Abstract
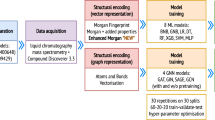
Metabolomics has emerged as a promising field in pharmaceuticals and preventive healthcare, offering practical applications in disease detection and drug testing. However, the analysis and interpretation of complex metabolic datasets remain challenging, with current methods relying heavily on limited and incompletely annotated biological pathways. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel approach that involves training machine learning classifiers on fingerprint-based encodings of metabolites to predict their response under specific experimental conditions. In this study, we evaluate our approach using a cellular model for the genetic disease Ataxia Telangiectasia (AT). Remarkably, some of our trained models predict affected metabolites with good performance, providing compelling evidence that the structural properties of metabolites hold predictive power over their response to specific conditions. Additionally, we suggest that evaluating the feature importance of the model can greatly assist researchers in identifying clusters of significant molecules and formulating hypotheses about affected pathways. Notably, our analysis of the AT cellular model identifies distinct groups of metabolites, some of which were already known to participate in the affected pathways, thereby validating existing knowledge. Moreover, we discovered metabolites not previously associated with AT, opening up novel opportunities for further exploration.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barupal, D.K., Haldiya, P.K., Wohlgemuth, G., Kind, T., Kothari, S.L., Pinkerton, K.E., Fiehn, O.: Metamapp: mapping and visualizing metabolomic data by integrating information from biochemical pathways and chemical and mass spectral similarity. BMC Bioinform. 13(1), 1–15 (2012)
Carhart, R.E., Smith, D.H., Venkataraghavan, R.: Atom pairs as molecular features in structure-activity studies: definition and applications. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 25(2), 64–73 (1985)
Carracedo-Reboredo, P., Liñares-Blanco, J., Rodríguez-Fernández, N., Cedrón, F., Novoa, F.J., Carballal, A., Maojo, V., Pazos, A., Fernandez-Lozano, C.: A review on machine learning approaches and trends in drug discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 19, 4538–4558 (2021)
Drexler, D.M., Reily, M.D., Shipkova, P.A.: Advances in mass spectrometry applied to pharmaceutical metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 399, 2645–2653 (2011)
Durant, J.L., Leland, B.A., Henry, D.R., Nourse, J.G.: Reoptimization of mdl keys for use in drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 42(6), 1273–1280 (2002)
Fernández, A., Garcia, S., Herrera, F., Chawla, N.V.: Smote for learning from imbalanced data: progress and challenges, marking the 15-year anniversary. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 61, 863–905 (2018)
Galal, A., Talal, M., Moustafa, A.: Applications of machine learning in metabolomics: disease modeling and classification. Front. Genet. 13, 1017340 (2022)
Glen, R.C., Bender, A., Arnby, C.H., Carlsson, L., Boyer, S., Smith, J.: Circular fingerprints: flexible molecular descriptors with applications from physical chemistry to adme. IDrugs 9(3), 199 (2006)
Harrigan, G.G., Goodacre, R.: Metabolic profiling: its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis: its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis. Springer Science & Business Media (2003)
Holmes, E., Wilson, I.D., Nicholson, J.K.: Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell 134(5), 714–717 (2008)
James, C.A.: Daylight theory manual (2004). http://www.daylight.com/dayhtml/doc/theory/theory.toc.html
Karp, P.D., Midford, P.E., Caspi, R., Khodursky, A.: Pathway size matters: the influence of pathway granularity on over-representation (enrichment analysis) statistics. BMC Genomics 22, 1–11 (2021)
Landrum, G.: Rdkit documentation. Release 1(1–79), 4 (2013)
Lavecchia, A.: Machine-learning approaches in drug discovery: methods and applications. Drug Discovery Today 20(3), 318–331 (2015)
Liebal, U.W., Phan, A.N., Sudhakar, M., Raman, K., Blank, L.M.: Machine learning applications for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Metabolites 10(6), 243 (2020)
Lo, Y.C., Rensi, S.E., Torng, W., Altman, R.B.: Machine learning in chemoinformatics and drug discovery. Drug Discovery Today 23(8), 1538–1546 (2018)
Lundberg, S.M., Lee, S.I.: A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017)
Mendez, K.M., Reinke, S.N., Broadhurst, D.I.: A comparative evaluation of the generalised predictive ability of eight machine learning algorithms across ten clinical metabolomics data sets for binary classification. Metabolomics 15, 1–15 (2019)
Menotta, M., Biagiotti, S., Spapperi, C., Orazi, S., Rossi, L., Chessa, L., Leuzzi, V., D’Agnano, D., Soresina, A., Micheli, R., et al.: Atm splicing variants as biomarkers for low dose dexamethasone treatment of at. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 12(1), 1–7 (2017)
Nilakantan, R., Bauman, N., Dixon, J.S., Venkataraghavan, R.: Topological torsion: a new molecular descriptor for sar applications. comparison with other descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 27(2), 82–85 (1987)
Noor, E., Cherkaoui, S., Sauer, U.: Biological insights through omics data integration. Current Opinion Syst. Biology 15, 39–47 (2019)
Puchades-Carrasco, L., Pineda-Lucena, A.: Metabolomics in pharmaceutical research and development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 35, 73–77 (2015)
Ricci, A., Biancucci, F., Morganti, G., Magnani, M., Menotta, M.: New human atm variants are able to regain atm functions in ataxia telangiectasia disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79(12), 601 (2022)
Rogers, D., Hahn, M.: Extended-connectivity fingerprints. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 50(5), 742–754 (2010)
Sirocchi, C., et al.: Machine learning-enabled prediction of metabolite response in genetic disorders. In: CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 3578, pp. 1–9 (2023)
Staszak, M., Staszak, K., Wieszczycka, K., Bajek, A., Roszkowski, K., Tylkowski, B.: Machine learning in drug design: Use of artificial intelligence to explore the chemical structure-biological activity relationship. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science 12(2), e1568 (2022)
Wieder, C., Frainay, C., Poupin, N., Rodríguez-Mier, P., Vinson, F., Cooke, J., Lai, R.P., Bundy, J.G., Jourdan, F., Ebbels, T.: Pathway analysis in metabolomics: recommendations for the use of over-representation analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 17(9), e1009105 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by the European Union - NextGenerationEU under the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) National Innovation Ecosystem grant ECS00000041 - VITALITY - CUP H33C22000430006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sirocchi, C. et al. (2025). Molecular Fingerprints-Based Machine Learning for Metabolic Profiling. In: Meo, R., Silvestri, F. (eds) Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2136. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74640-6_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-74639-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-74640-6
eBook Packages: Artificial Intelligence (R0)