Abstract
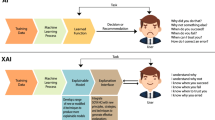
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is the most prevalent form of dementia globally, which presents a pressing health issue, especially in aging populations. Its early detection is critical to initiating appropriate care and therapeutic strategies. However, AD’s complex and multifaceted nature poses considerable challenges to accurate and early diagnosis. Machine learning (ML) models have emerged as promising disease detection and diagnosis tools, including AD. However, despite their superior predictive performance, these models are often viewed as “black boxes” due to their complex internal workings, which are not readily interpretable. This study aims to explore the application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques to enhance the interpretability of the best-performing ML classifier for AD detection. The robust analysis offers significant insights into the ML model’s decision-making processes, thereby enhancing their interpretability and bolstering confidence in their use for early AD detection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, P., Sun, F.: Aducanumab: the first targeted Alzheimer’s therapy. Drug Discoveries Ther. 15(3), 166–168 (2021)
Meng, W., et al.: Female perspective: the burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in china from: to 2019 and prediction of their prevalence up to 2044. Front. Public Health 11, 2023 (1990)
Angelopoulou, E., et al.: How telemedicine can improve the quality of care for patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias? A narrative review. Medicina 58(12), 1705 (2022)
Manemann, S.M., et al.: Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias and heart failure: a community study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 70(6), 1664–1672 (2022)
Ahmad, Z., Rahim, S., Zubair, M., Abdul-Ghafar, J.: Artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine, current applications and future role with special emphasis on its potential and promise in pathology: present and future impact, obstacles including costs and acceptance among pathologists, practical and philosophical considerations. a comprehensive review. Diagn. Pathol. 16, 1–16 (2021)
Dashwood, M., Churchhouse, G., Young, M., Kuruvilla, T.: Artificial intelligence as an aid to diagnosing dementia: an overview. Prog. Neurol. Psychiatry 25(3), 42–47 (2021)
Ali, S., et al.: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): what we know and what is left to attain trustworthy artificial intelligence. Inf. Fusion, 101805 (2023)
Gao, X.R., et al.: Explainable machine learning aggregates polygenic risk scores and electronic health records for Alzheimer’s disease prediction. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 450 (2023)
Ribeiro, M.T., Singh, S., Guestrin, C.: “Why should i trust you?” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1135–1144 (2016)
Lundberg, S.M., Lee, S.-I.: A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Haohui, L., Uddin, S.: Explainable stacking-based model for predicting hospital readmission for diabetic patients. Information 13(9), 436 (2022)
Basheer, S., Bhatia, S., Sakri, S.B.: Computational modeling of dementia prediction using deep neural network: analysis on oasis dataset. IEEE Access 9, 42449–42462 (2021)
Venugopalan, J., Tong, L., Hassanzadeh, H.R., Wang, M.D.: Multimodal deep learning models for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease stage. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 3254 (2021)
Raju, V.N.G., Prasanna Lakshmi, K., Jain, V.M., Kalidindi, A., Padma, V.: Study the influence of normalization/transformation process on the accuracy of supervised classification. In: 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), pp. 729–735. IEEE (2020)
Matloff, N.: Statistical Regression and Classification: From Linear Models to Machine Learning. CRC Press (2017)
Clark, L.A., Pregibon, D.: Tree-based models. In: Statistical Models in S, pp. 377–419. Routledge (2017)
Ali, H.A., Mohamed, C., Abdelhamid, B., Ourdani, N., El Alami, T.: A comparative evaluation use bagging and boosting ensemble classifiers. In: 2022 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision (ISCV), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2022)
Murphy, K.P.: Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. MIT Press (2012)
Kumar, M.: Using machine learning to predict heart-related diseases. IUP J. Comput. Sci. 16(3), 22–34 (2022)
Bentéjac, C., Csörgő, A., Martínez-Muñoz, G.: A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 54, 1937–1967 (2021)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press (2016)
Tharwat, A.: Linear vs. quadratic discriminant analysis classifier: a tutorial. Int. J. Appl. Pattern Recogn. 3(2), 145–180 (2016)
Sokolova, M., Japkowicz, N., Szpakowicz, S.: Beyond accuracy, F-score and ROC: a family of discriminant measures for performance evaluation. In: Sattar, A., Kang, B. (eds.) AI 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4304, pp. 1015–1021. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11941439_114
Miotto, R., Wang, F., Wang, S., Jiang, X., Dudley, J.T.: Deep learning for healthcare: review, opportunities and challenges. Briefings Bioinf. 19(6), 1236–1246 (2018)
Islam, J., Zhang, Y.: A novel deep learning based multi-class classification method for Alzheimer’s disease detection using brain MRI data. In: Zeng, Y., et al. (eds.) BI 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10654, pp. 213–222. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70772-3_20
Acknowledgment
The UAEU supported this research under grant number 12R000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nawaz, A., Ahmad, A. (2025). Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnostics: Insights into Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Meo, R., Silvestri, F. (eds) Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2136. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-74639-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-74640-6
eBook Packages: Artificial Intelligence (R0)