Abstract
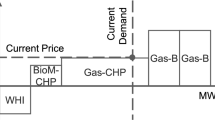
This paper presents Symbiosis, a web-based decision support tool developed to improve energy symbiosis within eco-industrial parks (EIPs). Symbiosis addresses the limitations of traditional desktop applications by offering a user-friendly, web-based interface that simplifies the modeling and visualization of energy flows among facilities. This tool is designed to be accessible to users with varying technical backgrounds. The effectiveness of Symbiosis was evaluated through a case study involving an industrial park with wind and photovoltaic energy sources and a greenhouse and brewery as energy consumers. The study assessed how replacing an existing greenhouse with a higher energy-consuming variant impacted the park’s energy balance. Symbiosis successfully modeled energy flows and visualized changes in energy surplus and deficit resulting from this replacement. The tool demonstrated its capability to provide insights into energy dynamics and optimize facility configurations to improve energy efficiency. The case study highlighted that Symbiosis is effective in visualizing and analyzing energy flows, supporting better decision-making for EIP management. However, it also revealed some limitations, such as performance issues with large datasets and the need for support for additional energy types. Future research should explore case studies in various EIP configurations and consider integrating optimization algorithms to enhance decision-making.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chertow, M.R.: Industrial symbiosis: literature and taxonomy. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 25, 313–337 (2000)
Jacobsen, N.B.: Industrial symbiosis in Kalundborg, Denmark: a quantitative assessment of economic and environmental aspects. J. Ind. Ecol. 10(1–2), 239–255 (2006)
Wang, Y., et al.: Smart solutions shape for sustainable low-carbon future: a review on smart cities and industrial parks in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 144, 103–117 (2019)
Butturi, M.A., et al.: Renewable energy in eco-industrial parks and urban-industrial symbiosis: a literature review and a conceptual synthesis. Appl. Energy 255 (2019)
Lawal, M., et al.: Industrial symbiosis tools—a review. J. Clean. Prod. 280, 124327 (2021)
Maqbool, A.S., Mendez Alva, F., Van Eetvelde, G.: An assessment of European information technology tools to support industrial symbiosis. Sustainability 11(1), 131 (2019)
Van Beers, D., Biswas, W.K.: A regional synergy approach to energy recovery: the case of the Kwinana industrial area Western Australia. Energy Convers. Manag. 49(11), 3051–3062 (2008)
Mancic, M., et al.: Software for energy system and building simulation: a review. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technology and Statistics in Economy and Education (ICAICTSEE) (2013)
Lütje, A., Leber, S., Scholten, J., Wohlgemuth, V.: Web tool for the identification of industrial symbioses in industrial parks. In: Kamilaris, A., Wohlgemuth, V., Karatzas, K., Athanasiadis, I.N. (eds.) Advances and New Trends in Environmental Informatics, pp. 19–34. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61969-5_2
van Beers, D., et al.: Lessons learned from the application of the UNIDO eco-industrial park toolbox in Viet Nam and other countries. Sustainability 11(17) (2019)
Misrol, M.A., et al.: Optimising renewable energy at the eco-industrial park: a mathematical modelling approach. Energy 261 (2022)
Yeo, Z., et al.: Tools for promoting industrial symbiosis: a systematic review. J. Ind. Ecol. 23(5), 1087–1108 (2019)
Afshari, H., Farel, R., Peng, Q.: Challenges of value creation in Eco-Industrial Parks (EIPs): a stakeholder perspective for optimizing energy exchanges. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 139, 315–325 (2018)
Andiappan, V., Tan, R.R., Ng, D.K.S.: Systematic allocation of cost savings among energy systems in an eco-industrial park. Chem. Eng. Trans. 45, 1657–1662 (2015)
Bozkır, S.A., et al.: Epesus: a developing web based energy & material flow analysis tool for eco-industrial parks. In: IADIS International Conference, ISPCM 2012, IADIS International Conference, TPMC 2012, IADIS, IAR 2012, Part of the IADIS Multi Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems 2012, MCCSIS 2012, pp. 122–126 (2012)
Angular, 30 June 2024. https://angular.io
Swagger, 30 June 2024. https://swagger.io/
OpenAPI, 30 June 2024. https://www.openapis.org
Spring Framework, 30 June 2024. https://spring.io/projects/spring-framework
MongoDB, 30 June 2024. https://www.mongodb.com
Acknowledgements
This paper is part of the IEA IETS Annex Task XXI: Decarbonizing industrial systems in a circular economy framework, funded by the Danish funding agency, the Danish Energy Technology Development and Demonstration (EUPD) program, Denmark (Case no. 134233-511205); part of the project “GreenLab designer Lite” collaborated with GreenLab Skive, funded by the Villum foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gärdström, H.F., Schwarz, H., Jørgensen, B.N., Ma, Z.G. (2025). Symbiosis: A Web-Based Decision Support Tool for Achieving Symbiosis in Industrial Parks. In: Jørgensen, B.N., Ma, Z.G., Wijaya, F.D., Irnawan, R., Sarjiya, S. (eds) Energy Informatics. EI.A 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15271. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74738-0_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-74738-0_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-74737-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-74738-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)