Abstract
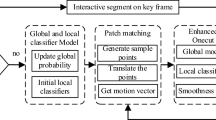
Interactive video segmentation aims to segment objects from videos using user information of object location. It allows for segmenting different objects from the same scene and has many applications, such as video editing and scene understanding. While in automatic video segmentation, the major challenges are temporal coherency and occlusion, interactive segmentation models must also handle unseen objects. This work proposes an interactive video segmentation strategy based on seed competition and user-drawn scribbles. Our proposal starts with a seed oversampling strategy and iteratively computes the optimum path forest for the seed set, maintaining the most relevant trees. Our Interactive Video Segmentation by Dynamic and Iterative Spanning Forest (iVSDISF) extends the Interactive Dynamic and Iterative Spanning Forest for videos, avoiding object leakage by dynamically creating trees at critical image positions. The proposed method is highly competitive with the state-of-the-art achieving the second highest score, in terms of IoU, considering all studied methods, and the best IoU among the ones without optical flow computation for SegTrackv2.
The authors thank the Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Minas Gerais – PUC-Minas, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – CAPES – (Grant PROAP 88887.842889/2023-00 – PUC/MG, Grant STIC-AMSUD 88887.878869/2023-00, Grant PDPG 88887.708960/2022-00 – PUC/MG - Informática, and Finance Code 001), the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq (Grants 407242/2021-0, 306573/2022-9, 442950/2023-3 and 304711/2023-3), Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais – FAPEMIG (Grant APQ-01079-23, Grant APQ-05058-23 and PCE-00417-24) and Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo – FAPESP (Grant 2023/14427-8).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avinash Ramakanth, S., Venkatesh Babu, R.: SeamSeg: video object segmentation using patch seams. In: CVPR, pp. 376–383 (2014)
Badrinarayanan, V., Budvytis, I., Cipolla, R.: Semi-supervised video segmentation using tree structured graphical models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(11), 2751–2764 (2013)
Badrinarayanan, V., Budvytis, I., Cipolla, R.: Mixture of trees probabilistic graphical model for video segmentation. IJCV 110, 14–29 (2014)
Borlido Barcelos, I., Belém, F., Miranda, P., Falcão, A.X., do Patrocínio, Z.K.G., Guimarães, S.J.F.: Towards interactive image segmentation by dynamic and iterative spanning forest. In: Lindblad, J., Malmberg, F., Sladoje, N. (eds.) DGMM 2021. LNCS, vol. 12708, pp. 351–364. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76657-3_25
Barcelos, I.B., Belém, F.D.C., João, L.D.M., Patrocínio, Z.K.G.D., Falcão, A.X., Guimarães, S.J.F.: A comprehensive review and new taxonomy on superpixel segmentation. ACM Comput. Surv. 56(8) (2024). https://doi.org/10.1145/3652509
Belém, F., Guimarães, S.J.F., Falcão, A.X.: Superpixel segmentation by object-based iterative spanning forest. In: Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., Morales, A. (eds.) CIARP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11401, pp. 334–341. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13469-3_39
Belém, F.C., et al.: Novel arc-cost functions and seed relevance estimations for compact and accurate superpixels. JMIV 65(5), 770–786 (2023)
Belém, F.C., Guimarães, S.J.F., Falcão, A.X.: Superpixel segmentation using dynamic and iterative spanning forest. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 27, 1440–1444 (2020)
Bragantini, J., Martins, S.B., Castelo-Fernandez, C., Falcão, A.X.: Graph-based image segmentation using dynamic trees. In: Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., Morales, A. (eds.) CIARP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11401, pp. 470–478. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13469-3_55
Cai, Z., Wen, L., Lei, Z., Vasconcelos, N., Li, S.Z.: Robust deformable and occluded object tracking with dynamic graph. TIP 23(12), 5497–5509 (2014)
Cappabianco, F.A., X, A.X.F., Yasuda, C.L., Udupa, J.K.: Brain tissue MR-image segmentation via optimum-path forest clustering. Comput. Vision Image Understand. 116(10), 1047–1059 (2012)
Chen, J., Paris, S., Durand, F.: Real-time edge-aware image processing with the bilateral grid. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers. SIGGRAPH ’07. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2007)
Chockalingam, P., Pradeep, N., Birchfield, S.: Adaptive fragments-based tracking of non-rigid objects using level sets. In: ICCV, pp. 1530–1537. IEEE (2009)
Condori, M.A.T., Mansilla, L.A.C., Miranda, P.A.V.: Bandeirantes: a graph-based approach for curve tracing and boundary tracking. In: Angulo, J., Velasco-Forero, S., Meyer, F. (eds.) ISMM 2017. LNCS, vol. 10225, pp. 95–106. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57240-6_8
Dutt Jain, S., Xiong, B., Grauman, K.: FusionSeg: learning to combine motion and appearance for fully automatic segmentation of generic objects in videos. In: CVPR, pp. 3664–3673 (2017)
Faktor, A., Irani, M.: Video object segmentation by non-local consensus voting. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. British Machine Vision Association (2014)
Falcão, A., Bragantini, J.: The role of optimum connectivity in image segmentation: can the algorithm learn object information during the process? In: Couprie, M., Cousty, J., Kenmochi, Y., Mustafa, N. (eds.) DGCI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11414, pp. 180–194. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14085-4_15
Falcão, A.X., Feng, C., Kustra, J., Telea, A.: Multiscale 2D medial axes and 3d surface skeletons by the image foresting transform. In: Skeletonization: Theory, Methods and Applications, p. 43 (2017)
Falcão, A.X., Stolfi, J., de Alencar Lotufo, R.: The image foresting transform: theory, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(1), 19–29 (2004)
Galvão, F.L., Guimarães, S.J.F., Falcão, A.X.: Image segmentation using dense and sparse hierarchies of superpixels. Pattern Recogn. 107532 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107532
Godec, M., Roth, P.M., Bischof, H.: Hough-based tracking of non-rigid objects. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 117(10), 1245–1256 (2013)
Grundmann, M., Kwatra, V., Han, M., Essa, I.: Efficient hierarchical graph-based video segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 2141–2148. IEEE (2010)
Hu, Y.-T., Huang, J.-B., Schwing, A.G.: Unsupervised video object segmentation using motion saliency-guided spatio-temporal propagation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11205, pp. 813–830. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_48
Jain, S.D., Grauman, K.: Supervoxel-consistent foreground propagation in video. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8692, pp. 656–671. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_43
Jang, W.D., Kim, C.S.: Semi-supervised video object segmentation using multiple random walkers. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2016)
Jerônimo, C., et al.: Graph-based supervoxel computation from iterative spanning forest. In: Lindblad, J., Malmberg, F., Sladoje, N. (eds.) DGMM 2021. LNCS, vol. 12708, pp. 404–415. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76657-3_29
Jun Koh, Y., Kim, C.S.: Primary object segmentation in videos based on region augmentation and reduction. In: CVPR, pp. 3442–3450 (2017)
Keuper, M., Andres, B., Brox, T.: Motion trajectory segmentation via minimum cost multicuts. In: ICCV, pp. 3271–3279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.374
Li, F., Kim, T., Humayun, A., Tsai, D., Rehg, J.M.: Video segmentation by tracking many figure-ground segments. In: ICCV (2013)
Liu, R., Wu, Z., Yu, S., Lin, S.: The emergence of objectness: learning zero-shot segmentation from videos. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 13137–13152 (2021)
Märki, N., Perazzi, F., Wang, O., Sorkine-Hornung, A.: Bilateral space video segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 743–751 (2016)
Papa, J.P., Falcão, A.X., Suzuki, C.T.: Supervised pattern classification based on optimum-path forest. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 19(2), 120–131 (2009)
Papazoglou, A., Ferrari, V.: Fast object segmentation in unconstrained video. In: ICCV, pp. 1777–1784 (2013)
Ponimatkin, G., Samet, N., Xiao, Y., Du, Y., Marlet, R., Lepetit, V.: A simple and powerful global optimization for unsupervised video object segmentation. In: WACV, pp. 5892–5903 (2023)
Rocha, L.M., Cappabianco, F.A., Falcão, A.X.: Data clustering as an optimum-path forest problem with applications in image analysis. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 19(2), 50–68 (2009)
Tokmakov, P., Alahari, K., Schmid, C.: Learning video object segmentation with visual memory. In: ICCV, pp. 4481–4490 (2017)
Tsai, D., Flagg, M., Nakazawa, A., Rehg, J.M.: Motion coherent tracking using multi-label MRF optimization. IJCV 100, 190–202 (2012)
Tsai, Y.H., Yang, M.H., Black, M.J.: Video segmentation via object flow. In: CVPR, pp. 3899–3908 (2016)
Varas, D., Marques, F.: Region-based particle filter for video object segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 3470–3477 (2014)
Vargas-Muñoz, J.E., Chowdhury, A.S., Alexandre, E.B., Galvão, F.L., Miranda, P.A.V., Falcão, A.X.: An iterative spanning forest framework for superpixel segmentation. TIP 28(7), 3477–3489 (2019)
Vieira, D., Barcelos, I.B., Belém, F., Patrocínio, Z.K.G., Falcão, A.X., Guimarães, S.J.F.: Streaming graph-based supervoxel computation based on dynamic iterative spanning forest. In: Vasconcelos, V., Domingues, I., Paredes, S. (eds.) CIARP 2023. LNCS, vol. 14470, pp. 90–104. Springer, Cham (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49249-5_7
Wang, H., Liu, W., Xing, W.: Video object segmentation via random walks on two-frame graphs comprising superpixels. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 80, 103293 (2021)
Wang, S., Lu, H., Yang, F., Yang, M.H.: Superpixel tracking. In: ICCV, pp. 1323–1330. IEEE (2011)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Porikli, F., Yang, R.: Semi-supervised video object segmentation with super-trajectories. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(4), 985–998 (2018)
Wen, L., Du, D., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z., Yang, M.H.: Jots: Joint online tracking and segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 2226–2234 (2015)
Winnemoller, H., Olsen, S.C., Gooch, B.: Real-time video abstraction. ACM Trans. Graph 25, 2006 (2006)
Yang, C., Lamdouar, H., Lu, E., Zisserman, A., Xie, W.: Self-supervised video object segmentation by motion grouping. In: ICCV, pp. 7177–7188 (2021)
Yang, Y., Lai, B., Soatto, S.: Dystab: unsupervised object segmentation via dynamic-static bootstrapping. In: CVPR, pp. 2825–2835. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, USA (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00285
Yang, Y., Loquercio, A., Scaramuzza, D., Soatto, S.: Unsupervised moving object detection via contextual information separation. In: CVPR, pp. 879–888 (2019)
Ye, V., Li, Z., Tucker, R., Kanazawa, A., Snavely, N.: Deformable sprites for unsupervised video decomposition. In: CVPR, pp. 2647–2656 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00268
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vieira, D., Barcelos, I.B., Patrocínio Jr, Z.K.G., Falcão, A., Guimarães, S.J.F. (2025). Towards Interactive Video Segmentation by Dynamic and Iterative Spanning Forest. In: Hernández-García, R., Barrientos, R.J., Velastin, S.A. (eds) Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications. CIARP 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15368. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-76607-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-76607-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-76606-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-76607-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)