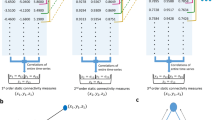
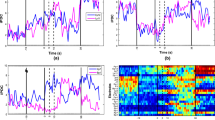
Abstract
Traditional Topological Data Analysis (TDA) methods, such as Persistent Homology (PH), rely on distance measures (e.g., cross-correlation, partial correlation, coherence, and partial coherence) that are symmetric by definition. While useful for studying topological patterns in functional brain connectivity, the main limitation of these methods is their inability to capture the directional dynamics - which are crucial for understanding effective brain connectivity. We propose the Causality-Based Topological Ranking (CBTR) method, which integrates Causal Inference (CI) to assess effective brain connectivity with Hodge Decomposition (HD) to rank brain regions based on their mutual influence. Our simulations confirm that the CBTR method accurately and consistently identifies hierarchical structures in multivariate time series data. Moreover, this method effectively identifies brain regions showing the most significant interaction changes with other regions during seizures using electroencephalogram (EEG) data. These results provide novel insights into the brain’s hierarchical organization and illuminate the impact of seizures on its dynamics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, H., Emerson, T., Kirby, M., Neville, R., Peterson, C., Shipman, P.: Persistence images: A stable vector representation of persistent homology. Journal of Machine Learning Research 18, 1–35 (2017). https://jmlr.org/papers/volume18/16-337/16-337.pdf
Bendich, P., Marron, J.S., Miller, E., Pieloch, A., Skwerer, S.: Persistent homology analysis of brain artery trees. The Annals of Applied Statistics 10, 198–218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1214/15-AOAS886
Bhatia, H., Norgard, G., Pascucci, V., Bremer, P.T.: The helmholtz-hodge decomposition-a survey. IEEE Trans. Visual Comput. Graphics 19(8), 1386–1404 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2012.316
Bromfield, E.B., Cavazos, J.E., Sirven, J.I.: An Introduction to Epilepsy. American Epilepsy Society (2006)
Bubenik, P.: Statistical topological data analysis using persistence landscapes. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 16, 77–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5555/2789272.2789275
Carlsson, G., Zomorodian, A., Collins, A., Guibas, L.: Persistence barcodes for shapes. p. 124-135. Association for Computing Machinery (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1057432.1057449
Cook, C.J., et al.: Effective connectivity within the default mode network in left temporal lobe epilepsy: findings from the epilepsy connectome project. Brain Connectivity 9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2018.0600
Edelsbrunner, H., Harer, J.: Persistent homology-a survey. Discret. Comput. Geom. 453, 257–282 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1090/conm/453/08802
Edelsbrunner, H., Letscher, D., Zomorodian, A.: Topological persistence and simplification 28, 511–533 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00454-002-2885-2
El-Yaagoubi, A.B., Jiao, S., Chung, M.K., Ombao, H.: Spectral topological data analysis of brain signals. arXiv:2401.05343 [q-bio.NC] (2024). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2401.05343
El-Yaagoubi, A.B., Ombao, H.: Topological data analysis for directed dependence networks of multivariate time series data. In: Research Papers in Statistical Inference for Time Series and Related Models, chap. 17. Springer (2023)
Friston, K., Moran, R., Seth, A.: Analysing connectivity with granger causality and dynamic causal modelling. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 23(2), 172–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2012.11.010
Friston, K.J.: Functional and effective connectivity: A review. Brain Connectivity 1, 13–36 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2011.0008
Gidea, M., Katz, Y.: Topological data analysis of financial time series: Landscapes of crashes. Phys. A 491, 820–834 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.09.028
Jiang, X., Lim, L.H., Yao, Y., Ye, Y.: Statistical ranking and combinatorial hodge theory. Math. Program. 127(1), 203–244 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-010-0419-x
Jiang, Y., Chen, D., Chen, X., Li, T., Wei, G.W., Pan, F.: Topological representations of crystalline compounds for the machine-learning prediction of materials properties. npj Computational Materials 7(28) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-021-00493-w
Lee, H., Kang, H., Chung, M.K., Kim, B.N., Lee, D.S.: Persistent brain network homology from the perspective of dendrogram. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31, 2267–2277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2012.2219590
Pearl, J.: Causality: Models. Cambridge University Press, Reasoning and Inference (2009)
Rabadan, R., Blumberg, A.J.: Topological Data Analysis for Genomics and Evolution. Cambridge University Press (2019)
Roebroeck, A., Formisano, E., Goebel, R.: Mapping directed influence over the brain using granger causality and fmri. Neuroimage 25(1), 230–242 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.11.017
Runge, J.: Discovering contemporaneous and lagged causal relations in autocorrelated nonlinear time series datasets. In: Peters, J., Sontag, D. (eds.) Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI). Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 124, pp. 1388–1397. PMLR (03–06 Aug 2020), https://proceedings.mlr.press/v124/runge20a.html
Runge, J., Nowack, P., Kretschmer, M., Flaxman, S., Sejdinovic, D.: Detecting and quantifying causal associations in large nonlinear time series datasets. Science Advances 5(11), eaau4996 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aau4996
Seth, A.K., Barrett, A.B., Barnett, L.: Granger causality analysis in neuroscience and neuroimaging. J. Neurosci. 35(8), 3293–3297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4399-14.2015
Stevenson, N.J., Tapani, K., Lauronen, L., Vanhatalo, S.: A dataset of neonatal eeg recordings with seizure annotations. Scientific Data 6, 190039 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2019.39
Weichwald, S., Peters, J.: Causality in cognitive neuroscience: Concepts, challenges, and distributional robustness. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 33(2), 226–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01623
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
El-Yaagoubi, A.B., Chung, M.K., Ombao, H. (2025). Topological Analysis of Seizure-Induced Changes in Brain Hierarchy Through Effective Connectivity. In: Chen, C., Singh, Y., Hu, X. (eds) Topology- and Graph-Informed Imaging Informatics. TGI3 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15239. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73967-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73967-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73966-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73967-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)