Abstract
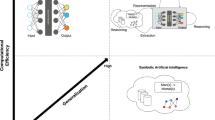
In this paper we argue that Neuro-Symbolic AI (NeSy-AI) should be applied for patient monitoring. In this context, we introduce patient monitoring as a special case of Human Activity Recognition and derive concrete requirements for this application area. We then present a process architecture and discuss why NeSy-AI should be applied for patient monitoring. To further support our argumentation, we show how NeSy-AI can help to overcome certain technical challenges that arise from this application area.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennetot, A., Laurent, J.L., Chatila, R., Díaz-Rodríguez, N.: Towards explainable neural-symbolic visual reasoning.(2019). In: IJCAI19 Neural-Symbolic Learning and Reasoning Workshop (2019). https://sites.google.com/view/nesy2019/home
Besold, T.R., et al.: Neural-symbolic learning and reasoning: a survey and interpretation. In: Neuro-Symbolic Artificial Intelligence: The State of the Art, pp. 1–51. IOS Press (2021)
Bollacker, K., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Li, X.: Extending knowledge graphs with subjective influence networks for personalized fashion. In: Portmann, E., Tabacchi, M.E., Seising, R., Habenstein, A. (eds.) Designing Cognitive Cities, pp. 203–233. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, Springer International Publishing, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00317-3_9
Confalonieri, R., Weyde, T., Besold, T.R., Moscoso del Prado Martín, F.: Using ontologies to enhance human understandability of global post-hoc explanations of black-box models. Artif. Intell. 296, 103471 (2021).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2021.103471. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0004370221000229
Daniels, Z.A., Frank, L.D., Menart, C., Raymer, M., Hitzler, P.: A framework for explainable deep neural models using external knowledge graphs. In: Pham, T., Solomon, L., Rainey, K. (eds.) Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Multi-Domain Operations Applications II, pp. 73. SPIE, Online Only, United States, April 2020. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2558083
De Raedt, L., Kimmig, A., Toivonen, H.: Problog: a probabilistic prolog and its application in link discovery. In: IJCAI 2007, Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2462–2467. IJCAI-INT JOINT CONF ARTIF INTELL (2007)
De Raedt, L., Manhaeve, R., Dumancic, S., Demeester, T., Kimmig, A.: Neuro-symbolic= neural+ logical+ probabilistic. In: NeSy’19@ IJCAI, the 14th International Workshop on Neural-Symbolic Learning and Reasoning (2019)
Donadello, I., Serafini, L., d’Avila Garcez, A.: Logic tensor networks for semantic image interpretation. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1596–1602. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, Melbourne, Australia, August 2017. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2017/221
Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Lamas, A., Sanchez, J., Franchi, G., Donadello, I., Tabik, S., Filliat, D., Cruz, P., Montes, R., Herrera, F.: EXplainable Neural-Symbolic Learning (X-NeSyL) methodology to fuse deep learning representations with expert knowledge graphs: The MonuMAI cultural heritage use case. Information Fusion 79, 58–83 (Mar 2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.09.022, https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1566253521001986
Fierens, D., Broeck, G.V.d., Renkens, J., Shterionov, D., Gutmann, B., Thon, I., Janssens, G., De Raedt, L.: Inference and learning in probabilistic logic programs using weighted Boolean formulas. Theory and Practice of Logic Programming 15(3), 358–401 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1471068414000076, http://arxiv.org/abs/1304.6810, arXiv:1304.6810 [cs]
Hitzler, P., Eberhart, A., Ebrahimi, M., Sarker, M.K., Zhou, L.: Neuro-symbolic approaches in artificial intelligence. National Sci. Rev. 9(6), nwac035 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac035
Hussain, Z., Sheng, M., Zhang, W.E.: Different approaches for human activity recognition: a survey. J. Network Comput. Appl. 167, 102738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102738. http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05074, arXiv:1906.05074 [cs]
Kamruzzaman Sarker, M., Zhou, L., Eberhart, A., Hitzler, P.: Neuro-symbolic artificial intelligence: Current trends. arXiv e-prints pp. arXiv–2105 (2021)
Krüger, F., Nyolt, M., Yordanova, K., Hein, A., Kirste, T.: Computational State Space Models for Activity and Intention Recognition. A Feasibility Study. PLOS ONE 9(11), e109381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109381
Manhaeve, R., Dumančič, S., Kimmig, A., Demeester, T., De Raedt, L.: DeepProbLog: Neural Probabilistic Logic Programming. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. vol. 31. Curran Associates, Inc. (2018). https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2018/hash/dc5d637ed5e62c36ecb73b654b05ba2a-Abstract.html
Yang, J., Lee, J., Choi, J.: Activity recognition based on rfid object usage for smart mobile devices. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 26(2), 239–246 (2011)
Acknowledgement
We want to thank GWA Hygiene for providing us with the sensors as well as the additional infrastructure which is necessary for a project like this.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fenske, O., Bader, S., Kirste, T. (2025). Neuro-symbolic Artificial Intelligence for Patient Monitoring. In: Meo, R., Silvestri, F. (eds) Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2136. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-74639-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-74640-6
eBook Packages: Artificial Intelligence (R0)