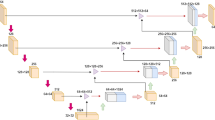
Abstract
Accurate segmentation of liver vessels is crucial for medical applications due to its pivotal role in diagnosing liver diseases, planning surgical interventions, and assessing treatment effectiveness. In this paper, we present a new dataset for liver vessel separation and propose two novel plug-and-play modules integrated into deep learning frameworks for liver vessel segmentation. The first module, termed as the skeleton tracking module, addresses the issue of segmentation fragmentation by effectively tracking the vessel skeletons. The second module, the graph attention module, is introduced for vessel separation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach through comprehensive experiments, showcasing significant improvements in segmentation accuracy. The dataset is publicly available, fostering research and development. https://github.com/oneway-phil/SKTS-GAT/tree/main.
First authors (C. Pei and W. Wang are with the same degree of contribution, they are the co-first authors).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonelli, M., et al.: The medical segmentation decathlon. Nat. Commun. 13(1), 4128 (2022)
Aoki, T., Kubota, K.: Preoperative portal vein embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: consensus and controversy. World J. Hepatol. 8(9), 439 (2016)
Cai, S., Tian, Y., Lui, H., Zeng, H., Wu, Y., Chen, G.: Dense-UNet: a novel multiphoton in vivo cellular image segmentation model based on a convolutional neural network. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 10(6), 1275 (2020)
Gupta, A., Dollar, P., Girshick, R.: LVIS: a dataset for large vocabulary instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5356–5364 (2019)
Heimann, T., et al.: Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 28(8), 1251–1265 (2009)
Huang, H., et al.: UNet 3+: A full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation. In: ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1055–1059. IEEE (2020)
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A., Petersen, J., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 18(2), 203–211 (2021)
Kavur, A.E., et al.: Chaos challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 69, 101950 (2021)
Nardelli, P., et al.: Pulmonary artery-vein classification in CT images using deep learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(11), 2428–2440 (2018)
Rahman, M.M., Marculescu, R.: G-CASCADE: efficient cascaded graph convolutional decoding for 2D medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 7728–7737 (2024)
Selle, D., Preim, B., Schenk, A., Peitgen, H.O.: Analysis of vasculature for liver surgical planning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(11), 1344–1357 (2002)
Soler, L., et al.: 3D image reconstruction for comparison of algorithm database 3 (2010). https://www.ircad.fr/research/datasets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01
Wang, W., et al.: AVDNet: joint coronary artery and vein segmentation with topological consistency. Med. Image Anal. 91, 102999 (2024)
Wetzel, S.G., Kirsch, E., Stock, K.W., Kolbe, M., Kaim, A., Radue, E.W.: Cerebral veins: comparative study of CT venography with intraarterial digital subtraction angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 20(2), 249–255 (1999)
Xie, K., Yang, J., Wei, D., Weng, Z., Fua, P.: Efficient anatomical labeling of pulmonary tree structures via implicit point-graph networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.17329 (2023)
Xu, S., Duan, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Sun, T., Tian, L.: Graph-and transformer-guided boundary aware network for medical image segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 242, 107849 (2023)
Yuan, Y., et al.: AFF-NET: an adaptive feature fusion network for liver vessel segmentation from CT images. In: 2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2023)
Zeng, Y.z., et al.: Automatic liver vessel segmentation using 3d region growing and hybrid active contour model. Comput. Biol. Med. 97, 63–73 (2018)
Zeng, Y.z., et al.: Liver vessel segmentation and identification based on oriented flux symmetry and graph cuts. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 150, 31–39 (2017)
Zhang, Z., Liu, Q., Wang, Y.: Road extraction by deep residual U-Net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 15(5), 749–753 (2018)
Zheng, H., et al.: Alleviating class-wise gradient imbalance for pulmonary airway segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(9), 2452–2462 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pei, C. et al. (2025). Deep Learning-Based Liver Vessel Separation with Plug-and-Play Modules: Skeleton Tracking and Graph Attention. In: Chen, C., Singh, Y., Hu, X. (eds) Topology- and Graph-Informed Imaging Informatics. TGI3 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15239. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73967-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73967-5_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73966-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73967-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)