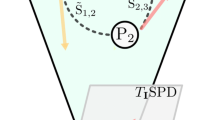
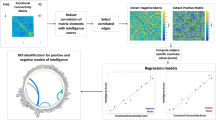
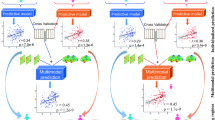
Abstract
This paper introduces the Relational Connectivity Transformer (RCT), a novel Graph-Transformer model designed for predicting absolute and residual full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ), performance IQ (PIQ), and verbal IQ (VIQ) scores from resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) data. Early prediction of neurocognitive impairments via IQ scores may allow for timely intervention. To this end, our RCT model leverages a relation-learning strategy from paired sample data via a novel graph-based transformer framework. Through a comprehensive comparison with state-of-the-art approaches in a 5-fold cross-validation setup, our model demonstrated superior performance. Statistical analysis confirmed the significant improvement (\(p<0.05\)) in FSIQ prediction, strengthening the efficacy of the proposed method. This work marks the first application of a Graph-Transformer in predicting IQ scores using rs-fMRI, introducing a novel learning strategy and contributing to the ongoing efforts to enhance the accuracy and reliability of human intelligence predictions based on functional brain connectivity. The code is available in this GitHub repository.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watson, C.G., Stopp, C., Wypij, D., Bellinger, D.C., Newburger, J.W., Rivkin, M.J.: Altered white matter microstructure correlates with IQ and processing speed in children and adolescents post-fontan. J. Pediatr. 200, 140–149 (2018)
Kessler, N., et al.: Structural brain abnormalities in adults with congenital heart disease: prevalence and association with estimated intelligence quotient. Int. J. Cardiol. 306, 61–66 (2020)
Urschel, S., et al.: Neurocognitive outcomes after heart transplantation in early childhood. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 37(6), 740–748 (2018)
Calderon, J., Bellinger, D.C.: Executive function deficits in congenital heart disease: why is intervention important? Cardiol. Young 25(7), 1238–1246 (2015)
Beames, J.R., Kikas, K., Werner-Seidler, A.: Prevention and early intervention of depression in young people: an integrated narrative review of affective awareness and ecological momentary assessment. BMC Psychol. 9(1), 113 (2021)
Saha, S., Pagnozzi, A., Bradford, D., Fripp, J.: Predicting fluid intelligence in adolescence from structural MRI with deep learning methods. Intelligence 88, 101568 (2021)
Hilger, K., Ekman, M., Fiebach, C.J., Basten, U.: Intelligence is associated with the modular structure of intrinsic brain networks. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 16088 (2017)
Dizaji, A.S., et al.: Linking brain biology to intellectual endowment: a review on the associations of human intelligence with neuroimaging data. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 12(1), 1 (2021)
Hilger, K., Ekman, M., Fiebach, C.J., Basten, U.: Efficient hubs in the intelligent brain: nodal efficiency of hub regions in the salience network is associated with general intelligence. Intelligence 60, 10–25 (2017)
Cole, M.W., Bassett, D.S., Power, J.D., Braver, T.S., Petersen, S.E.: Intrinsic and task-evoked network architectures of the human brain. Neuron 83(1), 238–251 (2014)
Shen, X., et al.: Using connectome-based predictive modeling to predict individual behavior from brain connectivity. Nat. Protocols 12(3), 506–518 (2017)
He, T., et al.: Deep neural networks and kernel regression achieve comparable accuracies for functional connectivity prediction of behavior and demographics. Neuroimage 206, 116276 (2020)
Qu, G., et al.: Interpretable cognitive ability prediction: a comprehensive gated graph transformer framework for analyzing functional brain networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 43(4), 1568–1578 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2023.3343365
Hanik, M., Demirtaş, M.A., Gharsallaoui, M.A., Rekik, I.: Predicting cognitive scores with graph neural networks through sample selection learning. Brain Imaging Behav. 16(3), 1123–1138 (2022)
Kawahara, J., et al.: BrainNetCNN: convolutional neural networks for brain networks; towards predicting neurodevelopment. Neuroimage 146, 1038–1049 (2017)
Kan, X., Cui, H., Lukemire, J., Guo, Y., Yang, C.: Fbnetgen: task-aware GNN-based fMRI analysis via functional brain network generation. In: International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, pp. 618–637. PMLR (2022)
Ying, C., et al.: Do transformers really perform badly for graph representation? Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 28877–28888 (2021)
Dwivedi, V., Bresson, X.: A generalization of transformer networks to graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.09699 (2020)
Kan, X., Dai, W., Cui, H., Zhang, Z., Guo, Y., Yang, C.: Brain network transformer. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 25586–25599 (2022)
He, S., Feng, Y., Grant, P.E., Ou, Y.: Deep relation learning for regression and its application to brain age estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 41(9), 2304–2317 (2022)
Di Martino, A., et al.: The autism brain imaging data exchange: towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 19(6), 659–667 (2014)
Craddock, R.C., James, G.A., Holtzheimer, P.E., III., Hu, X.P., Mayberg, H.S.: A whole brain fMRI atlas generated via spatially constrained spectral clustering. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33(8), 1914–1928 (2012)
Pohl, K.M., Thompson, W.K., Adeli, E., Linguraru, M.G.: Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Neurocognitive Prediction. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1st edn. Springer, Cham (2019)
Cui, H., et al.: Braingb: a benchmark for brain network analysis with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42(2), 493–506 (2022)
Glorot, X., Bengio, Y.: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, pp. 249–256 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hussain, M.A., Grant, E., Ou, Y. (2025). RCT: Relational Connectivity Transformer for Enhanced Prediction of Absolute and Residual Intelligence. In: Rekik, I., Adeli, E., Park, S.H., Cintas, C. (eds) Predictive Intelligence in Medicine. PRIME 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15155. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74561-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74561-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-74560-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-74561-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)