through 2D-LSTM neural network implementation. Photonics 11(3), 240 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030240
Roddier, F.: Adaptive Optics in Astronomy. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Tatulli, E., Ramaprakash, A.N.: Laser tomography adaptive optics: a performance study. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 30(12), 2482 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.30.002482
Torrey, L., Shavlik, J.: Transfer learning. In: Handbook of Research on Machine Learning Applications and Trends: Algorithms, Methods, and Techniques, pp. 242–264. IGI global (2010)
Tyson, R.K.: Principles of Adaptive Optics, p. 141056. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015)
Yang, H., Bharmal, N., Myers, R., Younger, E.: Laboratory demonstration of an alternative laser guide stars wavefront sensing technique—projected pupil plane pattern. J. Astron. Telescopes Instrum. Syst. 5, 029002 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JATIS.5.2.029002
Yang, H., Gonzalez Gutierrez, C., Bharmal, N.A., de Cos Juez, F.J.: Projected Pupil Plane Pattern (PPPP) with artificial neural networks. Mon. Not. RAS 487(1), 1480–1487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stz1362
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Buendía-Roca, A. et al. (2024). Reconstructing Turbulence-Distorted Wavefronts Through Laser-Beam Profiles. In: Zayas-Gato, F., Díaz-Longueira, A., Casteleiro-Roca, JL., Jove, E. (eds) Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Special Sessions III - Intelligent Systems Applications, 21st International Conference. DCAI 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 1173. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73910-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73910-1_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73909-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73910-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)